Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
508. Most Frequent Subtree Sum
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the most frequent subtree sum. If there is a tie, return all the values with the highest frequency in any order.
The subtree sum of a node is defined as the sum of all the node values formed by the subtree rooted at that node (including the node itself).
Example 1:
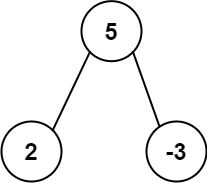
Input: root = [5,2,-3] Output: [2,-3,4]
Example 2:
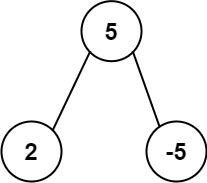
Input: root = [5,2,-5] Output: [2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private Map<Integer, Integer> counter; private int mx; public int[] findFrequentTreeSum(TreeNode root) { counter = new HashMap<>(); mx = Integer.MIN_VALUE; dfs(root); List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counter.entrySet()) { if (entry.getValue() == mx) { res.add(entry.getKey()); } } int[] ans = new int[res.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i) { ans[i] = res.get(i); } return ans; } private int dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int s = root.val + dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right); counter.put(s, counter.getOrDefault(s, 0) + 1); mx = Math.max(mx, counter.get(s)); return s; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: unordered_map<int, int> counter; int mx = 0; vector<int> findFrequentTreeSum(TreeNode* root) { mx = INT_MIN; dfs(root); vector<int> ans; for (auto& entry : counter) if (entry.second == mx) ans.push_back(entry.first); return ans; } int dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; int s = root->val + dfs(root->left) + dfs(root->right); ++counter[s]; mx = max(mx, counter[s]); return s; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def findFrequentTreeSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]: def dfs(root): if root is None: return 0 left, right = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right) s = root.val + left + right counter[s] += 1 return s counter = Counter() dfs(root) mx = max(counter.values()) return [k for k, v in counter.items() if v == mx] -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func findFrequentTreeSum(root *TreeNode) []int { counter := make(map[int]int) mx := 0 var dfs func(root *TreeNode) int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } s := root.Val + dfs(root.Left) + dfs(root.Right) counter[s]++ if mx < counter[s] { mx = counter[s] } return s } dfs(root) var ans []int for k, v := range counter { if v == mx { ans = append(ans, k) } } return ans } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function findFrequentTreeSum(root: TreeNode | null): number[] { const map = new Map<number, number>(); let max = 0; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => { if (root == null) { return 0; } const { val, left, right } = root; const sum = val + dfs(left) + dfs(right); map.set(sum, (map.get(sum) ?? 0) + 1); max = Math.max(max, map.get(sum)); return sum; }; dfs(root); const res = []; for (const [k, v] of map) { if (v === max) { res.push(k); } } return res; } -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; use std::collections::HashMap; impl Solution { fn dfs( root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, map: &mut HashMap<i32, i32>, max: &mut i32 ) -> i32 { if root.is_none() { return 0; } let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow(); let sum = node.val + Self::dfs(&node.left, map, max) + Self::dfs(&node.right, map, max); map.insert(sum, map.get(&sum).unwrap_or(&0) + 1); *max = (*max).max(map[&sum]); sum } pub fn find_frequent_tree_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> { let mut map = HashMap::new(); let mut max = 0; let mut res = Vec::new(); Self::dfs(&root, &mut map, &mut max); for (k, v) in map.into_iter() { if v == max { res.push(k); } } res } }