Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Description
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
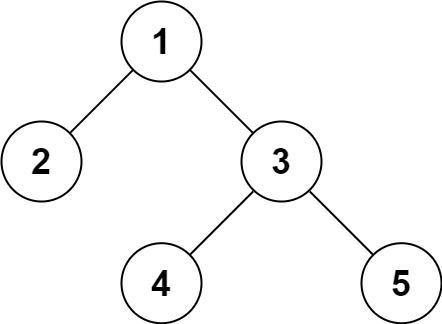
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
Pre-order traversal method.
For serialization, we start from the root node. If the node exists, store the value in the output string stream, and then recursively call the serialization function on its left and right child nodes.
For deserialization, we first read in the first character to generate a root node, and then recursively call the deserialization function on the left and right child nodes of the root node.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Codec { private static final String NULL = "#"; private static final String SEP = ","; // Encodes a tree to a single string. public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return ""; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); preorder(root, sb); return sb.toString(); } private void preorder(TreeNode root, StringBuilder sb) { if (root == null) { sb.append(NULL + SEP); return; } sb.append(root.val + SEP); preorder(root.left, sb); preorder(root.right, sb); } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { if (data == null || "".equals(data)) { return null; } List<String> vals = new LinkedList<>(); for (String x : data.split(SEP)) { vals.add(x); } return deserialize(vals); } private TreeNode deserialize(List<String> vals) { String first = vals.remove(0); if (NULL.equals(first)) { return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(first)); root.left = deserialize(vals); root.right = deserialize(vals); return root; } } // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: // Codec ser = new Codec(); // Codec deser = new Codec(); // TreeNode ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root)); -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Codec { public: // Encodes a tree to a single string. string serialize(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return ""; string s = ""; preorder(root, s); return s; } void preorder(TreeNode* root, string& s) { if (!root) s += "# "; else { s += to_string(root->val) + " "; preorder(root->left, s); preorder(root->right, s); } } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. TreeNode* deserialize(string data) { if (data == "") return nullptr; stringstream ss(data); return deserialize(ss); } TreeNode* deserialize(stringstream& ss) { string first; ss >> first; if (first == "#") return nullptr; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(first)); root->left = deserialize(ss); root->right = deserialize(ss); return root; } }; // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: // Codec ser, deser; // TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root)); -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Codec: def serialize(self, root): """Encodes a tree to a single string. :type root: TreeNode :rtype: str """ if root is None: return '' res = [] def preorder(root): if root is None: res.append("#,") return res.append(str(root.val) + ",") preorder(root.left) preorder(root.right) preorder(root) return ''.join(res) def deserialize(self, data): """Decodes your encoded data to tree. :type data: str :rtype: TreeNode """ if not data: return None vals = data.split(',') def inner(): first = vals.pop(0) if first == '#': return None return TreeNode(int(first), inner(), inner()) # seems using a constructor __init__(val, left, right) return inner() # Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: # ser = Codec() # deser = Codec() # ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root)) ############ from collections import deque # bfs, each level based class Codec: def serialize(self, root): """Encodes a tree to a single string. :type root: TreeNode :rtype: str """ ret = [] queue = deque([root]) while queue: top = queue.popleft() if not top: ret.append("None") continue else: ret.append(str(top.val)) queue.append(top.left) queue.append(top.right) return ",".join(ret) def deserialize(self, data): """Decodes your encoded data to tree. :type data: str :rtype: TreeNode """ data = data.split(",") if data[0] == "None": return None root = TreeNode(int(data[0])) queue = deque([root]) i = 0 while queue and i < len(data): top = queue.popleft() i += 1 left = right = None if i < len(data) and data[i] != "None": left = TreeNode(int(data[i])) queue.append(left) i += 1 if i < len(data) and data[i] != "None": right = TreeNode(int(data[i])) queue.append(right) top.left = left top.right = right return root # Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: # codec = Codec() # codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root)) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ /* * Encodes a tree to a single string. */ function serialize(root: TreeNode | null): string { if (root == null) { return '#'; } const { val, left, right } = root; return `${val},${serialize(left)},${serialize(right)}`; } /* * Decodes your encoded data to tree. */ function deserialize(data: string): TreeNode | null { const n = data.length; if (n === 1) { return