Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2360. Longest Cycle in a Graph
Description
You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from node i, then edges[i] == -1.
Return the length of the longest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
Example 1:
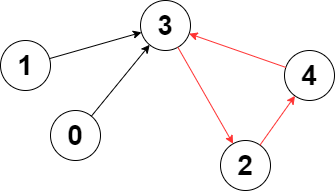
Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3] Output: 3 Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2. The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
Example 2:
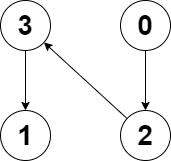
Input: edges = [2,-1,3,1] Output: -1 Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 105-1 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int longestCycle(int[] edges) { int n = edges.length; boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; int ans = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } int j = i; List<Integer> cycle = new ArrayList<>(); for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.add(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (int k = 0; k < cycle.size(); ++k) { if (cycle.get(k) == j) { ans = Math.max(ans, cycle.size() - k); break; } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int longestCycle(vector<int>& edges) { int n = edges.size(); vector<bool> vis(n); int ans = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } int j = i; vector<int> cycle; for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.push_back(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (int k = 0; k < cycle.size(); ++k) { if (cycle[k] == j) { ans = max(ans, (int) cycle.size() - k); break; } } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def longestCycle(self, edges: List[int]) -> int: n = len(edges) vis = [False] * n ans = -1 for i in range(n): if vis[i]: continue j = i cycle = [] while j != -1 and not vis[j]: vis[j] = True cycle.append(j) j = edges[j] if j == -1: continue m = len(cycle) k = next((k for k in range(m) if cycle[k] == j), inf) ans = max(ans, m - k) return ans -
func longestCycle(edges []int) int { vis := make([]bool, len(edges)) ans := -1 for i := range edges { if vis[i] { continue } j := i cycle := []int{} for ; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j] { vis[j] = true cycle = append(cycle, j) } if j == -1 { continue } for k := range cycle { if cycle[k] == j { ans = max(ans, len(cycle)-k) break } } } return ans } -
function longestCycle(edges: number[]): number { const n = edges.length; const vis = new Array(n).fill(false); let ans = -1; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (vis[i]) { continue; } let j = i; const cycle: number[] = []; for (; j != -1 && !vis[j]; j = edges[j]) { vis[j] = true; cycle.push(j); } if (j == -1) { continue; } for (let k = 0; k < cycle.length; ++k) { if (cycle[k] == j) { ans = Math.max(ans, cycle.length - k); break; } } } return ans; } -
impl Solution { pub fn longest_cycle(edges: Vec<i32>) -> i32 { let n = edges.len(); let mut vis = vec![false; n]; let mut ans = -1; for i in 0..n { if vis[i] { continue; } let mut j = i as i32; let mut cycle = Vec::new(); while j != -1 && !vis[j as usize] { vis[j as usize] = true; cycle.push(j); j = edges[j as usize]; } if j == -1 { continue; } for k in 0..cycle.len() { if cycle[k] == j { ans = ans.max((cycle.len() - k) as i32); break; } } } ans } }