Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1388. Pizza With 3n Slices
Description
There is a pizza with 3n slices of varying size, you and your friends will take slices of pizza as follows:
- You will pick any pizza slice.
- Your friend Alice will pick the next slice in the anti-clockwise direction of your pick.
- Your friend Bob will pick the next slice in the clockwise direction of your pick.
- Repeat until there are no more slices of pizzas.
Given an integer array slices that represent the sizes of the pizza slices in a clockwise direction, return the maximum possible sum of slice sizes that you can pick.
Example 1:
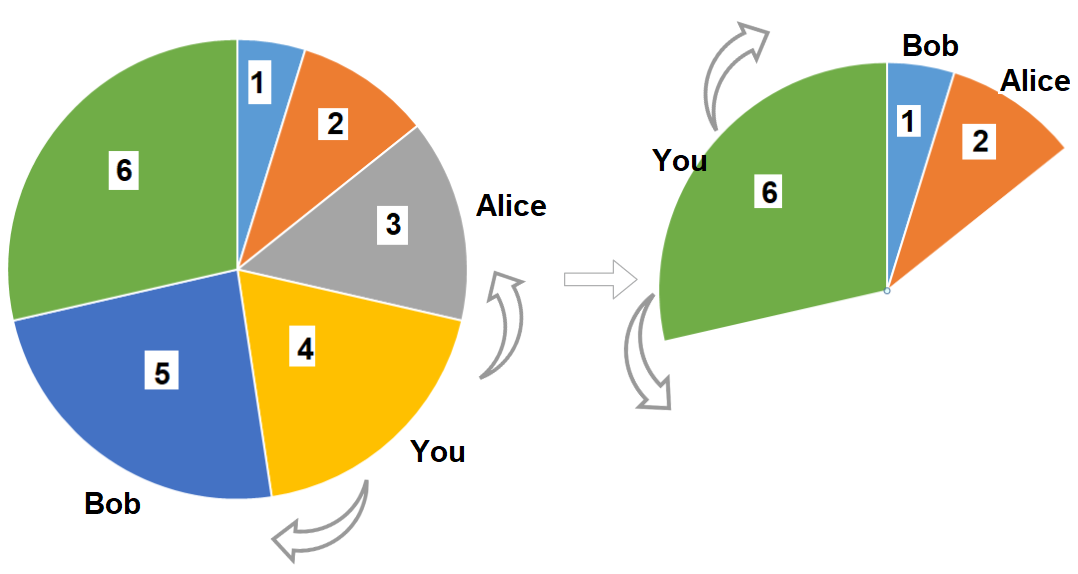
Input: slices = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 10 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 4, Alice and Bob will pick slices with size 3 and 5 respectively. Then Pick slices with size 6, finally Alice and Bob will pick slice of size 2 and 1 respectively. Total = 4 + 6.
Example 2:
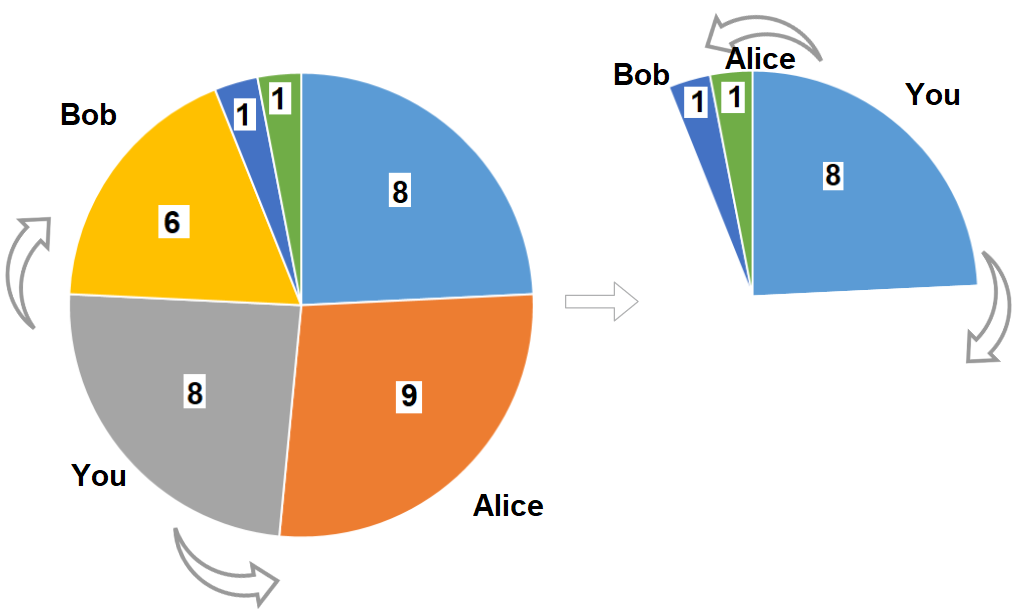
Input: slices = [8,9,8,6,1,1] Output: 16 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 8 in each turn. If you pick slice with size 9 your partners will pick slices of size 8.
