Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2508. Add Edges to Make Degrees of All Nodes Even
Description
There is an undirected graph consisting of n nodes numbered from 1 to n. You are given the integer n and a 2D array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi. The graph can be disconnected.
You can add at most two additional edges (possibly none) to this graph so that there are no repeated edges and no self-loops.
Return true if it is possible to make the degree of each node in the graph even, otherwise return false.
The degree of a node is the number of edges connected to it.
Example 1:
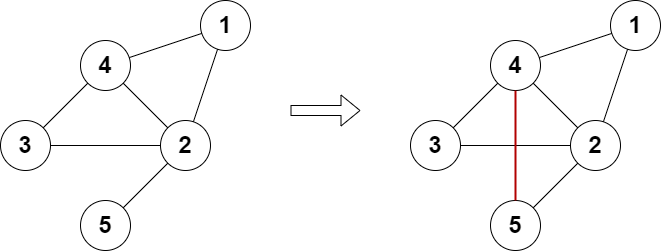
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,2],[1,4],[2,5]] Output: true Explanation: The above diagram shows a valid way of adding an edge. Every node in the resulting graph is connected to an even number of edges.
Example 2:
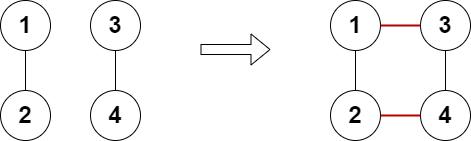
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[3,4]] Output: true Explanation: The above diagram shows a valid way of adding two edges.
Example 3:
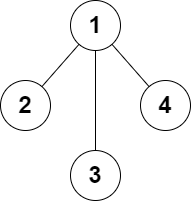
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4]] Output: false Explanation: It is not possible to obtain a valid graph with adding at most 2 edges.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 1052 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public boolean isPossible(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges) { Set<Integer>[] g = new Set[n + 1]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new HashSet<>()); for (var e : edges) { int a = e.get(0), b = e.get(1); g[a].add(b); g[b].add(a); } List<Integer> vs = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (g[i].size() % 2 == 1) { vs.add(i); } } if (vs.size() == 0) { return true; } if (vs.size() == 2) { int a = vs.get(0), b = vs.get(1); if (!g[a].contains(b)) { return true; } for (int c = 1; c <= n; ++c) { if (a != c && b != c && !g[a].contains(c) && !g[c].contains(b)) { return true; } } return false; } if (vs.size() == 4) { int a = vs.get(0), b = vs.get(1), c = vs.get(2), d = vs.get(3); if (!g[a].contains(b) && !g[c].contains(d)) { return true; } if (!g[a].contains(c) && !g[b].contains(d)) { return true; } if (!g[a].contains(d) && !g[b].contains(c)) { return true; } return false; } return false; } } -
class Solution { public: bool isPossible(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<unordered_set<int>> g(n + 1); for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].insert(b); g[b].insert(a); } vector<int> vs; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (g[i].size() % 2) { vs.emplace_back(i); } } if (vs.size() == 0) { return true; } if (vs.size() == 2) { int a = vs[0], b = vs[1]; if (!g[a].count(b)) return true; for (int c = 1; c <= n; ++c) { if (a != b && b != c && !g[a].count(c) && !g[c].count(b)) { return true; } } return false; } if (vs.size() == 4) { int a = vs[0], b = vs[1], c = vs[2], d = vs[3]; if (!g[a].count(b) && !g[c].count(d)) return true; if (!g[a].count(c) && !g[b].count(d)) return true; if (!g[a].count(d) && !g[b].count(c)) return true; return false; } return false; } }; -
class Solution: def isPossible(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> bool: g = defaultdict(set) for a, b in edges: g[a].add(b) g[b].add(a) vs = [i for i, v in g.items() if len(v) & 1] if len(vs) == 0: return True if len(vs) == 2: a, b = vs if a not in g[b]: return True return any(a not in g[c] and c not in g[b] for c in range(1, n + 1)) if len(vs) == 4: a, b, c, d = vs if a not in g[b] and c not in g[d]: return True if a not in g[c] and b not in g[d]: return True if a not in g[d] and b not in g[c]: return True return False return False -
func isPossible(n int, edges [][]int) bool { g := make([]map[int]bool, n+1) for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] if g[a] == nil { g[a] = map[int]bool{} } if g[b] == nil { g[b] = map[int]bool{} } g[a][b], g[b][a] = true, true } vs := []int{} for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { if len(g[i])%2 == 1 { vs = append(vs, i) } } if len(vs) == 0 { return true } if len(vs) == 2 { a, b := vs[0], vs[1] if !g[a][b] { return true } for c := 1; c <= n; c++ { if a != c && b != c && !g[a][c] && !g[c][b] { return true } } return false } if len(vs) == 4 { a, b, c, d := vs[0], vs[1], vs[2], vs[3] if !g[a][b] && !g[c][d] { return true } if !g[a][c] && !g[b][d] { return true } if !g[a][d] && !g[b][c] { return true } return false } return false }