Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
296. Best Meeting Point
Description
Given an m x n binary grid grid where each 1 marks the home of one friend, return the minimal total travel distance.
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Example 1:
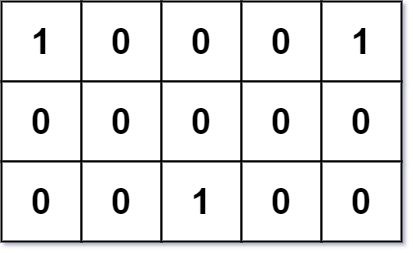
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]] Output: 6 Explanation: Given three friends living at (0,0), (0,4), and (2,2). The point (0,2) is an ideal meeting point, as the total travel distance of 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 is minimal. So return 6.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200grid[i][j]is either0or1.- There will be at least two friends in the
grid.
Solutions
First look at the situation where there are two points A and B in one dimension.
______A_____P_______B_______
It can be found that as long as the meeting is that the location P is in the interval [A, B], no matter where it is, the sum of the distances is the distance between A and B. If P is not between [A, B], then the sum of the distances is Will be greater than the distance between A and B, now add two more points C and D:
______C_____A_____P_______B______D______
The best position of point P is in the interval [A, B], so that the sum of the distances from the four points is the AB distance plus the CD distance.
Just sort the positions, then subtract the first coordinate from the last coordinate, which is the CD distance, and subtract the second coordinate from the penultimate, the second coordinate, which is the AB distance. And so on, until the middle stop.
The one-dimensional situation is analyzed, and the two-dimensional situation is the addition of two one-dimensional results.
-
class Solution { public int minTotalDistance(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; List<Integer> rows = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> cols = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { rows.add(i); cols.add(j); } } } Collections.sort(cols); int i = rows.get(rows.size() >> 1); int j = cols.get(cols.size() >> 1); return f(rows, i) + f(cols, j); } private int f(List<Integer> arr, int x) { int s = 0; for (int v : arr) { s += Math.abs(v - x); } return s; } } -
class Solution { public: int minTotalDistance(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); vector<int> rows; vector<int> cols; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j]) { rows.emplace_back(i); cols.emplace_back(j); } } } sort(cols.begin(), cols.end()); int i = rows[rows.size() / 2]; int j = cols[cols.size() / 2]; auto f = [](vector<int>& arr, int x) { int s = 0; for (int v : arr) { s += abs(v - x); } return s; }; return f(rows, i) + f(cols, j); } }; -
''' >>> sum(a for a in range(6)) 15 >>> sum([a for a in range(6)]) 15 ''' class Solution: def minTotalDistance(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: def f(arr, x): return sum(abs(v - x) for v in arr) rows, cols = [], [] for i, row in enumerate(grid): for j, v in enumerate(row): if v: rows.append(i) cols.append(j) cols.sort() row_mid_val = rows[len(rows) >> 1] col_mid_val = cols[len(cols) >> 1] return f(rows, row_mid_val) + f(cols, col_mid_val) ############ ''' >>> ppl = [ [11,22], [33,44], [55,66] ] >>> m=30 >>> n=50 >>> a = map(lambda p: abs(p[0]-m) + abs(p[1]-n), ppl) >>> a <map object at 0x10f865c30> >>> sum(a) 97 ''' class Solution(object): def minTotalDistance(self, grid): """ :type grid: List[List[int]] :rtype: int """ iList, jList, ppl = [], [], [] for i in range(0, len(grid)): for j in range(0, len(grid[0])): if grid[i][j] == 1: ppl.append((i, j)) iList.append(i) jList.append(j) jList.sort() m = iList[len(iList) / 2] n = jList[len(jList) / 2] return sum( map( lambda p: abs(p[0] - m) + abs(p[1] - n), ppl ) ) -
func minTotalDistance(grid [][]int) int { rows, cols := []int{}, []int{} for i, row := range grid { for j, v := range row { if v == 1 { rows = append(rows, i) cols = append(cols, j) } } } sort.Ints(cols) i := rows[len(rows)>>1] j := cols[len(cols)>>1] f := func(arr []int, x int) int { s := 0 for _, v := range arr { s += abs(v - x) } return s } return f(rows, i) + f(cols, j) } func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x } return x } -
impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn min_total_distance(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let n = grid.len(); let m = grid[0].len(); let mut row_vec = Vec::new(); let mut col_vec = Vec::new(); // Initialize the two vector for i in 0..n { for j in 0..m { if grid[i][j] == 1 { row_vec.push(i as i32); col_vec.push(j as i32); } } } // Since the row vector is originally sorted, we only need to sort the col vector here col_vec.sort(); Self::compute_manhattan_dis(&row_vec, row_vec[row_vec.len() / 2]) + Self::compute_manhattan_dis(&col_vec, col_vec[col_vec.len() / 2]) } #[allow(dead_code)] fn compute_manhattan_dis(v: &Vec<i32>, e: i32) -> i32 { let mut ret = 0; for num in v { ret += (num - e).abs(); } ret } }