Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2360.html
2360. Longest Cycle in a Graph
- Difficulty: Hard.
- Related Topics: Depth-First Search, Graph, Topological Sort.
- Similar Questions: Strange Printer II.
Problem
You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from node i, then edges[i] == -1.
Return the length of the **longest cycle in the graph**. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
Example 1:
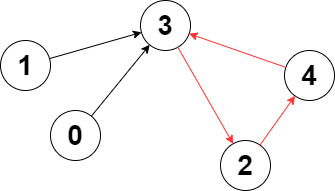
Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2.
The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
Example 2:
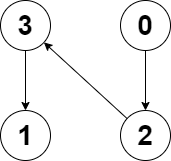
Input: edges = [2,-1,3,1]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
Constraints:
-
n == edges.length -
2 <= n <= 105 -
-1 <= edges[i] < n -
edges[i] != i
Solution
-
class Solution { public int longestCycle(int[] edges) { int n = edges.length; boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; boolean[] dfsvis = new boolean[n]; int[] path = new int[n]; int maxLength = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { path[i] = 1; maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, dfs(i, 1, path, vis, dfsvis, edges)); } } return maxLength; } private int dfs( int node, int pathLength, int[] path, boolean[] vis, boolean[] dfsvis, int[] edges) { vis[node] = true; dfsvis[node] = true; int length = -1; if (edges[node] != -1 && !vis[edges[node]]) { path[edges[node]] = pathLength + 1; length = dfs(edges[node], pathLength + 1, path, vis, dfsvis, edges); } else if (edges[node] != -1 && dfsvis[edges[node]]) { length = pathLength - path[edges[node]] + 1; } dfsvis[node] = false; return length; } } ############ class Solution { public int longestCycle(int[] edges) { int n = edges.length; boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; int ans = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } int j = i; List<Integer> cycle = new ArrayList<>(); for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.add(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (int k = 0; k < cycle.size(); ++k) { if (cycle.get(k) == j) { ans = Math.max(ans, cycle.size() - k); break; } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution: def longestCycle(self, edges: List[int]) -> int: n = len(edges) vis = [False] * n ans = -1 for i in range(n): if vis[i]: continue curr = i cycle = [] while curr != -1 and not vis[curr]: vis[curr] = True cycle.append(curr) curr = edges[curr] if curr == -1: continue for j, v in enumerate(cycle): if v == curr: ans = max(ans, len(cycle) - j) break return ans ############ # 2360. Longest Cycle in a Graph # https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-cycle-in-a-graph/ class Solution: def longestCycle(self, edges: List[int]) -> int: n = len(edges) visited = [False] * n res = -1 for node in range(n): dist = {} d = 0 while node != -1 and not visited[node]: visited[node] = True dist[node] = d node = edges[node] d += 1 if node != -1 and node in dist: res = max(res, d - dist[node]) return res -
class Solution { public: int longestCycle(vector<int>& edges) { int n = edges.size(); vector<bool> vis(n); int ans = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } int j = i; vector<int> cycle; for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.push_back(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (int k = 0; k < cycle.size(); ++k) { if (cycle[k] == j) { ans = max(ans, (int) cycle.size() - k); break; } } } return ans; } }; -
func longestCycle(edges []int) int { vis := make([]bool, len(edges)) ans := -1 for i := range edges { if vis[i] { continue } j := i cycle := []int{} for ; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j] { vis[j] = true cycle = append(cycle, j) } if j == -1 { continue } for k := range cycle { if cycle[k] == j { ans = max(ans, len(cycle)-k) break } } } return ans } func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } return b } -
function longestCycle(edges: number[]): number { const n = edges.length; const vis = new Array(n).fill(false); let ans = -1; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } let j = i; const cycle: number[] = []; for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.push(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (let k = 0; k < cycle.length; ++k) { if (cycle[k] == j) { ans = Math.max(ans, cycle.length - k); break; } } } return ans; }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).