Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1505. Minimum Possible Integer After at Most K Adjacent Swaps On Digits
Description
You are given a string num representing the digits of a very large integer and an integer k. You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer at most k times.
Return the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string.
Example 1:
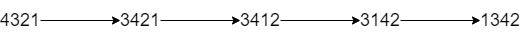
Input: num = "4321", k = 4 Output: "1342" Explanation: The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
Example 2:
Input: num = "100", k = 1 Output: "010" Explanation: It's ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
Example 3:
Input: num = "36789", k = 1000 Output: "36789" Explanation: We can keep the number without any swaps.
Constraints:
1 <= num.length <= 3 * 104numconsists of only digits and does not contain leading zeros.1 <= k <= 109
Solutions
Segment Tree.
-
class Solution { public String minInteger(String num, int k) { Queue<Integer>[] pos = new Queue[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { pos[i] = new ArrayDeque<>(); } int n = num.length(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { pos[num.charAt(i) - '0'].offer(i + 1); } StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); BinaryIndexedTree tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v) { if (!pos[v].isEmpty()) { Queue<Integer> q = pos[v]; int j = q.peek(); int dist = tree.query(n) - tree.query(j) + j - i; if (dist <= k) { k -= dist; q.poll(); ans.append(v); tree.update(j, 1); break; } } } } return ans.toString(); } } class BinaryIndexedTree { private int n; private int[] c; public BinaryIndexedTree(int n) { this.n = n; c = new int[n + 1]; } public void update(int x, int delta) { while (x <= n) { c[x] += delta; x += lowbit(x); } } public int query(int x) { int s = 0; while (x > 0) { s += c[x]; x -= lowbit(x); } return s; } public static int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; } } -
class BinaryIndexedTree { public: int n; vector<int> c; BinaryIndexedTree(int _n) : n(_n) , c(_n + 1) {} void update(int x, int delta) { while (x <= n) { c[x] += delta; x += lowbit(x); } } int query(int x) { int s = 0; while (x > 0) { s += c[x]; x -= lowbit(x); } return s; } int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; } }; class Solution { public: string minInteger(string num, int k) { vector<queue<int>> pos(10); int n = num.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) pos[num[i] - '0'].push(i + 1); BinaryIndexedTree* tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(n); string ans = ""; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v) { auto& q = pos[v]; if (!q.empty()) { int j = q.front(); int dist = tree->query(n) - tree->query(j) + j - i; if (dist <= k) { k -= dist; q.pop(); ans += (v + '0'); tree->update(j, 1); break; } } } } return ans; } }; -
class BinaryIndexedTree: def __init__(self, n): self.n = n self.c = [0] * (n + 1) @staticmethod def lowbit(x): return x & -x def update(self, x, delta): while x <= self.n: self.c[x] += delta x += BinaryIndexedTree.lowbit(x) def query(self, x): s = 0 while x: s += self.c[x] x -= BinaryIndexedTree.lowbit(x) return s class Solution: def minInteger(self, num: str, k: int) -> str: pos = defaultdict(deque) for i, v in enumerate(num, 1): pos[int(v)].append(i) ans = [] n = len(num) tree = BinaryIndexedTree(n) for i in range(1, n + 1): for v in range(10): q = pos[v] if q: j = q[0] dist = tree.query(n) - tree.query(j) + j - i if dist <= k: k -= dist q.popleft() ans.append(str(v)) tree.update(j, 1) break return ''.join(ans) -
type BinaryIndexedTree struct { n int c []int } func newBinaryIndexedTree(n int) *BinaryIndexedTree { c := make([]int, n+1) return &BinaryIndexedTree{n, c} } func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) lowbit(x int) int { return x & -x } func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) update(x, delta int) { for x <= this.n { this.c[x] += delta x += this.lowbit(x) } } func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) query(x int) int { s := 0 for x > 0 { s += this.c[x] x -= this.lowbit(x) } return s } func minInteger(num string, k int) string { pos := make([][]int, 10) for i, c := range num { pos[c-'0'] = append(pos[c-'0'], i+1) } n := len(num) tree := newBinaryIndexedTree(n) var ans strings.Builder for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { for v := 0; v < 10; v++ { if len(pos[v]) > 0 { j := pos[v][0] dist := tree.query(n) - tree.query(j) + j - i if dist <= k { k -= dist pos[v] = pos[v][1:] ans.WriteByte(byte(v + '0')) tree.update(j, 1) break } } } } return ans.String() }