Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
588. Design In-Memory File System
Description
Design a data structure that simulates an in-memory file system.
Implement the FileSystem class:
FileSystem()Initializes the object of the system.List<String> ls(String path)- If
pathis a file path, returns a list that only contains this file's name. - If
pathis a directory path, returns the list of file and directory names in this directory.
- If
void mkdir(String path)Makes a new directory according to the givenpath. The given directory path does not exist. If the middle directories in the path do not exist, you should create them as well.void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- If
filePathdoes not exist, creates that file containing givencontent. - If
filePathalready exists, appends the givencontentto original content.
- If
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)Returns the content in the file atfilePath.
Example 1:
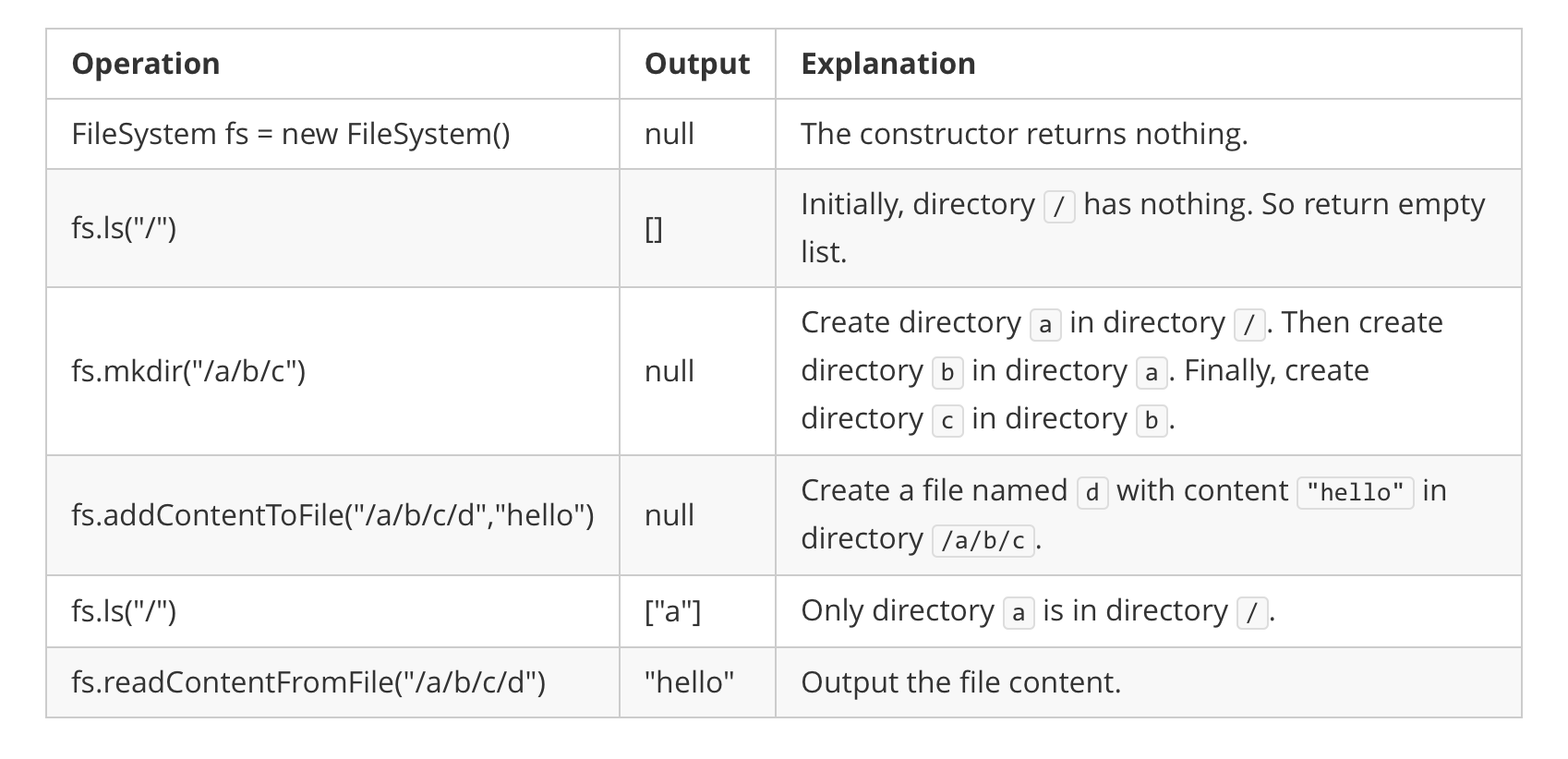
Input
["FileSystem", "ls", "mkdir", "addContentToFile", "ls", "readContentFromFile"]
[[], ["/"], ["/a/b/c"], ["/a/b/c/d", "hello"], ["/"], ["/a/b/c/d"]]
Output
[null, [], null, null, ["a"], "hello"]
Explanation
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // return "hello"
Constraints:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100pathandfilePathare absolute paths which begin with'/'and do not end with'/'except that the path is just"/".- You can assume that all directory names and file names only contain lowercase letters, and the same names will not exist in the same directory.
- You can assume that all operations will be passed valid parameters, and users will not attempt to retrieve file content or list a directory or file that does not exist.
1 <= content.length <= 50- At most
300calls will be made tols,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile.
Solutions
This solution defines two classes, Trie and FileSystem, that work together to simulate a basic file system.
