Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
549. Binary Tree Longest Consecutive Sequence II
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest consecutive path in the tree.
A consecutive path is a path where the values of the consecutive nodes in the path differ by one. This path can be either increasing or decreasing.
- For example,
[1,2,3,4]and[4,3,2,1]are both considered valid, but the path[1,2,4,3]is not valid.
On the other hand, the path can be in the child-Parent-child order, where not necessarily be parent-child order.
Example 1:
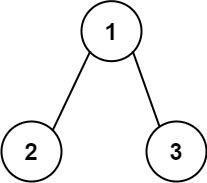
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The longest consecutive path is [1, 2] or [2, 1].
Example 2:
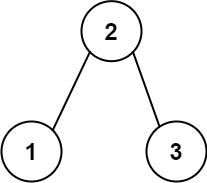
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: 3 Explanation: The longest consecutive path is [1, 2, 3] or [3, 2, 1].
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -3 * 104 <= Node.val <= 3 * 104
Solutions
Approach Overview
The solution employs Depth-First Search (DFS) to traverse the tree. At each node, it calculates two things:
- The length of the longest increasing consecutive path (
incr) ending at that node. - The length of the longest decreasing consecutive path (
decr) ending at that node.
It returns these lengths as a pair [incr, decr] for each node. The overall longest path that can be formed is the sum of increasing and decreasing paths minus 1 (to avoid double-counting the current node) at any node. This sum is tracked globally using the variable ans.
DFS Function Details
-
Base Case: If the current node (
root) isNone, it returns[0, 0]indicating no consecutive path. -
Recursive Case:
- It initializes
incranddecrto 1 for the current node since a node on its own forms a consecutive sequence of length 1. - It then recursively calls
dfson both the left and right children of the current node, receiving their respective longest increasing and decreasing paths as[i1, d1]and[i2, d2]. - For both children, it checks if the child’s value forms a consecutive sequence with the current node (
root.val). If so, it updatesincrordecraccordingly. If the left child’s value is one less than the current node’s value,incris incremented; if it’s one more,decris incremented. The same logic applies to the right child, with the additional step of taking the maximum between the current value ofincrordecrand the value obtained from the right child. This ensures that we consider the longest path possible. - It updates the global
ansvariable with the maximum value found so far.ansis calculated as the sum ofincranddecrminus 1 (since the root node is counted in bothincranddecr, it should be subtracted once to get the actual length of the path).
- It initializes
Global Variable ans
ansis used to track the maximum length of the consecutive path found at any point during the traversal of the tree. It is marked asnonlocalwithin the nesteddfsfunction to update its value across recursive calls.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; public int longestConsecutive(TreeNode root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return new int[] {0, 0}; } int incr = 1, decr = 1; int[] left = dfs(root.left); int[] right = dfs(root.right); if (root.left != null) { if (root.left.val + 1 == root.val) { incr = left[0] + 1; } if (root.left.val - 1 == root.val) { decr = left[1] + 1; } } if (root.right != null) { if (root.right.val + 1 == root.val) { incr = Math.max(incr, right[0] + 1); } if (root.right.val - 1 == root.val) { decr = Math.max(decr, right[1] + 1); } } ans = Math.max(ans, incr + decr - 1); return new int[] {incr, decr}; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int ans; int longestConsecutive(TreeNode* root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return {0, 0}; int incr = 1, decr = 1; auto left = dfs(root->left); auto right = dfs(root->right); if (root->left) { if (root->left->val + 1 == root->val) incr = left[0] + 1; if (root->left->val - 1 == root->val) decr = left[1] + 1; } if (root->right) { if (root->right->val + 1 == root->val) incr = max(incr, right[0] + 1); if (root->right->val - 1 == root->val) decr = max(decr, right[1] + 1); } ans = max(ans, incr + decr - 1); return {incr, decr}; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None ''' >>> float('-inf')+1 -inf >>> float('-inf')-1 -inf ''' class Solution(object): def longestConsecutive(self, root): """ :type root: TreeNode :rtype: int """ def dfs(root): if not root: # val, increasing length, decreasing length, max length return float('-inf'), 0, 0, 0 # inc/dec starting from root inc = dec = 1 left, leftInc, leftDec, leftMax = dfs(root.left) right, rightInc, rightDec, rightMax = dfs(root.right) if root.val + 1 == left: inc = max(leftInc + 1, inc) if root.val - 1 == left: dec = max(leftDec + 1, dec) if root.val + 1 == right: inc = max(rightInc + 1, inc) if root.val - 1 == right: dec = max(rightDec + 1, dec) # note: max may occur in children subtree, not current root's tree return root.val, inc, dec, max(inc + dec - 1, leftMax, rightMax, inc, dec) # -1 because root is counted twice, even left/right both null return dfs(root)[3] ############ # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def longestConsecutive(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: def dfs(root): if root is None: return [0, 0] nonlocal ans incr = decr = 1 i1, d1 = dfs(root.left) i2, d2 = dfs(root.right) if root.left: if root.left.val + 1 == root.val: incr = i1 + 1 if root.left.val - 1 == root.val: decr = d1 + 1 if root.right: if root.right.val + 1 == root.val: incr = max(incr, i2 + 1) # incr1 and incr2 must be in different tree branches, eg. left child cannot be both increasing and decreasing. Same as decr1 and decr2 if root.right.val - 1 == root.val: decr = max(decr, d2 + 1) ans = max(ans, incr + decr - 1) # -1 because root is counted twice, even left/right both null return [incr, decr] ans = 0 dfs(root) return ans ############ class Solution: # issue with this solution, duplicated dfs() search def longestConsecutive(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: def helper(node: TreeNode, diff: int) -> int: if not node: return 0 left = right = 0 if node.left and node.val - node.left.val == diff: left = 1 + helper(node.left, diff) if node.right and node.val - node.right.val == diff: right = 1 + helper(node.right, diff) return max(left, right) if not root: return 0 res = helper(root, 1) + helper(root, -1) + 1 # +1 is increasing, -1 is decreasing return max(res, max(longestConsecutive(root.left), longestConsecutive(root.right))) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func longestConsecutive(root *TreeNode) int { ans := 0 var dfs func(root *TreeNode) []int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) []int { if root == nil { return []int{0, 0} } incr, decr := 1, 1 left := dfs(root.Left) right := dfs(root.Right) if root.Left != nil { if root.Left.Val+1 == root.Val { incr = left[0] + 1 } if root.Left.Val-1 == root.Val { decr = left[1] + 1 } } if root.Right != nil { if root.Right.Val+1 == root.Val { incr = max(incr, right[0]+1) } if root.Right.Val-1 == root.Val { decr = max(decr, right[1]+1) } } ans = max(ans, incr+decr-1) return []int{incr, decr} } dfs(root) return ans }