Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/1971.html
1971. Find if Path Exists in Graph
Level
Easy
Description
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [u_i, v_i] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex u_i and vertex v_i. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex start to vertex end.
Given edges and the integers n, start, and end, return true if there is a valid path from start to end, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
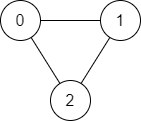
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], start = 0, end = 2
Output: true
Explanation: There are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
Example 2:
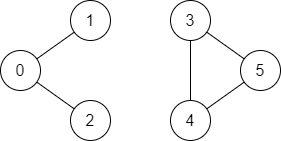
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], start = 0, end = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 10^50 <= edges.length <= 2 * 10^5edges[i].length == 21 <= u_i, v_i <= n - 1u_i != v_i1 <= start, end <= n - 1- There are no duplicate edges.
- There are no self edges.
Solution
Use hash map to store each vertex’s adjacent vertices. Then do breadth first search starting from vertex start. If end can be reached, return true. Otherwise, return false.
-
class Solution { public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int start, int end) { Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>(); for (int[] edge : edges) { int node0 = edge[0], node1 = edge[1]; List<Integer> list0 = map.getOrDefault(node0, new ArrayList<Integer>()); List<Integer> list1 = map.getOrDefault(node1, new ArrayList<Integer>()); list0.add(node1); list1.add(node0); map.put(node0, list0); map.put(node1, list1); } boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); visited[start] = true; queue.offer(start); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int node = queue.poll(); if (node == end) return true; List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(node, new ArrayList<Integer>()); for (int next : list) { if (!visited[next]) { visited[next] = true; queue.offer(next); } } } return false; } } ############ class Solution { private int[] p; public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) { p = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } for (int[] e : edges) { p[find(e[0])] = find(e[1]); } return find(source) == find(destination); } private int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-if-path-exists-in-graph/ // Time: O(N + E) // Space: O(N) class UnionFind { vector<int> id; public: UnionFind(int n) : id(n) { iota(begin(id), end(id), 0); } int find(int a) { return id[a] == a ? a : (id[a] = find(id[a])); } void connect(int a, int b) { id[find(a)] = find(b); } bool connected(int a, int b) { return find(a) == find(b); } }; class Solution { public: bool validPath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& E, int start, int end) { UnionFind uf(n); for (auto &e : E) { uf.connect(e[0], e[1]); } return uf.connected(start, end); } }; -
class Solution: def validPath( self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int ) -> bool: def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] p = list(range(n)) for u, v in edges: p[find(u)] = find(v) return find(source) == find(destination) -
func validPath(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool { p := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i } var find func(x int) int find = func(x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p[x]) } return p[x] } for _, e := range edges { p[find(e[0])] = find(e[1]) } return find(source) == find(destination) } -
impl Solution { pub fn valid_path(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, source: i32, destination: i32) -> bool { let mut disjoint_set: Vec<i32> = vec![0; n as usize]; // Initialize the set for i in 0..n { disjoint_set[i as usize] = i; } // Traverse the edges for p_vec in &edges { let parent_one = Solution::find(p_vec[0], &mut disjoint_set); let parent_two = Solution::find(p_vec[1], &mut disjoint_set); disjoint_set[parent_one as usize] = parent_two; } let p_s = Solution::find(source, &mut disjoint_set); let p_d = Solution::find(destination, &mut disjoint_set); p_s == p_d } pub fn find(x: i32, d_set: &mut Vec<i32>) -> i32 { if d_set[x as usize] != x { d_set[x as usize] = Solution::find(d_set[x as usize], d_set); } d_set[x as usize] } }