Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1506. Find Root of N-Ary Tree
Description
You are given all the nodes of an N-ary tree as an array of Node objects, where each node has a unique value.
Return the root of the N-ary tree.
Custom testing:
An N-ary tree can be serialized as represented in its level order traversal where each group of children is separated by the null value (see examples).
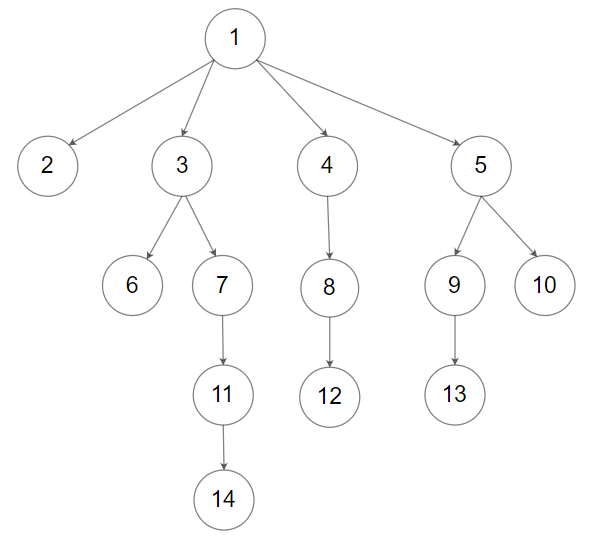
For example, the above tree is serialized as [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14].
The testing will be done in the following way:
- The input data should be provided as a serialization of the tree.
- The driver code will construct the tree from the serialized input data and put each
Nodeobject into an array in an arbitrary order. - The driver code will pass the array to
findRoot, and your function should find and return the rootNodeobject in the array. - The driver code will take the returned
Nodeobject and serialize it. If the serialized value and the input data are the same, the test passes.
Example 1:
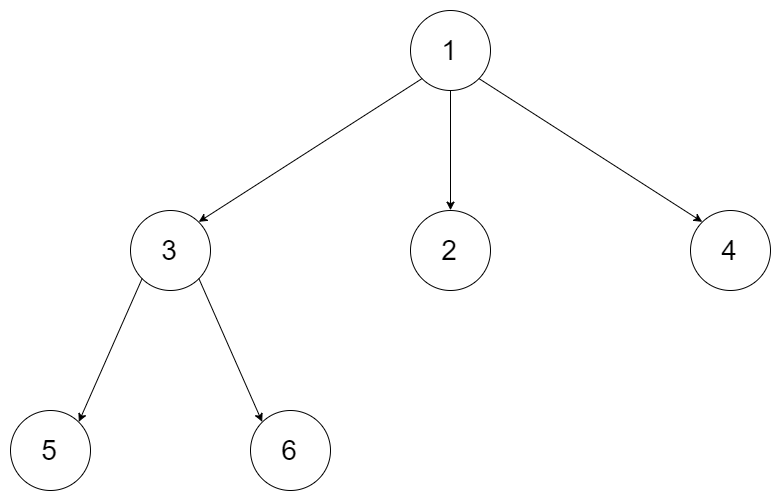
Input: tree = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Explanation: The tree from the input data is shown above. The driver code creates the tree and gives findRoot the Node objects in an arbitrary order. For example, the passed array could be [Node(5),Node(4),Node(3),Node(6),Node(2),Node(1)] or [Node(2),Node(6),Node(1),Node(3),Node(5),Node(4)]. The findRoot function should return the root Node(1), and the driver code will serialize it and compare with the input data. The input data and serialized Node(1) are the same, so the test passes.
Example 2:

Input: tree = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Constraints:
- The total number of nodes is between
[1, 5 * 104]. - Each node has a unique value.
Follow up:
- Could you solve this problem in constant space complexity with a linear time algorithm?
Solutions
-
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() { children = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; children = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val,ArrayList<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public Node findRoot(List<Node> tree) { int x = 0; for (Node node : tree) { x ^= node.val; for (Node child : node.children) { x ^= child.val; } } for (int i = 0;; ++i) { if (tree.get(i).val == x) { return tree.get(i); } } } } -
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* findRoot(vector<Node*> tree) { int x = 0; for (Node* node : tree) { x ^= node->val; for (Node* child : node->children) { x ^= child->val; } } for (int i = 0;; ++i) { if (tree[i]->val == x) { return tree[i]; } } } }; -
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val=None, children=None): self.val = val self.children = children if children is not None else [] """ class Solution: def findRoot(self, tree: List['Node']) -> 'Node': x = 0 for node in tree: x ^= node.val for child in node.children: x ^= child.val return next(node for node in tree if node.val == x) -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Children []*Node * } */ func findRoot(tree []*Node) *Node { x := 0 for _, node := range tree { x ^= node.Val for _, child := range node.Children { x ^= child.Val } } for i := 0; ; i++ { if tree[i].Val == x { return tree[i] } } } -
/** * Definition for Node. * class Node { * val: number * children: Node[] * constructor(val?: number, children?: Node[]) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.children = (children===undefined ? [] : children) * } * } */ function findRoot(tree: Node[]): Node | null { let x = 0; for (const node of tree) { x ^= node.val; for (const child of node.children) { x ^= child.val; } } return tree.find(node => node.val === x) || null; }