Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1627. Graph Connectivity With Threshold
Description
We have n cities labeled from 1 to n. Two different cities with labels x and y are directly connected by a bidirectional road if and only if x and y share a common divisor strictly greater than some threshold. More formally, cities with labels x and y have a road between them if there exists an integer z such that all of the following are true:
x % z == 0,y % z == 0, andz > threshold.
Given the two integers, n and threshold, and an array of queries, you must determine for each queries[i] = [ai, bi] if cities ai and bi are connected directly or indirectly. (i.e. there is some path between them).
Return an array answer, where answer.length == queries.length and answer[i] is true if for the ith query, there is a path between ai and bi, or answer[i] is false if there is no path.
Example 1:
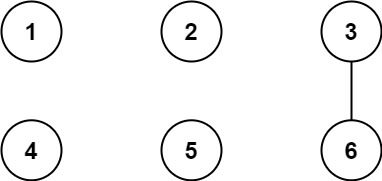
Input: n = 6, threshold = 2, queries = [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]] Output: [false,false,true] Explanation: The divisors for each number: 1: 1 2: 1, 2 3: 1, 3 4: 1, 2, 4 5: 1, 5 6: 1, 2, 3, 6 Using the underlined divisors above the threshold, only cities 3 and 6 share a common divisor, so they are the only ones directly connected. The result of each query: [1,4] 1 is not connected to 4 [2,5] 2 is not connected to 5 [3,6] 3 is connected to 6 through path 3--6
Example 2:
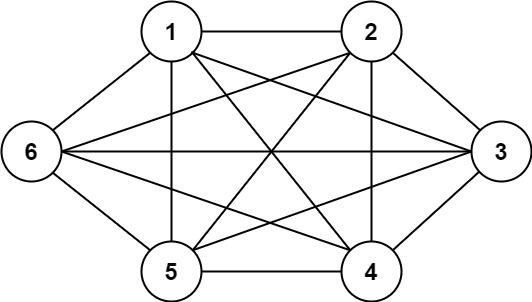
Input: n = 6, threshold = 0, queries = [[4,5],[3,4],[3,2],[2,6],[1,3]] Output: [true,true,true,true,true] Explanation: The divisors for each number are the same as the previous example. However, since the threshold is 0, all divisors can be used. Since all numbers share 1 as a divisor, all cities are connected.
Example 3:
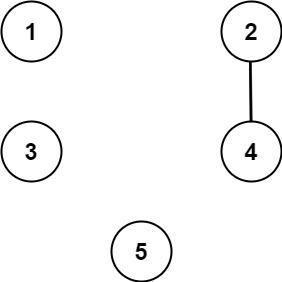
Input: n = 5, threshold = 1, queries = [[4,5],[4,5],[3,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: [false,false,false,false,false] Explanation: Only cities 2 and 4 share a common divisor 2 which is strictly greater than the threshold 1, so they are the only ones directly connected. Please notice that there can be multiple queries for the same pair of nodes [x, y], and that the query [x, y] is equivalent to the query [y, x].
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1040 <= threshold <= n1 <= queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= citiesai != bi
Solutions
Solution 1: Union-Find
We can enumerate $z$ and its multiples, and use union-find to connect them. In this way, for each query $[a, b]$, we only need to determine whether $a$ and $b$ are in the same connected component.
The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n \times (\alpha(n) + q))$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ and $q$ are the number of nodes and queries, respectively, and $\alpha$ is the inverse function of the Ackermann function.
-
class UnionFind { private int[] p; private int[] size; public UnionFind(int n) { p = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; size[i] = 1; } } public int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } public boolean union(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } } class Solution { public List<Boolean> areConnected(int n, int threshold, int[][] queries) { UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n + 1); for (int a = threshold + 1; a <= n; ++a) { for (int b = a + a; b <= n; b += a) { uf.union(a, b); } } List<Boolean> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (var q : queries) { ans.add(uf.find(q[0]) == uf.find(q[1])); } return ans; } } -
class UnionFind { public: UnionFind(int n) { p = vector<int>(n); size = vector<int>(n, 1); iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); } bool unite(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } private: vector<int> p, size; }; class Solution { public: vector<bool> areConnected(int n, int threshold, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { UnionFind uf(n + 1); for (int a = threshold + 1; a <= n; ++a) { for (int b = a + a; b <= n; b += a) { uf.unite(a, b); } } vector<bool> ans; for (auto& q : queries) { ans.push_back(uf.find(q[0]) == uf.find(q[1])); } return ans; } }; -
class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n): self.p = list(range(n)) self.size = [1] * n def find(self, x): if self.p[x] != x: self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]) return self.p[x] def union(self, a, b): pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b) if pa == pb: return False if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]: self.p[pb] = pa self.size[pa] += self.size[pb] else: self.p[pa] = pb self.size[pb] += self.size[pa] return True class Solution: def areConnected( self, n: int, threshold: int, queries: List[List[int]] ) -> List[bool]: uf = UnionFind(n + 1) for a in range(threshold + 1, n + 1): for b in range(a + a, n + 1, a): uf.union(a, b) return [uf.find(a) == uf.find(b) for a, b in queries] -
type unionFind struct { p, size []int } func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind { p := make([]int, n) size := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i size[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{p, size} } func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int { if uf.p[x] != x { uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x]) } return uf.p[x] } func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool { pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b) if pa == pb { return false } if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] { uf.p[pb] = pa uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb] } else { uf.p[pa] = pb uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa] } return true } func areConnected(n int, threshold int, queries [][]int) []bool { uf := newUnionFind(n + 1) for a := threshold + 1; a <= n; a++ { for b := a + a; b <= n; b += a { uf.union(a, b) } } ans := make([]bool, len(queries)) for i, q := range queries { ans[i] = uf.find(q[0]) == uf.find(q[1]) } return ans } -
class UnionFind { p: number[]; size: number[]; constructor(n: number) { this.p = Array(n) .fill(0) .map((_, i) => i); this.size = Array(n).fill(1); } find(x: number): number { if (this.p[x] !== x) { this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]); } return this.p[x]; } union(a: number, b: number): boolean { const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)]; if (pa === pb) { return false; } if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) { this.p[pb] = pa; this.size[pa] += this.size[pb]; } else { this.p[pa] = pb; this.size[pb] += this.size[pa]; } return true; } } function areConnected(n: number, threshold: number, queries: number[][]): boolean[] { const uf = new UnionFind(n + 1); for (let a = threshold + 1; a <= n; ++a) { for (let b = a * 2; b <= n; b += a) { uf.union(a, b); } } return queries.map(([a, b]) => uf.find(a) === uf.find(b)); }