Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1669. Merge In Between Linked Lists
Description
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m respectively.
Remove list1's nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2 in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure indicate the result:
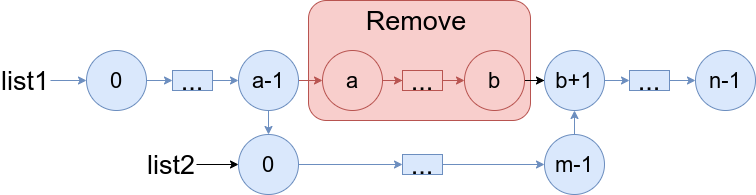
Build the result list and return its head.
Example 1:
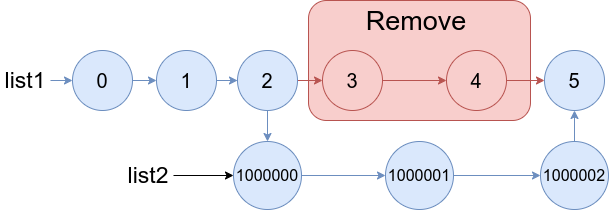
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002] Output: [0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5] Explanation: We remove the nodes 3 and 4 and put the entire list2 in their place. The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Example 2:
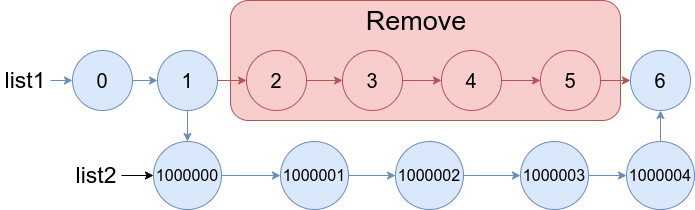
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004] Output: [0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6] Explanation: The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Constraints:
3 <= list1.length <= 1041 <= a <= b < list1.length - 11 <= list2.length <= 104
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) { ListNode p = list1, q = list1; while (--a > 0) { p = p.next; } while (b-- > 0) { q = q.next; } p.next = list2; while (p.next != null) { p = p.next; } p.next = q.next; q.next = null; return list1; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) { auto p = list1, q = list1; while (--a) { p = p->next; } while (b--) { q = q->next; } p->next = list2; while (p->next) { p = p->next; } p->next = q->next; q->next = nullptr; return list1; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def mergeInBetween( self, list1: ListNode, a: int, b: int, list2: ListNode ) -> ListNode: p = q = list1 for _ in range(a - 1): p = p.next for _ in range(b): q = q.next p.next = list2 while p.next: p = p.next p.next = q.next q.next = None return list1 -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func mergeInBetween(list1 *ListNode, a int, b int, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode { p, q := list1, list1 for ; a > 1; a-- { p = p.Next } for ; b > 0; b-- { q = q.Next } p.Next = list2 for p.Next != nil { p = p.Next } p.Next = q.Next q.Next = nil return list1 } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function mergeInBetween( list1: ListNode | null, a: number, b: number, list2: ListNode | null, ): ListNode | null { let p = list1; let q = list1; while (--a > 0) { p = p.next; } while (b-- > 0) { q = q.next; } p.next = list2; while (p.next) { p = p.next; } p.next = q.next; q.next = null; return list1; } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode MergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) { ListNode p = list1, q = list1; while (--a > 0) { p = p.next; } while (b-- > 0) { q = q.next; } p.next = list2; while (p.next != null) { p = p.next; } p.next = q.next; q.next = null; return list1; } }