Related to 1166-Design-File-System
Trie Class
The Trie class is a variation of the standard trie (prefix tree) data structure, commonly used for efficient storage and retrieval of string keys (like file paths in this case). It has the following attributes and methods:
- Attributes:
name: Stores the name of a file.isFile: A boolean flag indicating whether the node represents a file (True) or a directory (False).content: A list to store the content of the file. It’s only used if the node is a file.children: A dictionary that maps a part of the path to its childTrienode.
insertMethod:- Takes a
path(string) and aisFile(boolean) as input. - Splits the
pathand traverses the trie, creating new nodes if a part of the path doesn’t exist inchildren. - Sets the
isFileflag andnamefor a node if it’s a file. - Returns the last node in the path.
- Takes a
searchMethod:- Takes a
path(string) and searches for it in the trie. - Splits the
pathand traverses the trie according to the path parts. - Returns the node if found, otherwise returns
None.
- Takes a
FileSystem Class
The FileSystem class uses the Trie to implement basic file system operations:
- Attributes:
root: ATrieobject that acts as the root of the file system.
lsMethod:- Lists the contents of a directory or the name of a file at a given
path. - If the
pathis a file, returns a list containing only its name. - If the
pathis a directory, returns a sorted list of its children.
- Lists the contents of a directory or the name of a file at a given
mkdirMethod:- Creates a directory at the specified
path. - Uses the
insertmethod of theTrieclass, marking the path as a directory (not a file).
- Creates a directory at the specified
addContentToFileMethod:- Adds
contentto a file at the specifiedfilePath. - If the file doesn’t exist, it’s created.
- The content is appended to the
contentlist of the file’s node.
- Adds
readContentFromFileMethod:- Reads and returns the content of the file at the specified
filePath. - Joins and returns the elements of the
contentlist of the file’s node.
- Reads and returns the content of the file at the specified
-
class Trie { String name; boolean isFile; StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder(); Map<String, Trie> children = new HashMap<>(); Trie insert(String path, boolean isFile) { Trie node = this; String[] ps = path.split("/"); for (int i = 1; i < ps.length; ++i) { String p = ps[i]; if (!node.children.containsKey(p)) { node.children.put(p, new Trie()); } node = node.children.get(p); } node.isFile = isFile; if (isFile) { node.name = ps[ps.length - 1]; } return node; } Trie search(String path) { Trie node = this; String[] ps = path.split("/"); for (int i = 1; i < ps.length; ++i) { String p = ps[i]; if (!node.children.containsKey(p)) { return null; } node = node.children.get(p); } return node; } } class FileSystem { private Trie root = new Trie(); public FileSystem() { } public List<String> ls(String path) { List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>(); Trie node = root.search(path); if (node == null) { return ans; } if (node.isFile) { ans.add(node.name); return ans; } for (String v : node.children.keySet()) { ans.add(v); } Collections.sort(ans); return ans; } public void mkdir(String path) { root.insert(path, false); } public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) { Trie node = root.insert(filePath, true); node.content.append(content); } public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) { Trie node = root.search(filePath); return node.content.toString(); } } /** * Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such: * FileSystem obj = new FileSystem(); * List<String> param_1 = obj.ls(path); * obj.mkdir(path); * obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content); * String param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath); */ -
''' >>> "/a/b/c".split('/') ['', 'a', 'b', 'c'] ''' class Trie: def __init__(self): self.name = None self.isFile = False self.content = [] self.children = {} def insert(self, path, isFile): node = self ps = path.split('/') for p in ps[1:]: if p not in node.children: node.children[p] = Trie() node = node.children[p] node.isFile = isFile if isFile: node.name = ps[-1] return node def search(self, path): node = self if path == '/': return node ps = path.split('/') for p in ps[1:]: if p not in node.children: return None node = node.children[p] return node class FileSystem: def __init__(self): self.root = Trie() def ls(self, path: str) -> List[str]: node = self.root.search(path) if node is None: return [] if node.isFile: return [node.name] return sorted(node.children.keys()) def mkdir(self, path: str) -> None: self.root.insert(path, False) def addContentToFile(self, filePath: str, content: str) -> None: node = self.root.insert(filePath, True) node.content.append(content) def readContentFromFile(self, filePath: str) -> str: node = self.root.search(filePath) return ''.join(node.content) # Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = FileSystem() # param_1 = obj.ls(path) # obj.mkdir(path) # obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content) # param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath) -
type Trie struct { name string isFile bool content strings.Builder children map[string]*Trie } func newTrie() *Trie { m := map[string]*Trie{} return &Trie{children: m} } func (this *Trie) insert(path string, isFile bool) *Trie { node := this ps := strings.Split(path, "/") for _, p := range ps[1:] { if _, ok := node.children[p]; !ok { node.children[p] = newTrie() } node, _ = node.children[p] } node.isFile = isFile if isFile { node.name = ps[len(ps)-1] } return node } func (this *Trie) search(path string) *Trie { if path == "/" { return this } node := this ps := strings.Split(path, "/") for _, p := range ps[1:] { if _, ok := node.children[p]; !ok { return nil } node, _ = node.children[p] } return node } type FileSystem struct { root *Trie } func Constructor() FileSystem { root := newTrie() return FileSystem{root} } func (this *FileSystem) Ls(path string) []string { var ans []string node := this.root.search(path) if node == nil { return ans } if node.isFile { ans = append(ans, node.name) return ans } for v := range node.children { ans = append(ans, v) } sort.Strings(ans) return ans } func (this *FileSystem) Mkdir(path string) { this.root.insert(path, false) } func (this *FileSystem) AddContentToFile(filePath string, content string) { node := this.root.insert(filePath, true) node.content.WriteString(content) } func (this *FileSystem) ReadContentFromFile(filePath string) string { node := this.root.search(filePath) return node.content.String() } /** * Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such: * obj := Constructor(); * param_1 := obj.Ls(path); * obj.Mkdir(path); * obj.AddContentToFile(filePath,content); * param_4 := obj.ReadContentFromFile(filePath); */