Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1660. Correct a Binary Tree
Description
You have a binary tree with a small defect. There is exactly one invalid node where its right child incorrectly points to another node at the same depth but to the invalid node's right.
Given the root of the binary tree with this defect, root, return the root of the binary tree after removing this invalid node and every node underneath it (minus the node it incorrectly points to).
Custom testing:
The test input is read as 3 lines:
TreeNode rootint fromNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)int toNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)
After the binary tree rooted at root is parsed, the TreeNode with value of fromNode will have its right child pointer pointing to the TreeNode with a value of toNode. Then, root is passed to correctBinaryTree.
Example 1:
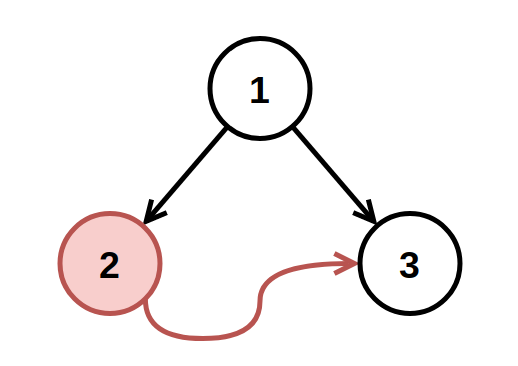
Input: root = [1,2,3], fromNode = 2, toNode = 3 Output: [1,null,3] Explanation: The node with value 2 is invalid, so remove it.
Example 2:
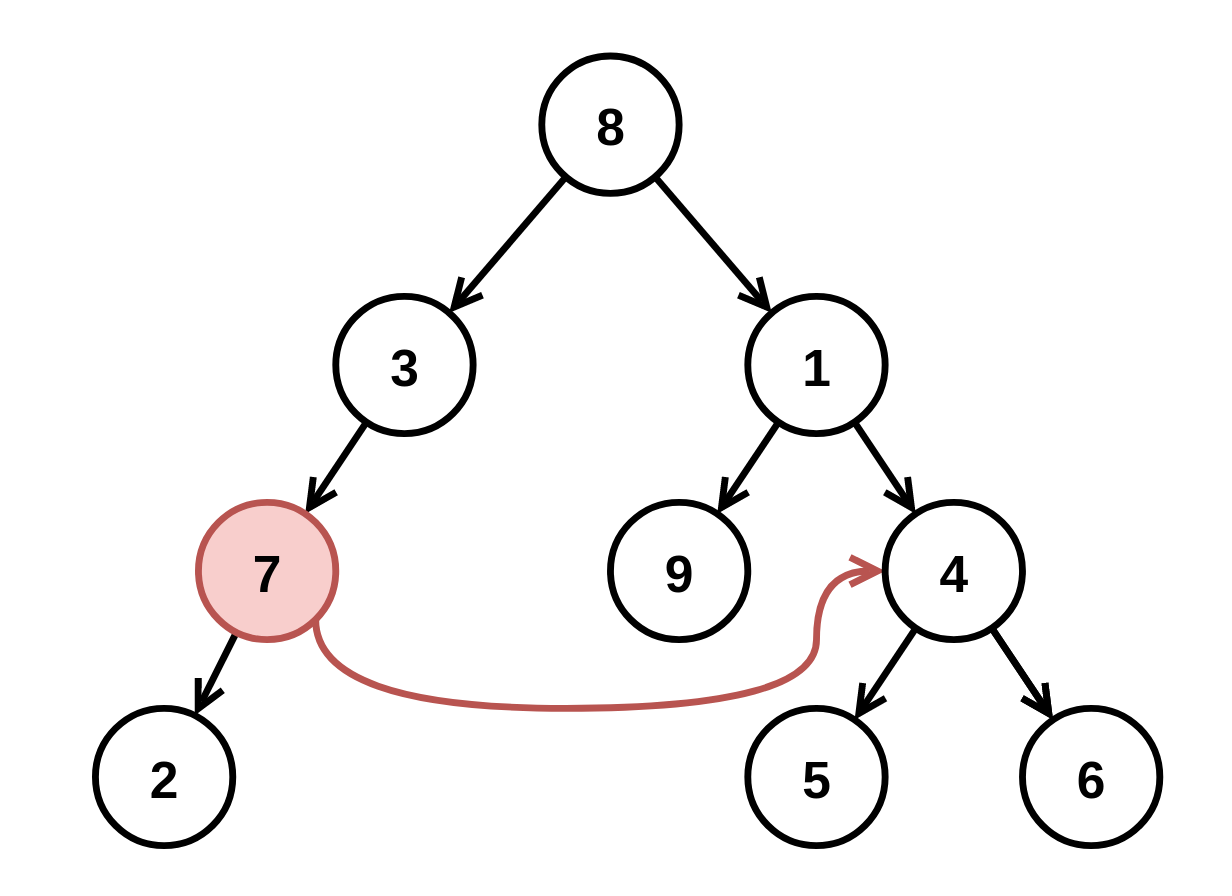
Input: root = [8,3,1,7,null,9,4,2,null,null,null,5,6], fromNode = 7, toNode = 4 Output: [8,3,1,null,null,9,4,null,null,5,6] Explanation: The node with value 7 is invalid, so remove it and the node underneath it, node 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[3, 104]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. fromNode != toNodefromNodeandtoNodewill exist in the tree and will be on the same depth.toNodeis to the right offromNode.fromNode.rightisnullin the initial tree from the test data.