Constraints:
3 * n == slices.length1 <= slices.length <= 5001 <= slices[i] <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1: Dynamic Programming
We can transform this problem into: In a circular array of length $3n$, select $n$ non-adjacent numbers so that the sum of these $n$ numbers is maximized.
The proof is as follows:
- When $n = 1$, we can choose any number in the array.
- When $n > 1$, there must exist a number such that there are two consecutive numbers on one side of it that have not been selected, and at least one number on the other side has not been selected. Therefore, we can remove this number and the numbers on both sides of it from the array, and then the remaining $3(n - 1)$ numbers form a new circular array. The problem scale is reduced to selecting $n - 1$ non-adjacent numbers in a circular array of length $3(n - 1)$, so that the sum of these $n - 1$ numbers is maximized.
Therefore, the problem we need to solve can be transformed into: In a circular array of length $3n$, select $n$ non-adjacent numbers so that the sum of these $n$ numbers is maximized.
In a circular array, if the first number is selected, the last number cannot be selected. If the last number is selected, the first number cannot be selected. Therefore, we can split the circular array into two arrays, one is without the first number, and the other is without the last number. Then solve the maximum value of these two arrays separately, and finally take the larger of the two maximum values.
We use a function $g(nums)$, which represents the maximum sum of selecting $n$ non-adjacent numbers in the array $nums$. Then our goal is to find the larger value between $g(slices)$ and $g(slices[1:])$.
The solution method of function $g(nums)$ is as follows:
We denote the length of array $nums$ as $m$, and define $f[i][j]$ as the maximum sum of selecting $j$ non-adjacent numbers in the first $i$ numbers of array $nums$.
Consider $f[i][j]$, if we do not select the $i$-th number, then $f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j]$. If we select the $i$-th number, then $f[i][j] = f[i - 2][j - 1] + nums[i - 1]$. Therefore, we can get the state transition equation:
\[f[i][j] = \max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 2][j - 1] + nums[i - 1])\]Finally, return $f[m][n]$.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n^2)$. Where $n$ is the length of the array $slices$.
-
class Solution { private int n; public int maxSizeSlices(int[] slices) { n = slices.length / 3; int[] nums = new int[slices.length - 1]; System.arraycopy(slices, 1, nums, 0, nums.length); int a = g(nums); System.arraycopy(slices, 0, nums, 0, nums.length); int b = g(nums); return Math.max(a, b); } private int g(int[] nums) { int m = nums.length; int[][] f = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], (i >= 2 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1]); } } return f[m][n]; } } -
class Solution { public: int maxSizeSlices(vector<int>& slices) { int n = slices.size() / 3; auto g = [&](vector<int>& nums) -> int { int m = nums.size(); int f[m + 1][n + 1]; memset(f, 0, sizeof f); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], (i >= 2 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1]); } } return f[m][n]; }; vector<int> nums(slices.begin(), slices.end() - 1); int a = g(nums); nums = vector<int>(slices.begin() + 1, slices.end()); int b = g(nums); return max(a, b); } }; -
class Solution: def maxSizeSlices(self, slices: List[int]) -> int: def g(nums: List[int]) -> int: m = len(nums) f = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)] for i in range(1, m + 1): for j in range(1, n + 1): f[i][j] = max( f[i - 1][j], (f[i - 2][j - 1] if i >= 2 else 0) + nums[i - 1] ) return f[m][n] n = len(slices) // 3 a, b = g(slices[:-1]), g(slices[1:]) return max(a, b) -
func maxSizeSlices(slices []int) int { n := len(slices) / 3 g := func(nums []int) int { m := len(nums) f := make([][]int, m+1) for i := range f { f[i] = make([]int, n+1) } for i := 1; i <= m; i++ { for j := 1; j <= n; j++ { f[i][j] = max(f[i-1][j], nums[i-1]) if i >= 2 { f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i-2][j-1]+nums[i-1]) } } } return f[m][n] } a, b := g(slices[:len(slices)-1]), g(slices[1:]) return max(a, b) } -
function maxSizeSlices(slices: number[]): number { const n = Math.floor(slices.length / 3); const g = (nums: number[]): number => { const m = nums.length; const f: number[][] = Array(m + 1) .fill(0) .map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(0)); for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], (i > 1 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1]); } } return f[m][n]; }; const a = g(slices.slice(0, -1)); const b = g(slices.slice(1)); return Math.max(a, b); }