Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2130. Maximum Twin Sum of a Linked List
Description
In a linked list of size n, where n is even, the ith node (0-indexed) of the linked list is known as the twin of the (n-1-i)th node, if 0 <= i <= (n / 2) - 1.
- For example, if
n = 4, then node0is the twin of node3, and node1is the twin of node2. These are the only nodes with twins forn = 4.
The twin sum is defined as the sum of a node and its twin.
Given the head of a linked list with even length, return the maximum twin sum of the linked list.
Example 1:
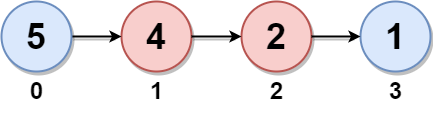
Input: head = [5,4,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: Nodes 0 and 1 are the twins of nodes 3 and 2, respectively. All have twin sum = 6. There are no other nodes with twins in the linked list. Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is 6.
Example 2:
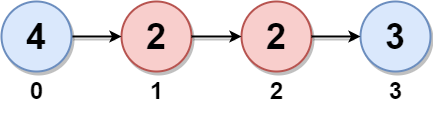
Input: head = [4,2,2,3] Output: 7 Explanation: The nodes with twins present in this linked list are: - Node 0 is the twin of node 3 having a twin sum of 4 + 3 = 7. - Node 1 is the twin of node 2 having a twin sum of 2 + 2 = 4. Thus, the maximum twin sum of the linked list is max(7, 4) = 7.
Example 3:
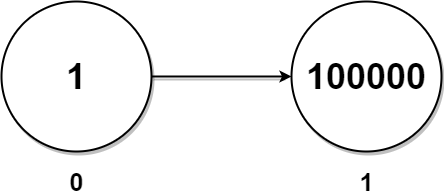
Input: head = [1,100000] Output: 100001 Explanation: There is only one node with a twin in the linked list having twin sum of 1 + 100000 = 100001.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is an even integer in the range
[2, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public int pairSum(ListNode head) { List<Integer> s = new ArrayList<>(); for (; head != null; head = head.next) { s.add(head.val); } int ans = 0, n = s.size(); for (int i = 0; i < (n >> 1); ++i) { ans = Math.max(ans, s.get(i) + s.get(n - 1 - i)); } return ans; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int pairSum(ListNode* head) { vector<int> s; for (; head != nullptr; head = head->next) s.push_back(head->val); int ans = 0, n = s.size(); for (int i = 0; i < (n >> 1); ++i) ans = max(ans, s[i] + s[n - i - 1]); return ans; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def pairSum(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> int: s = [] while head: s.append(head.val) head = head.next n = len(s) return max(s[i] + s[-(i + 1)] for i in range(n >> 1)) -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func pairSum(head *ListNode) int { var s []int for ; head != nil; head = head.Next { s = append(s, head.Val) } ans, n := 0, len(s) for i := 0; i < (n >> 1); i++ { if ans < s[i]+s[n-i-1] { ans = s[i] + s[n-i-1] } } return ans } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function pairSum(head: ListNode | null): number { const arr = []; let node = head; while (node) { arr.push(node.val); node = node.next; } const n = arr.length; let ans = 0; for (let i = 0; i < n >> 1; i++) { ans = Math.max(ans, arr[i] + arr[n - 1 - i]); } return ans; } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } impl Solution { pub fn pair_sum(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> i32 { let mut arr = Vec::new(); let mut node = &head; while node.is_some() { let t = node.as_ref().unwrap(); arr.push(t.val); node = &t.next; } let n = arr.len(); let mut ans = 0; for i in 0..n >> 1 { ans = ans.max(arr[i] + arr[n - 1 - i]); } ans } }