Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1719. Number Of Ways To Reconstruct A Tree
Description
You are given an array pairs, where pairs[i] = [xi, yi], and:
- There are no duplicates.
xi < yi
Let ways be the number of rooted trees that satisfy the following conditions:
- The tree consists of nodes whose values appeared in
pairs. - A pair
[xi, yi]exists inpairsif and only ifxiis an ancestor ofyioryiis an ancestor ofxi. - Note: the tree does not have to be a binary tree.
Two ways are considered to be different if there is at least one node that has different parents in both ways.
Return:
0ifways == 01ifways == 12ifways > 1
A rooted tree is a tree that has a single root node, and all edges are oriented to be outgoing from the root.
An ancestor of a node is any node on the path from the root to that node (excluding the node itself). The root has no ancestors.
Example 1:
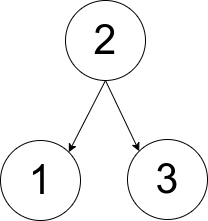
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3]] Output: 1 Explanation: There is exactly one valid rooted tree, which is shown in the above figure.
Example 2:
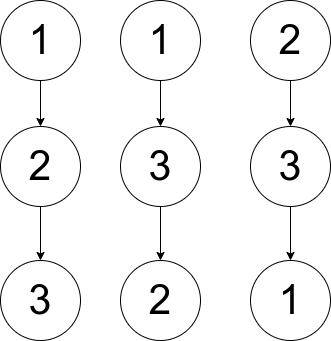
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[1,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: There are multiple valid rooted trees. Three of them are shown in the above figures.
Example 3:
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,4],[1,5]] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no valid rooted trees.
Constraints:
1 <= pairs.length <= 1051 <= xi < yi <= 500- The elements in
pairsare unique.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) { boolean[][] g = new boolean[510][510]; List<Integer>[] v = new List[510]; Arrays.setAll(v, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int[] p : pairs) { int x = p[0], y = p[1]; g[x][y] = true; g[y][x] = true; v[x].add(y); v[y].add(x); } List<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 510; ++i) { if (!v[i].isEmpty()) { nodes.add(i); g[i][i] = true; } } nodes.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> v[a].size())); boolean equal = false; int root = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); ++i) { int x = nodes.get(i); int j = i + 1; for (; j < nodes.size() && !g[x][nodes.get(j)]; ++j) ; if (j < nodes.size()) { int y = nodes.get(j); if (v[x].size() == v[y].size()) { equal = true; } for (int z : v[x]) { if (!g[y][z]) { return 0; } } } else { ++root; } } if (root > 1) { return 0; } return equal ? 2 : 1; } } -
class Solution { public: int checkWays(vector<vector<int>>& pairs) { vector<vector<bool>> g(510, vector<bool>(510)); vector<vector<int>> v(510); for (auto& p : pairs) { int x = p[0], y = p[1]; g[x][y] = g[y][x] = 1; v[x].push_back(y); v[y].push_back(x); } vector<int> nodes; for (int i = 1; i <= 500; ++i) { if (v[i].size()) { nodes.push_back(i); g[i][i] = 1; } } sort(nodes.begin(), nodes.end(), [&](int x, int y) -> bool { return v[x].size() < v[y].size(); }); bool equal = 0; int root = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); ++i) { int x = nodes[i]; int j = i + 1; for (; j < nodes.size() && !g[x][nodes[j]]; ++j) ; if (j < nodes.size()) { int y = nodes[j]; if (v[x].size() == v[y].size()) equal = 1; for (int z : v[x]) if (!g[y][z]) return 0; } else ++root; } if (root > 1) return 0; if (equal) return 2; return 1; } }; -
class Solution: def checkWays(self, pairs: List[List[int]]) -> int: g = [[False] * 510 for _ in range(510)] v = defaultdict(list) for x, y in pairs: g[x][y] = g[y][x] = True v[x].append(y) v[y].append(x) nodes = [] for i in range(510): if v[i]: nodes.append(i) g[i][i] = True nodes.sort(key=lambda x: len(v[x])) equal = False root = 0 for i, x in enumerate(nodes): j = i + 1 while j < len(nodes) and not g[x][nodes[j]]: j += 1 if j < len(nodes): y = nodes[j] if len(v[x]) == len(v[y]): equal = True for z in v[x]: if not g[y][z]: return 0 else: root += 1 if root > 1: return 0 return 2 if equal else 1 -
func checkWays(pairs [][]int) int { g := make([][]bool, 510) v := make([][]int, 510) for i := range g { g[i] = make([]bool, 510) } for _, p := range pairs { x, y := p[0], p[1] g[x][y] = true g[y][x] = true v[x] = append(v[x], y) v[y] = append(v[y], x) } var nodes []int for i := 1; i <= 500; i++ { if len(v[i]) > 0 { nodes = append(nodes, i) g[i][i] = true } } sort.Slice(nodes, func(i, j int) bool { return len(v[nodes[i]]) < len(v[nodes[j]]) }) equal := false root := 0 for i, x := range nodes { j := i + 1 for ; j < len(nodes) && !g[x][nodes[j]]; j++ { } if j < len(nodes) { y := nodes[j] if len(v[x]) == len(v[y]) { equal = true } for _, z := range v[x] { if !g[y][z] { return 0 } } } else { root++ } } if root > 1 { return 0 } if equal { return 2 } return 1 }