Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2189. Number of Ways to Build House of Cards
Description
You are given an integer n representing the number of playing cards you have. A house of cards meets the following conditions:
- A house of cards consists of one or more rows of triangles and horizontal cards.
- Triangles are created by leaning two cards against each other.
- One card must be placed horizontally between all adjacent triangles in a row.
- Any triangle on a row higher than the first must be placed on a horizontal card from the previous row.
- Each triangle is placed in the leftmost available spot in the row.
Return the number of distinct house of cards you can build using all n cards. Two houses of cards are considered distinct if there exists a row where the two houses contain a different number of cards.
Example 1:
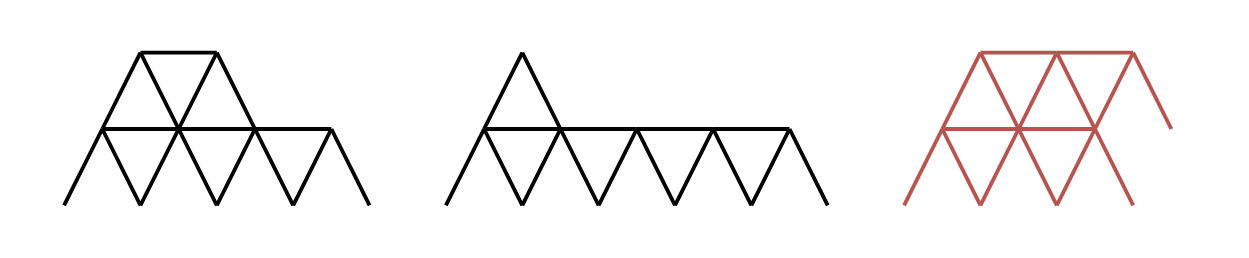
Input: n = 16 Output: 2 Explanation: The two valid houses of cards are shown. The third house of cards in the diagram is not valid because the rightmost triangle on the top row is not placed on top of a horizontal card.
Example 2:

Input: n = 2 Output: 1 Explanation: The one valid house of cards is shown.
Example 3:
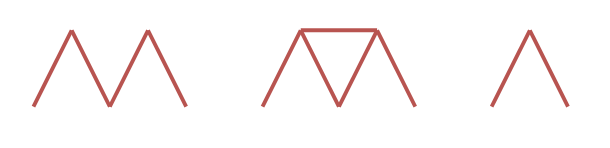
Input: n = 4 Output: 0 Explanation: The three houses of cards in the diagram are not valid. The first house of cards needs a horizontal card placed between the two triangles. The second house of cards uses 5 cards. The third house of cards uses 2 cards.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 500
Solutions
-
class Solution { private Integer[][] f; public int houseOfCards(int n) { f = new Integer[n + 1][n / 3]; return dfs(n, 0); } private int dfs(int n, int k) { int x = 3 * k + 2; if (x > n) { return 0; } if (x == n) { return 1; } if (f[n][k] != null) { return f[n][k]; } return f[n][k] = dfs(n - x, k + 1) + dfs(n, k + 1); } } -
class Solution { public: int houseOfCards(int n) { int f[n + 1][n / 3 + 1]; memset(f, -1, sizeof(f)); function<int(int, int)> dfs = [&](int n, int k) -> int { int x = 3 * k + 2; if (x > n) { return 0; } if (x == n) { return 1; } if (f[n][k] != -1) { return f[n][k]; } return f[n][k] = dfs(n - x, k + 1) + dfs(n, k + 1); }; return dfs(n, 0); } }; -
class Solution: def houseOfCards(self, n: int) -> int: @cache def dfs(n: int, k: int) -> int: x = 3 * k + 2 if x > n: return 0 if x == n: return 1 return dfs(n - x, k + 1) + dfs(n, k + 1) return dfs(n, 0) -
func houseOfCards(n int) int { f := make([][]int, n+1) for i := range f { f[i] = make([]int, n/3+1) for j := range f[i] { f[i][j] = -1 } } var dfs func(n, k int) int dfs = func(n, k int) int { x := 3*k + 2 if x > n { return 0 } if x == n { return 1 } if f[n][k] == -1 { f[n][k] = dfs(n-x, k+1) + dfs(n, k+1) } return f[n][k] } return dfs(n, 0) } -
function houseOfCards(n: number): number { const f: number[][] = Array(n + 1) .fill(0) .map(() => Array(Math.floor(n / 3) + 1).fill(-1)); const dfs = (n: number, k: number): number => { const x = k * 3 + 2; if (x > n) { return 0; } if (x === n) { return 1; } if (f[n][k] === -1) { f[n][k] = dfs(n - x, k + 1) + dfs(n, k + 1); } return f[n][k]; }; return dfs(n, 0); }