Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/431.html
Design an algorithm to encode an N-ary tree into a binary tree and decode the binary tree to get the original N-ary tree. An N-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than N children. Similarly, a binary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than 2 children. There is no restriction on how your encode/decode algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that an N-ary tree can be encoded to a binary tree and this binary tree can be decoded to the original N-nary tree structure.
For example, you may encode the following 3-ary tree to a binary tree in this way:
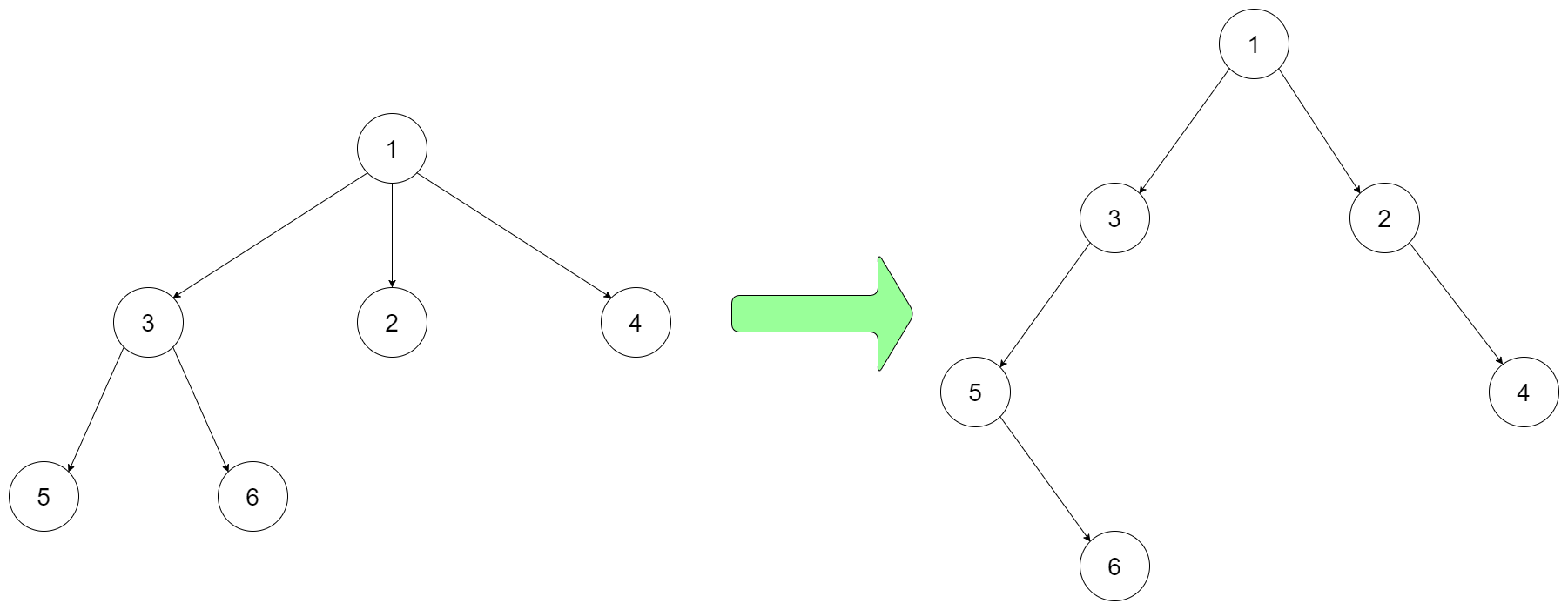
Note that the above is just an example which might or might not work. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Note:
Nis in the range of[1, 1000]- Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your encode and decode algorithms should be stateless.
