Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1634. Add Two Polynomials Represented as Linked Lists
Description
A polynomial linked list is a special type of linked list where every node represents a term in a polynomial expression.
Each node has three attributes:
coefficient: an integer representing the number multiplier of the term. The coefficient of the term9x4is9.power: an integer representing the exponent. The power of the term9x4is4.next: a pointer to the next node in the list, ornullif it is the last node of the list.
For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 is represented by the polynomial linked list illustrated below:
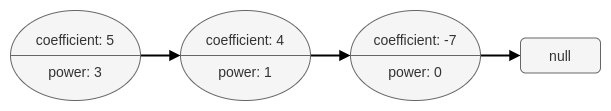
The polynomial linked list must be in its standard form: the polynomial must be in strictly descending order by its power value. Also, terms with a coefficient of 0 are omitted.
Given two polynomial linked list heads, poly1 and poly2, add the polynomials together and return the head of the sum of the polynomials.
PolyNode format:
The input/output format is as a list of n nodes, where each node is represented as its [coefficient, power]. For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 would be represented as: [[5,3],[4,1],[-7,0]].
Example 1:
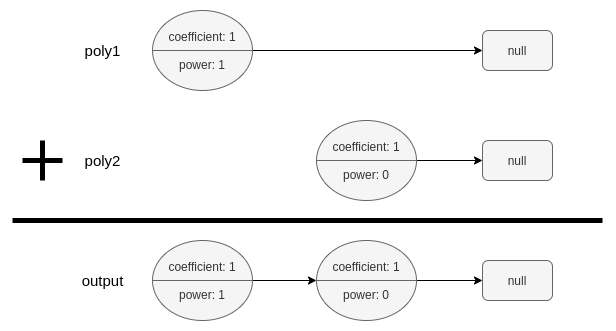
Input: poly1 = [[1,1]], poly2 = [[1,0]] Output: [[1,1],[1,0]] Explanation: poly1 = x. poly2 = 1. The sum is x + 1.
Example 2:
Input: poly1 = [[2,2],[4,1],[3,0]], poly2 = [[3,2],[-4,1],[-1,0]] Output: [[5,2],[2,0]] Explanation: poly1 = 2x2 + 4x + 3. poly2 = 3x2 - 4x - 1. The sum is 5x2 + 2. Notice that we omit the "0x" term.
Example 3:
Input: poly1 = [[1,2]], poly2 = [[-1,2]] Output: [] Explanation: The sum is 0. We return an empty list.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 104-109 <= PolyNode.coefficient <= 109PolyNode.coefficient != 00 <= PolyNode.power <= 109PolyNode.power > PolyNode.next.power
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for polynomial singly-linked list. * class PolyNode { * int coefficient, power; * PolyNode next = null; * PolyNode() {} * PolyNode(int x, int y) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; } * PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode next) { this.coefficient = x; this.power = y; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public PolyNode addPoly(PolyNode poly1, PolyNode poly2) { PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode(); PolyNode curr = dummy; while (poly1 != null && poly2 != null) { if (poly1.power > poly2.power) { curr.next = poly1; poly1 = poly1.next; curr = curr.next; } else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) { curr.next = poly2; poly2 = poly2.next; curr = curr.next; } else { int c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient; if (c != 0) { curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power); curr = curr.next; } poly1 = poly1.next; poly2 = poly2.next; } } if (poly1 == null) { curr.next = poly2; } if (poly2 == null) { curr.next = poly1; } return dummy.next; } } -
/** * Definition for polynomial singly-linked list-> * struct PolyNode { * int coefficient, power; * PolyNode *next; * PolyNode(): coefficient(0), power(0), next(nullptr) {}; * PolyNode(int x, int y): coefficient(x), power(y), next(nullptr) {}; * PolyNode(int x, int y, PolyNode* next): coefficient(x), power(y), next(next) {}; * }; */ class Solution { public: PolyNode* addPoly(PolyNode* poly1, PolyNode* poly2) { PolyNode* dummy = new PolyNode(); PolyNode* curr = dummy; while (poly1 && poly2) { if (poly1->power > poly2->power) { curr->next = poly1; poly1 = poly1->next; curr = curr->next; } else if (poly1->power < poly2->power) { curr->next = poly2; poly2 = poly2->next; curr = curr->next; } else { int c = poly1->coefficient + poly2->coefficient; if (c != 0) { curr->next = new PolyNode(c, poly1->power); curr = curr->next; } poly1 = poly1->next; poly2 = poly2->next; } } if (!poly1) { curr->next = poly2; } if (!poly2) { curr->next = poly1; } return dummy->next; } }; -
# Definition for polynomial singly-linked list. # class PolyNode: # def __init__(self, x=0, y=0, next=None): # self.coefficient = x # self.power = y # self.next = next class Solution: def addPoly(self, poly1: "PolyNode", poly2: "PolyNode") -> "PolyNode": dummy = curr = PolyNode() while poly1 and poly2: if poly1.power > poly2.power: curr.next = poly1 poly1 = poly1.next curr = curr.next elif poly1.power < poly2.power: curr.next = poly2 poly2 = poly2.next curr = curr.next else: if c := poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient: curr.next = PolyNode(c, poly1.power) curr = curr.next poly1 = poly1.next poly2 = poly2.next curr.next = poly1 or poly2 return dummy.next -
/** * Definition for polynomial singly-linked list. * function PolyNode(x=0, y=0, next=null) { * this.coefficient = x; * this.power = y; * this.next = next; * } */ /** * @param {PolyNode} poly1 * @param {PolyNode} poly2 * @return {PolyNode} */ var addPoly = function (poly1, poly2) { const dummy = new PolyNode(); let curr = dummy; while (poly1 && poly2) { if (poly1.power > poly2.power) { curr.next = poly1; poly1 = poly1.next; curr = curr.next; } else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) { curr.next = poly2; poly2 = poly2.next; curr = curr.next; } else { const c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient; if (c != 0) { curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power); curr = curr.next; } poly1 = poly1.next; poly2 = poly2.next; } } curr.next = poly1 || poly2; return dummy.next; }; -
/** * Definition for polynomial singly-linked list. * public class PolyNode { * public int coefficient, power; * public PolyNode next; * * public PolyNode(int x=0, int y=0, PolyNode next=null) { * this.coefficient = x; * this.power = y; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public PolyNode AddPoly(PolyNode poly1, PolyNode poly2) { PolyNode dummy = new PolyNode(); PolyNode curr = dummy; while (poly1 != null && poly2 != null) { if (poly1.power > poly2.power) { curr.next = poly1; poly1 = poly1.next; curr = curr.next; } else if (poly1.power < poly2.power) { curr.next = poly2; poly2 = poly2.next; curr = curr.next; } else { int c = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient; if (c != 0) { curr.next = new PolyNode(c, poly1.power); curr = curr.next; } poly1 = poly1.next; poly2 = poly2.next; } } if (poly1 == null) { curr.next = poly2; } if (poly2 == null) { curr.next = poly1; } return dummy.next; } }