null; } const vals = data.split(',').reverse(); const renew = () => { const val = vals.pop(); if (val == null || val === '#') { return null; } return new TreeNode(Number(val), renew(), renew()); }; return renew(); } /** * Your functions will be called as such: * deserialize(serialize(root)); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.left = this.right = null; * } */ /** * Encodes a tree to a single string. * * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {string} */ var serialize = function (root) { return rserialize(root, ''); }; /** * Decodes your encoded data to tree. * * @param {string} data * @return {TreeNode} */ var deserialize = function (data) { const dataArray = data.split(','); return rdeserialize(dataArray); }; const rserialize = (root, str) => { if (root === null) { str += '#,'; } else { str += root.val + '' + ','; str = rserialize(root.left, str); str = rserialize(root.right, str); } return str; }; const rdeserialize = dataList => { if (dataList[0] === '#') { dataList.shift(); return null; } const root = new TreeNode(parseInt(dataList[0])); dataList.shift(); root.left = rdeserialize(dataList); root.right = rdeserialize(dataList); return root; }; /** * Your functions will be called as such: * deserialize(serialize(root)); */ -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; struct Codec {} /** * `&self` means the method takes an immutable reference. * If you need a mutable reference, change it to `&mut self` instead. */ impl Codec { fn new() -> Self { Codec {} } fn serialize(&self, root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> String { if root.is_none() { return String::from("#"); } let mut node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut(); let left = node.left.take(); let right = node.right.take(); format!("{},{},{}", self.serialize(right), self.serialize(left), node.val) } fn deserialize(&self, data: String) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { if data.len() == 1 { return None; } Self::renew(&mut data.split(",").collect()) } fn renew(vals: &mut Vec<&str>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { let val = vals.pop().unwrap_or("#"); if val == "#" { return None; } Some( Rc::new( RefCell::new(TreeNode { val: val.parse().unwrap(), left: Self::renew(vals), right: Self::renew(vals), }) ) ) } }/** * Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: * let obj = Codec::new(); * let data: String = obj.serialize(strs); * let ans: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> = obj.deserialize(data); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ type Codec struct { } func Constructor() Codec { return Codec{} } // Serializes a tree to a single string. func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string { if root == nil { return "" } q := []*TreeNode{root} ans := []string{} for len(q) > 0 { node := q[0] q = q[1:] if node != nil { ans = append(ans, strconv.Itoa(node.Val)) q = append(q, node.Left) q = append(q, node.Right) } else { ans = append(ans, "#") } } return strings.Join(ans, ",") } // Deserializes your encoded data to tree. func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode { if data == "" { return nil } vals := strings.Split(data, ",") v, _ := strconv.Atoi(vals[0]) i := 1 root := &TreeNode{Val: v} q := []*TreeNode{root} for len(q) > 0 { node := q[0] q = q[1:] if x, err := strconv.Atoi(vals[i]); err == nil { node.Left = &TreeNode{Val: x} q = append(q, node.Left) } i++ if x, err := strconv.Atoi(vals[i]); err == nil { node.Right = &TreeNode{Val: x} q = append(q, node.Right) } i++ } return root } /** * Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: * ser := Constructor(); * deser := Constructor(); * data := ser.serialize(root); * ans := deser.deserialize(data); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * public int val; * public TreeNode left; * public TreeNode right; * public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Codec { // Encodes a tree to a single string. public string serialize(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } List<string> ans = new List<string>(); Queue<TreeNode> q = new Queue<TreeNode>(); q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { TreeNode node = q.Dequeue(); if (node != null) { ans.Add(node.val.ToString()); q.Enqueue(node.left); q.Enqueue(node.right); } else { ans.Add("#"); } } return string.Join(",", ans); } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. public TreeNode deserialize(string data) { if (data == null) { return null; } string[] vals = data.Split(','); int i = 0; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(int.Parse(vals[i++])); Queue<TreeNode> q = new Queue<TreeNode>(); q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { TreeNode node = q.Dequeue(); if (vals[i] != "#") { node.left = new TreeNode(int.Parse(vals[i])); q.Enqueue(node.left); } i++; if (vals[i] != "#") { node.right = new TreeNode(int.Parse(vals[i])); q.Enqueue(node.right); } i++; } return root; } } // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: // Codec codec = new Codec(); // codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));