Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2584. Split the Array to Make Coprime Products
Description
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n.
A split at an index i where 0 <= i <= n - 2 is called valid if the product of the first i + 1 elements and the product of the remaining elements are coprime.
- For example, if
nums = [2, 3, 3], then a split at the indexi = 0is valid because2and9are coprime, while a split at the indexi = 1is not valid because6and3are not coprime. A split at the indexi = 2is not valid becausei == n - 1.
Return the smallest index i at which the array can be split validly or -1 if there is no such split.
Two values val1 and val2 are coprime if gcd(val1, val2) == 1 where gcd(val1, val2) is the greatest common divisor of val1 and val2.
Example 1:
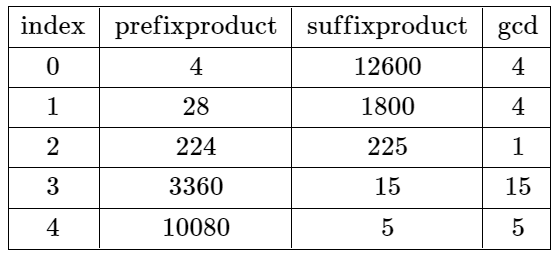
Input: nums = [4,7,8,15,3,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The table above shows the values of the product of the first i + 1 elements, the remaining elements, and their gcd at each index i. The only valid split is at index 2.
Example 2:
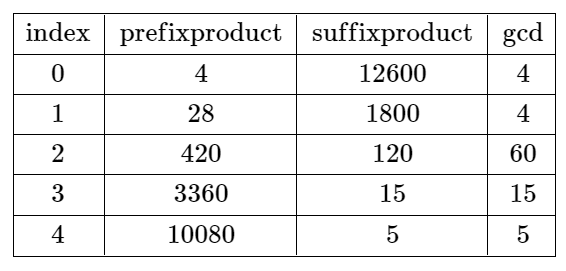
Input: nums = [4,7,15,8,3,5] Output: -1 Explanation: The table above shows the values of the product of the first i + 1 elements, the remaining elements, and their gcd at each index i. There is no valid split.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1041 <= nums[i] <= 106
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int findValidSplit(int[] nums) { Map<Integer, Integer> first = new HashMap<>(); int n = nums.length; int[] last = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { last[i] = i; } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int x = nums[i]; for (int j = 2; j <= x / j; ++j) { if (x % j == 0) { if (first.containsKey(j)) { last[first.get(j)] = i; } else { first.put(j, i); } while (x % j == 0) { x /= j; } } } if (x > 1) { if (first.containsKey(x)) { last[first.get(x)] = i; } else { first.put(x, i); } } } int mx = last[0]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (mx < i) { return mx; } mx = Math.max(mx, last[i]); } return -1; } } -
class Solution { public: int findValidSplit(vector<int>& nums) { unordered_map<int, int> first; int n = nums.size(); vector<int> last(n); iota(last.begin(), last.end(), 0); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int x = nums[i]; for (int j = 2; j <= x / j; ++j) { if (x % j == 0) { if (first.count(j)) { last[first[j]] = i; } else { first[j] = i; } while (x % j == 0) { x /= j; } } } if (x > 1) { if (first.count(x)) { last[first[x]] = i; } else { first[x] = i; } } } int mx = last[0]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (mx < i) { return mx; } mx = max(mx, last[i]); } return -1; } }; -
class Solution: def findValidSplit(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: first = {} n = len(nums) last = list(range(n)) for i, x in enumerate(nums): j = 2 while j <= x // j: if x % j == 0: if j in first: last[first[j]] = i else: first[j] = i while x % j == 0: x //= j j += 1 if x > 1: if x in first: last[first[x]] = i else: first[x] = i mx = last[0] for i, x in enumerate(last): if mx < i: return mx mx = max(mx, x) return -1 -
func findValidSplit(nums []int) int { first := map[int]int{} n := len(nums) last := make([]int, n) for i := range last { last[i] = i } for i, x := range nums { for j := 2; j <= x/j; j++ { if x%j == 0 { if k, ok := first[j]; ok { last[k] = i } else { first[j] = i } for x%j == 0 { x /= j } } } if x > 1 { if k, ok := first[x]; ok { last[k] = i } else { first[x] = i } } } mx := last[0] for i, x := range last { if mx < i { return mx } mx = max(mx, x) } return -1 }