Solutions
The solution aims to remove the problematic node that causes this invalidity, ensuring the binary tree does not contain any cycles.
Approach
The solution employs a recursive Depth-First Search (DFS) strategy to traverse the tree and identify the invalid node. A set named vis (short for “visited”) is used to keep track of all visited nodes during the traversal.
Recursive Function: dfs
-
Base Case: If the current node (
root) isNoneor the right child of the current node is already in thevisset, the function returnsNone. The latter condition indicates that the current node’s right child points back to a node on the path from the root, making the current node the one that needs to be removed to correct the tree. -
Recursive Step:
- Before exploring the children of the current node, the node itself is added to the
visset to mark it as visited. - The function then recursively calls itself on the right child (
root.right = dfs(root.right)) and the left child (root.left = dfs(root.left)), in that order. This order is crucial because the problem condition specifically involves the right child, so checking it first ensures that any invalidity is caught as early as possible. - After possibly correcting the right and left subtrees, the function returns the current node (
root), which is either unmodified if it and its subtrees were valid or adjusted if a subtree contained an invalid node.
- Before exploring the children of the current node, the node itself is added to the
Set vis
- The
visset plays a critical role in identifying cycles caused by a node’s right child. By adding each visited node to this set, the algorithm can immediately recognize when a right child points back to an earlier node in the traversal path. This detection mechanism allows the algorithm to identify the exact node that needs to be removed to break the cycle and correct the tree.
Return Value
The corrected tree is returned by calling dfs on the original tree’s root. If the tree was already valid, it remains unchanged. If an invalid node was found, the tree is modified by removing this node, effectively breaking the cycle and ensuring the tree is a valid binary tree.
Example
Given a binary tree where a node’s right child creates a cycle by pointing back to one of its ancestors, this method will identify the problematic node and return a new tree where this node has been removed, thus eliminating the cycle and correcting the tree.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private Set<TreeNode> vis = new HashSet<>(); public TreeNode correctBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root); } private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null || vis.contains(root.right)) { return null; } vis.add(root); root.right = dfs(root.right); root.left = dfs(root.left); return root; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* correctBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) { unordered_set<TreeNode*> vis; function<TreeNode*(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) -> TreeNode* { if (!root || vis.count(root->right)) { return nullptr; } vis.insert(root); root->right = dfs(root->right); root->left = dfs(root->left); return root; }; return dfs(root); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right # iteration class Solution: def correctBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: seen = set() queue = [root] while queue: node = queue.pop(0) if node.right and node.right in seen: # Remove the incorrect right child node.right = None break seen.add(node) # right first if node.right: queue.append(node.right) if node.left: queue.append(node.left) return root ############# class Solution: # recursive def correctBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: def dfs(root): if root is None or root.right in vis: return None # so will skip the invalid node vis.add(root) root.right = dfs(root.right) root.left = dfs(root.left) return root vis = set() return dfs(root) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {number} from * @param {number} to * @return {TreeNode} */ var correctBinaryTree = function (root) { const dfs = root => { if (!root || vis.has(root.right)) { return null; } vis.add(root); root.right = dfs(root.right); root.left = dfs(root.left); return root; }; const vis = new Set(); return dfs(root); };