Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1582. Special Positions in a Binary Matrix
Description
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the number of special positions in mat.
A position (i, j) is called special if mat[i][j] == 1 and all other elements in row i and column j are 0 (rows and columns are 0-indexed).
Example 1:
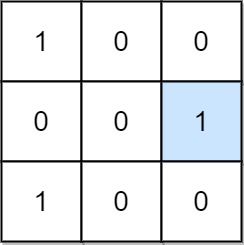
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]] Output: 1 Explanation: (1, 2) is a special position because mat[1][2] == 1 and all other elements in row 1 and column 2 are 0.
Example 2:
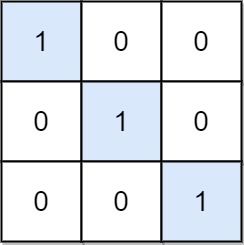
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 2) are special positions.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int numSpecial(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; int[] r = new int[m]; int[] c = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { r[i] += mat[i][j]; c[j] += mat[i][j]; } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] == 1 && r[i] == 1 && c[j] == 1) { ++ans; } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int numSpecial(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); vector<int> r(m), c(n); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { r[i] += mat[i][j]; c[j] += mat[i][j]; } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] == 1 && r[i] == 1 && c[j] == 1) { ++ans; } } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def numSpecial(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int: m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0]) r = [0] * m c = [0] * n for i, row in enumerate(mat): for j, v in enumerate(row): r[i] += v c[j] += v ans = 0 for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if mat[i][j] == 1 and r[i] == 1 and c[j] == 1: ans += 1 return ans -
func numSpecial(mat [][]int) int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) r, c := make([]int, m), make([]int, n) for i, row := range mat { for j, v := range row { r[i] += v c[j] += v } } ans := 0 for i, x := range r { for j, y := range c { if mat[i][j] == 1 && x == 1 && y == 1 { ans++ } } } return ans } -
function numSpecial(mat: number[][]): number { const m = mat.length; const n = mat[0].length; const rows = new Array(m).fill(0); const cols = new Array(n).fill(0); for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] === 1) { rows[i]++; cols[j]++; } } } let res = 0; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] === 1 && rows[i] === 1 && cols[j] === 1) { res++; } } } return res; } -
impl Solution { pub fn num_special(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let m = mat.len(); let n = mat[0].len(); let mut rows = vec![0; m]; let mut cols = vec![0; n]; for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { rows[i] += mat[i][j]; cols[j] += mat[i][j]; } } let mut res = 0; for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { if mat[i][j] == 1 && rows[i] == 1 && cols[j] == 1 { res += 1; } } } res } } -
public class Solution { public int NumSpecial(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.Length; int n = mat[0].Length; int[] rows = new int[m]; int[] cols = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { rows[i] += mat[i][j]; cols[j] += mat[i][j]; } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] == 1 && rows[i] == 1 && cols[j] == 1) { ans++; } } } return ans; } }