Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
148. Sort List
Description
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:
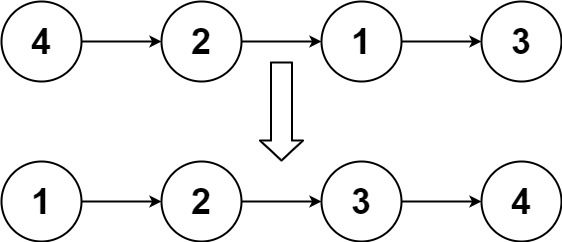
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
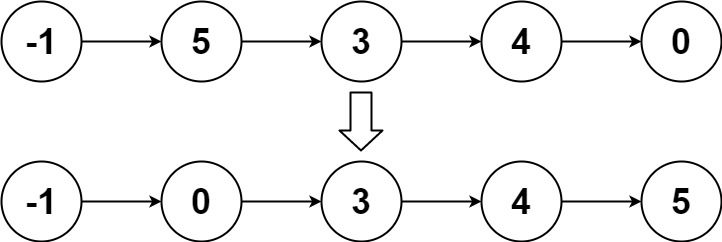
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Solutions
The problem specifies a time complexity constraint of O(n log n), which narrows down the suitable sorting algorithms to:
- Quick sort,
- Merge sort, and
- Heap sort.
Given the nature of singly linked lists, merge sort emerges as the most appropriate choice.
To implement merge sort on a linked list, it’s essential first to identify the middle node of the list. This can be achieved by employing two pointers:
- The fast pointer advances two steps at a time, while the slow pointer progresses one step.
- When the fast pointer reaches the end of the list, the slow pointer will be at the midpoint, effectively marking the middle node.
Once the middle node is identified, the list is divided into two halves. Each half is then sorted independently via merge sort. Following the sorting of both halves, they are merged together.
To merge two halves of a list, the process consistently selects the node with the smaller value between the two halves and appends it to the resulting sorted list. This step is repeated until all nodes are merged into a single, sorted sequence.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode t = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode l1 = sortList(head); ListNode l2 = sortList(t); ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val <= l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return dummy.next; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) { if (!head || !head->next) return head; auto* slow = head; auto* fast = head->next; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } auto* t = slow->next; slow->next = nullptr; auto* l1 = sortList(head); auto* l2 = sortList(t); auto* dummy = new ListNode(); auto* cur = dummy; while (l1 && l2) { if (l1->val <= l2->val) { cur->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { cur->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } cur = cur->next; } cur->next = l1 ? l1 : l2; return dummy->next; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: if head is None or head.next is None: return head slow, fast = head, head.next while fast and fast.next: slow, fast = slow.next, fast.next.next t = slow.next slow.next = None l1, l2 = self.sortList(head), self.sortList(t) dummy = ListNode() cur = dummy while l1 and l2: if l1.val <= l2.val: cur.next = l1 l1 = l1.next else: cur.next = l2 l2 = l2.next cur = cur.next cur.next = l1 or l2 # add the rest return dummy.next -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func sortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode { if head == nil || head.Next == nil { return head } slow, fast := head, head.Next for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil { slow, fast = slow.Next, fast.Next.Next } t := slow.Next slow.Next = nil l1, l2 := sortList(head), sortList(t) dummy := &ListNode{} cur := dummy for l1 != nil && l2 != nil { if l1.Val <= l2.Val { cur.Next = l1 l1 = l1.Next } else { cur.Next = l2 l2 = l2.Next } cur = cur.Next } if l1 != nil { cur.Next = l1 } else { cur.Next = l2 } return dummy.Next } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function sortList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // 快慢指针定位中点 let slow: ListNode = head, fast: ListNode = head.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } // 归并排序 let mid: ListNode = slow.next; slow.next = null; let l1: ListNode = sortList(head); let l2: ListNode = sortList(mid); let dummy: ListNode = new ListNode(); let cur: ListNode = dummy; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val <= l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return dummy.next; } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {ListNode} */ var sortList = function (head) { if (!head || !head.next) { return head; } let slow = head; let fast = head.next; while (fast && fast.next) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } let t = slow.next; slow.next = null; let l1 = sortList(head); let l2 = sortList(t); const dummy = new ListNode(); let cur = dummy; while (l1 && l2) { if (l1.val <= l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 || l2; return dummy.next; }; -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode SortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode t = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode l1 = SortList(head); ListNode l2 = SortList(t); ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val <= l2.val) { cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return dummy.next; } } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } impl Solution { pub fn sort_list(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { fn merge(l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>, l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { match (l1, l2) { (None, Some(node)) | (Some(node), None) => Some(node), (Some(mut node1), Some(mut node2)) => { if node1.val < node2.val { node1.next = merge(node1.next.take(), Some(node2)); Some(node1) } else { node2.next = merge(Some(node1), node2.next.take()); Some(node2) } } _ => None, } } fn sort(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { if head.is_none() || head.as_ref().unwrap().next.is_none() { return head; } let mut head = head; let mut length = 0; let mut cur = &head; while cur.is_some() { length += 1; cur = &cur.as_ref().unwrap().next; } let mut cur = &mut head; for _ in 0..length / 2 - 1 { cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next; } let right = cur.as_mut().unwrap().next.take(); merge(sort(head), sort(right)) } sort(head) } }