Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1632. Rank Transform of a Matrix
Description
Given an m x n matrix, return a new matrix answer where answer[row][col] is the rank of matrix[row][col].
The rank is an integer that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
- The rank is an integer starting from
1. - If two elements
pandqare in the same row or column, then:- If
p < qthenrank(p) < rank(q) - If
p == qthenrank(p) == rank(q) - If
p > qthenrank(p) > rank(q)
- If
- The rank should be as small as possible.
The test cases are generated so that answer is unique under the given rules.
Example 1:
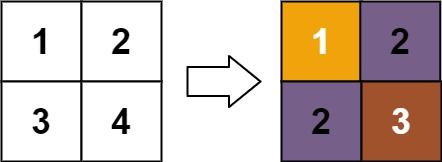
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]] Output: [[1,2],[2,3]] Explanation: The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column. The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
Example 2:
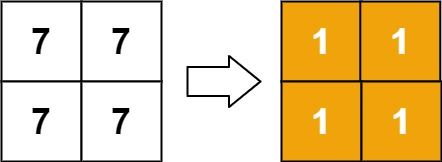
Input: matrix = [[7,7],[7,7]] Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Example 3:
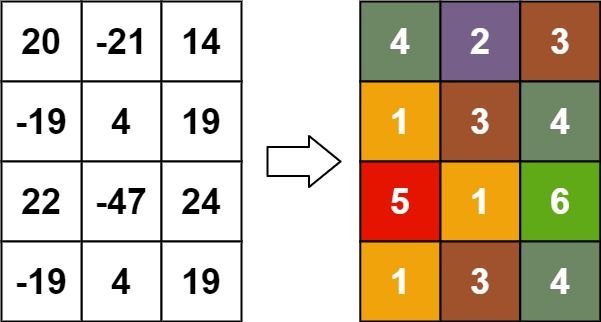
Input: matrix = [[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]] Output: [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500-109 <= matrix[row][col] <= 109
Solutions
-
class UnionFind { private int[] p; private int[] size; public UnionFind(int n) { p = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; size[i] = 1; } } public int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } public void union(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa != pb) { if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } } } public void reset(int x) { p[x] = x; size[x] = 1; } } class Solution { public int[][] matrixRankTransform(int[][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length; TreeMap<Integer, List<int[]>> d = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { d.computeIfAbsent(matrix[i][j], k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(new int[] {i, j}); } } int[] rowMax = new int[m]; int[] colMax = new int[n]; int[][] ans = new int[m][n]; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m + n); int[] rank = new int[m + n]; for (var ps : d.values()) { for (var p : ps) { uf.union(p[0], p[1] + m); } for (var p : ps) { int i = p[0], j = p[1]; rank[uf.find(i)] = Math.max(rank[uf.find(i)], Math.max(rowMax[i], colMax[j])); } for (var p : ps) { int i = p[0], j = p[1]; ans[i][j] = 1 + rank[uf.find(i)]; rowMax[i] = ans[i][j]; colMax[j] = ans[i][j]; } for (var p : ps) { uf.reset(p[0]); uf.reset(p[1] + m); } } return ans; } } -
class UnionFind { public: UnionFind(int n) { p = vector<int>(n); size = vector<int>(n, 1); iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); } void unite(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa != pb) { if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } } } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } void reset(int x) { p[x] = x; size[x] = 1; } private: vector<int> p, size; }; class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> matrixRankTransform(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(); map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> d; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { d[matrix[i][j]].push_back({i, j}); } } vector<int> rowMax(m); vector<int> colMax(n); vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n)); UnionFind uf(m + n); vector<int> rank(m + n); for (auto& [_, ps] : d) { for (auto& [i, j] : ps) { uf.unite(i, j + m); } for (auto& [i, j] : ps) { rank[uf.find(i)] = max({rank[uf.find(i)], rowMax[i], colMax[j]}); } for (auto& [i, j] : ps) { ans[i][j] = rowMax[i] = colMax[j] = 1 + rank[uf.find(i)]; } for (auto& [i, j] : ps) { uf.reset(i); uf.reset(j + m); } } return ans; } }; -
class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n): self.p = list(range(n)) self.size = [1] * n def find(self, x): if self.p[x] != x: self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]) return self.p[x] def union(self, a, b): pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b) if pa != pb: if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]: self.p[pb] = pa self.size[pa] += self.size[pb] else: self.p[pa] = pb self.size[pb] += self.size[pa] def reset(self, x): self.p[x] = x self.size[x] = 1 class Solution: def matrixRankTransform(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) d = defaultdict(list) for i, row in enumerate(matrix): for j, v in enumerate(row): d[v].append((i, j)) row_max = [0] * m col_max = [0] * n ans = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] uf = UnionFind(m + n) for v in sorted(d): rank = defaultdict(int) for i, j in d[v]: uf.union(i, j + m) for i, j in d[v]: rank[uf.find(i)] = max(rank[uf.find(i)], row_max[i], col_max[j]) for i, j in d[v]: ans[i][j] = row_max[i] = col_max[j] = 1 + rank[uf.find(i)] for i, j in d[v]: uf.reset(i) uf.reset(j + m) return ans -
type unionFind struct { p, size []int } func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind { p := make([]int, n) size := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i size[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{p, size} } func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int { if uf.p[x] != x { uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x]) } return uf.p[x] } func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) { pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b) if pa != pb { if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] { uf.p[pb] = pa uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb] } else { uf.p[pa] = pb uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa] } } } func (uf *unionFind) reset(x int) { uf.p[x] = x uf.size[x] = 1 } func matrixRankTransform(matrix [][]int) [][]int { m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) type pair struct{ i, j int } d := map[int][]pair{} for i, row := range matrix { for j, v := range row { d[v] = append(d[v], pair{i, j}) } } rowMax := make([]int, m) colMax := make([]int, n) ans := make([][]int, m) for i := range ans { ans[i] = make([]int, n) } vs := []int{} for v := range d { vs = append(vs, v) } sort.Ints(vs) uf := newUnionFind(m + n) rank := make([]int, m+n) for _, v := range vs { ps := d[v] for _, p := range ps { uf.union(p.i, p.j+m) } for _, p := range ps { i, j := p.i, p.j rank[uf.find(i)] = max(rank[uf.find(i)], max(rowMax[i], colMax[j])) } for _, p := range ps { i, j := p.i, p.j ans[i][j] = 1 + rank[uf.find(i)] rowMax[i], colMax[j] = ans[i][j], ans[i][j] } for _, p := range ps { uf.reset(p.i) uf.reset(p.j + m) } } return ans }