Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1569. Number of Ways to Reorder Array to Get Same BST
Description
Given an array nums that represents a permutation of integers from 1 to n. We are going to construct a binary search tree (BST) by inserting the elements of nums in order into an initially empty BST. Find the number of different ways to reorder nums so that the constructed BST is identical to that formed from the original array nums.
- For example, given
nums = [2,1,3], we will have 2 as the root, 1 as a left child, and 3 as a right child. The array[2,3,1]also yields the same BST but[3,2,1]yields a different BST.
Return the number of ways to reorder nums such that the BST formed is identical to the original BST formed from nums.
Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
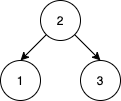
Input: nums = [2,1,3] Output: 1 Explanation: We can reorder nums to be [2,3,1] which will yield the same BST. There are no other ways to reorder nums which will yield the same BST.
Example 2:
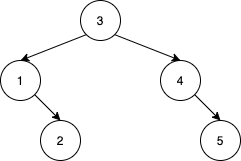
Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2] Output: 5 Explanation: The following 5 arrays will yield the same BST: [3,1,2,4,5] [3,1,4,2,5] [3,1,4,5,2] [3,4,1,2,5] [3,4,1,5,2]
Example 3:
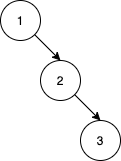
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no other orderings of nums that will yield the same BST.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= nums.length- All integers in
numsare distinct.
Solutions
Solution 1: Combination Counting + Recursion
We design a function $dfs(nums)$, which is used to calculate the number of solutions of the binary search tree with $nums$ as nodes. Then the answer is $dfs(nums)-1$, because $dfs(nums)$ calculates the number of solutions of the binary search tree with $nums$ as nodes, while the problem requires the number of solutions of the binary search tree with $nums$ as nodes after reordering, so the answer needs to be subtracted by one.
Next, let’s take a look at how $dfs(nums)$ is calculated.
For an array $nums$, its first element is the root node, so its left subtree elements are smaller than it, and its right subtree elements are larger than it. So we can divide the array into three parts, the first part is the root node, the second part is the elements of the left subtree, denoted as $left$, and the third part is the elements of the right subtree, denoted as $right$. Then, the number of elements in the left subtree is $m$, and the number of elements in the right subtree is $n$, so the number of solutions for $left$ and $right$ are $dfs(left)$ and $dfs(right)$ respectively. We can choose $m$ positions from $m + n$ positions in array $nums$ to place the elements of the left subtree, and the remaining $n$ positions to place the elements of the right subtree, so that we can ensure that the reordered binary search tree is the same as the original array $nums$. Therefore, the calculation method of $dfs(nums)$ is:
\[dfs(nums) = C_{m+n}^m \times dfs(left) \times dfs(right)\]where $C_{m+n}^m$ represents the number of schemes to select $m$ positions from $m + n$ positions, which we can get through preprocessing.
Note the modulo operation of the answer, because the value of $dfs(nums)$ may be very large, so we need to take the modulo of each step in the calculation process, and finally take the modulo of the entire result.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n^2)$. Where $n$ is the length of array $nums$.
-
class Solution { private int[][] c; private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7; public int numOfWays(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; c = new int[n][n]; c[0][0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { c[i][0] = 1; for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) { c[i][j] = (c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1]) % mod; } } List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int x : nums) { list.add(x); } return (dfs(list) - 1 + mod) % mod; } private int dfs(List<Integer> nums) { if (nums.size() < 2) { return 1; } List<Integer> left = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> right = new ArrayList<>(); for (int x : nums) { if (x < nums.get(0)) { left.add(x); } else if (x > nums.get(0)) { right.add(x); } } int m = left.size(), n = right.size(); int a = dfs(left), b = dfs(right); return (int) ((long) a * b % mod * c[m + n][n] % mod); } } -
class Solution { public: int numOfWays(vector<int>& nums) { int n = nums.size(); const int mod = 1e9 + 7; int c[n][n]; memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); c[0][0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { c[i][0] = 1; for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) { c[i][j] = (c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1]) % mod; } } function<int(vector<int>)> dfs = [&](vector<int> nums) -> int { if (nums.size() < 2) { return 1; } vector<int> left, right; for (int& x : nums) { if (x < nums[0]) { left.push_back(x); } else if (x > nums[0]) { right.push_back(x); } } int m = left.size(), n = right.size(); int a = dfs(left), b = dfs(right); return c[m + n][m] * 1ll * a % mod * b % mod; }; return (dfs(nums) - 1 + mod) % mod; } }; -
class Solution: def numOfWays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: def dfs(nums): if len(nums) < 2: return 1 left = [x for x in nums if x < nums[0]] right = [x for x in nums if x > nums[0]] m, n = len(left), len(right) a, b = dfs(left), dfs(right) return (((c[m + n][m] * a) % mod) * b) % mod n = len(nums) mod = 10**9 + 7 c = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)] c[0][0] = 1 for i in range(1, n): c[i][0] = 1 for j in range(1, i + 1): c[i][j] = (c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1]) % mod return (dfs(nums) - 1 + mod) % mod -
func numOfWays(nums []int) int { n := len(nums) const mod = 1e9 + 7 c := make([][]int, n) for i := range c { c[i] = make([]int, n) } c[0][0] = 1 for i := 1; i < n; i++ { c[i][0] = 1 for j := 1; j <= i; j++ { c[i][j] = (c[i-1][j] + c[i-1][j-1]) % mod } } var dfs func(nums []int) int dfs = func(nums []int) int { if len(nums) < 2 { return 1 } var left, right []int for _, x := range nums[1:] { if x < nums[0] { left = append(left, x) } else { right = append(right, x) } } m, n := len(left), len(right) a, b := dfs(left), dfs(right) return c[m+n][m] * a % mod * b % mod } return (dfs(nums) - 1 + mod) % mod } -
function numOfWays(nums: number[]): number { const n = nums.length; const mod = 1e9 + 7; const c = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(0)); c[0][0] = 1; for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) { c[i][0] = 1; for (let j = 1; j <= i; ++j) { c[i][j] = (c[i - 1][j - 1] + c[i - 1][j]) % mod; } } const dfs = (nums: number[]): number => { if (nums.length < 2) { return 1; } const left: number[] = []; const right: number[] = []; for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i) { if (nums[i] < nums[0]) { left.push(nums[i]); } else { right.push(nums[i]); } } const m = left.length; const n = right.length; const a = dfs(left); const b = dfs(right); return Number((BigInt(c[m + n][m]) * BigInt(a) * BigInt(b)) % BigInt(mod)); }; return (dfs(nums) - 1 + mod) % mod; }