Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
587. Erect the Fence
Description
You are given an array trees where trees[i] = [xi, yi] represents the location of a tree in the garden.
Fence the entire garden using the minimum length of rope, as it is expensive. The garden is well-fenced only if all the trees are enclosed.
Return the coordinates of trees that are exactly located on the fence perimeter. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
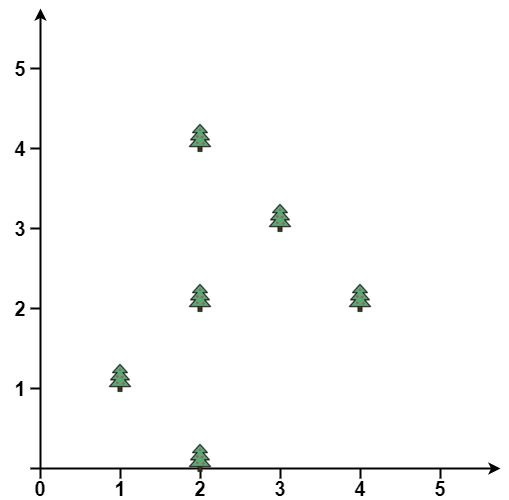
Input: trees = [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]] Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]] Explanation: All the trees will be on the perimeter of the fence except the tree at [2, 2], which will be inside the fence.
Example 2:
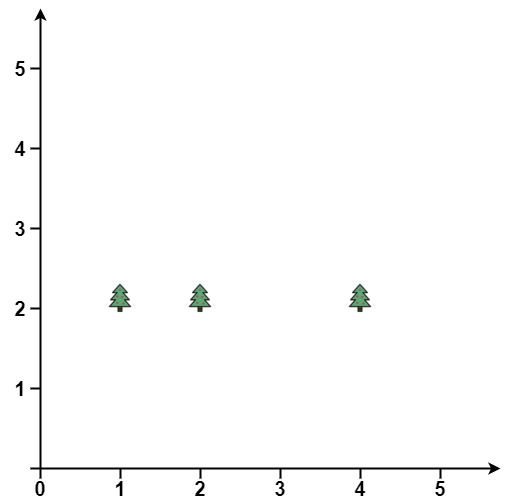
Input: trees = [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]] Output: [[4,2],[2,2],[1,2]] Explanation: The fence forms a line that passes through all the trees.
Constraints:
1 <= trees.length <= 3000trees[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100- All the given positions are unique.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int[][] outerTrees(int[][] trees) { int n = trees.length; if (n < 4) { return trees; } Arrays.sort(trees, (a, b) -> { return a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]; }); boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; int[] stk = new int[n + 10]; int cnt = 1; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { while (cnt > 1 && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) { vis[stk[--cnt]] = false; } vis[i] = true; stk[cnt++] = i; } int m = cnt; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } while (cnt > m && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) { --cnt; } stk[cnt++] = i; } int[][] ans = new int[cnt - 1][2]; for (int i = 0; i < ans.length; ++i) { ans[i] = trees[stk[i]]; } return ans; } private int cross(int[] a, int[] b, int[] c) { return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]); } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> outerTrees(vector<vector<int>>& trees) { int n = trees.size(); if (n < 4) return trees; sort(trees.begin(), trees.end()); vector<int> vis(n); vector<int> stk(n + 10); int cnt = 1; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { while (cnt > 1 && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) vis[stk[--cnt]] = false; vis[i] = true; stk[cnt++] = i; } int m = cnt; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) { if (vis[i]) continue; while (cnt > m && cross(trees[stk[cnt - 1]], trees[stk[cnt - 2]], trees[i]) < 0) --cnt; stk[cnt++] = i; } vector<vector<int>> ans; for (int i = 0; i < cnt - 1; ++i) ans.push_back(trees[stk[i]]); return ans; } int cross(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c) { return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]); } }; -
class Solution: def outerTrees(self, trees: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: def cross(i, j, k): a, b, c = trees[i], trees[j], trees[k] return (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) - (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]) n = len(trees) if n < 4: return trees trees.sort() vis = [False] * n stk = [0] for i in range(1, n): while len(stk) > 1 and cross(stk[-2], stk[-1], i) < 0: vis[stk.pop()] = False vis[i] = True stk.append(i) m = len(stk) for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1): if vis[i]: continue while len(stk) > m and cross(stk[-2], stk[-1], i) < 0: stk.pop() stk.append(i) stk.pop() return [trees[i] for i in stk] -
func outerTrees(trees [][]int) [][]int { n := len(trees) if n < 4 { return trees } sort.Slice(trees, func(i, j int) bool { if trees[i][0] == trees[j][0] { return trees[i][1] < trees[j][1] } return trees[i][0] < trees[j][0] }) cross := func(i, j, k int) int { a, b, c := trees[i], trees[j], trees[k] return (b[0]-a[0])*(c[1]-b[1]) - (b[1]-a[1])*(c[0]-b[0]) } vis := make([]bool, n) stk := []int{0} for i := 1; i < n; i++ { for len(stk) > 1 && cross(stk[len(stk)-1], stk[len(stk)-2], i) < 0 { vis[stk[len(stk)-1]] = false stk = stk[:len(stk)-1] } vis[i] = true stk = append(stk, i) } m := len(stk) for i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- { if vis[i] { continue } for len(stk) > m && cross(stk[len(stk)-1], stk[len(stk)-2], i) < 0 { stk = stk[:len(stk)-1] } stk = append(stk, i) } var ans [][]int for i := 0; i < len(stk)-1; i++ { ans = append(ans, trees[stk[i]]) } return ans }