这道题让我们将一棵N叉树编码为二叉树,其实还需要将二叉树解码回N叉树。题目中说了具体的编解码的方法无所谓,那么就怎么简单怎么来呗。首先想一下这道题的难点是什么,N叉树的特点的每个结点最多有N个子结点,而二叉树的每个结点最多只能有两个子结点,那么多余的子结点怎么办,当然只能继续子结点下继续累加,就像泡泡龙游戏一样,一个挂一个的。如何累,得确定一套具体的规则,这样解码的时候,反向来一遍就可以了。对于当前结点 root 的N个子结点的处理办法是,将第一个结点挂到二叉树的左子结点上,然后将后面的结点依次挂到右子结点,和右子结点的右子结点上,这样做的好处是,同一层的子结点都挂在右子结点上,而这些子结点自己的子结点都会挂在左子结点上,听起来很晕是么,那就举例说明一下吧,就用题目中的例子中的树好了(注意题目中说只要能把N叉树编码成二叉树,然后再解码回原N叉树,并不 care 到底编码成啥样的二叉树)。
N-ary Tree:
1
/ | \
3 2 4
/ \
5 6
Binary Tree:
1
/
3
/ \
5 2
\ \
6 4
我们可以看出,N叉树根结点1的第一个子结点3被挂到了二叉树的左子结点上,同一层的结点2挂到了结点3的右子结点上,同一层的结点4被挂到了结点2的右子结点上。而结点3本身的子结点也按照这个规律,第一个子结点5挂到了结点3的左子结点上,而同一排的结点6挂到了结点5的右子结点上。
对于解码,也是同样的规律,先根据根结点值新建一个空的N叉树结点,由于我们的编码规律,根结点是一定没有右子结点的,所以取出左子结点 cur,并且开始循环,如果 cur 结点存在,那么我们对 cur 递归调用解码函数,将返回的结点加入当前N叉树结点的 children 数组中,然后 cur 再赋值为其右子结点,继续递归调用解码函数,再加入 children 数组,如此便可将二叉树还原为之前的N叉树,参见代码如下:
-
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Codec { // Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree. public TreeNode encode(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root.val); if (root.children == null || root.children.isEmpty()) { return node; } TreeNode left = encode(root.children.get(0)); node.left = left; for (int i = 1; i < root.children.size(); i++) { left.right = encode(root.children.get(i)); left = left.right; } return node; } // Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree. public Node decode(TreeNode data) { if (data == null) { return null; } Node node = new Node(data.val, new ArrayList<>()); if (data.left == null) { return node; } TreeNode left = data.left; while (left != null) { node.children.add(decode(left)); left = left.right; } return node; } } // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: // Codec codec = new Codec(); // codec.decode(codec.encode(root)); -
class Codec { public: // Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree. TreeNode* encode(Node* root) { if (!root) return NULL; TreeNode *res = new TreeNode(root->val); if (!root->children.empty()) { res->left = encode(root->children[0]); } TreeNode *cur = res->left; for (int i = 1; i < root->children.size(); ++i) { cur->right = encode(root->children[i]); cur = cur->right; } return res; } // Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree. Node* decode(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return NULL; Node *res = new Node(root->val, {}); TreeNode *cur = root->left; while (cur) { res->children.push_back(decode(cur)); cur = cur->right; } return res; } }; -
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val: Optional[int] = None, children: Optional[List['Node']] = None): self.val = val self.children = children """ """ # Definition for a binary tree node. class TreeNode: def __init__(self, x): self.val = x self.left = None self.right = None """ class Codec: # Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree. def encode(self, root: "Optional[Node]") -> Optional[TreeNode]: if root is None: return None node = TreeNode(root.val) if not root.children: return node left = self.encode(root.children[0]) node.left = left for child in root.children[1:]: left.right = self.encode(child) left = left.right return node # Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree. def decode(self, data: Optional[TreeNode]) -> "Optional[Node]": if data is None: return None node = Node(data.val, []) if data.left is None: return node left = data.left while left: node.children.append(self.decode(left)) left = left.right return node # Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: # codec = Codec() # codec.decode(codec.encode(root)) -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Children []*Node * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ type Codec struct { } func Constructor() *Codec { return &Codec{} } // Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree. func (this *Codec) encode(root *Node) *TreeNode { if root == nil { return nil } node := &TreeNode{Val: root.Val} if len(root.Children) == 0 { return node } left := this.encode(root.Children[0]) node.Left = left for i := 1; i < len(root.Children); i++ { left.Right = this.encode(root.Children[i]) left = left.Right } return node } // Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree. func (this *Codec) decode(data *TreeNode) *Node { if data == nil { return nil } node := &Node{Val: data.Val, Children: []*Node{} } if data.Left == nil { return node } left := data.Left for left != nil { node.Children = append(node.Children, this.decode(left)) left = left.Right } return node } /** * Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: * obj := Constructor(); * bst := obj.encode(root); * ans := obj.decode(bst); */ -
/** * Definition for _Node. * class _Node { * val: number * children: _Node[] * * constructor(v: number) { * this.val = v; * this.children = []; * } * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ class Codec { constructor() {} // Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree. serialize(root: _Node | null): TreeNode | null { if (root === null) { return null; } const node = new TreeNode(root.val); if (root.children.length === 0) { return node; } let left: TreeNode | null = this.serialize(root.children[0]); node.left = left; for (let i = 1; i < root.children.length; i++) { if (left) { left.right = this.serialize(root.children[i]); left = left.right; } } return node; } // Decodes your binary tree back to an n-ary tree. deserialize(root: TreeNode | null): _Node | null { if (root === null) { return null; } const node = new _Node(root.val); if (root.left === null) { return node; } let left: TreeNode | null = root.left; while (left !== null) { node.children.push(this.deserialize(left)); left = left.right; } return node; } } // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: // Codec codec = new Codec(); // codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));