Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1515. Best Position for a Service Centre
Description
A delivery company wants to build a new service center in a new city. The company knows the positions of all the customers in this city on a 2D-Map and wants to build the new center in a position such that the sum of the euclidean distances to all customers is minimum.
Given an array positions where positions[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the ith customer on the map, return the minimum sum of the euclidean distances to all customers.
In other words, you need to choose the position of the service center [xcentre, ycentre] such that the following formula is minimized:
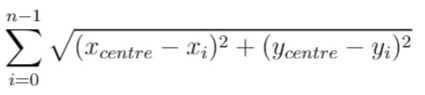
Answers within 10-5 of the actual value will be accepted.
Example 1:
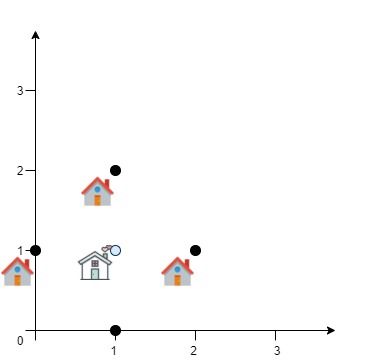
Input: positions = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]] Output: 4.00000 Explanation: As shown, you can see that choosing [xcentre, ycentre] = [1, 1] will make the distance to each customer = 1, the sum of all distances is 4 which is the minimum possible we can achieve.
Example 2:
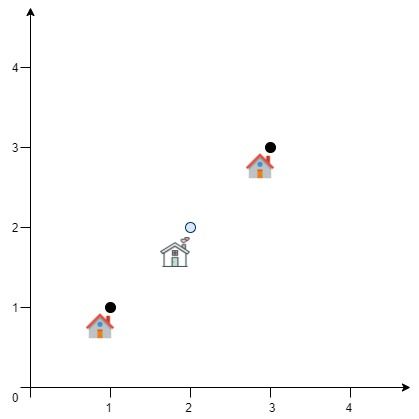
Input: positions = [[1,1],[3,3]] Output: 2.82843 Explanation: The minimum possible sum of distances = sqrt(2) + sqrt(2) = 2.82843
Constraints:
1 <= positions.length <= 50positions[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100
Solutions
-
class Solution { public double getMinDistSum(int[][] positions) { int n = positions.length; double x = 0, y = 0; for (int[] p : positions) { x += p[0]; y += p[1]; } x /= n; y /= n; double decay = 0.999; double eps = 1e-6; double alpha = 0.5; while (true) { double gradX = 0, gradY = 0; double dist = 0; for (int[] p : positions) { double a = x - p[0], b = y - p[1]; double c = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b); gradX += a / (c + 1e-8); gradY += b / (c + 1e-8); dist += c; } double dx = gradX * alpha, dy = gradY * alpha; if (Math.abs(dx) <= eps && Math.abs(dy) <= eps) { return dist; } x -= dx; y -= dy; alpha *= decay; } } } -
class Solution { public: double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& positions) { int n = positions.size(); double x = 0, y = 0; for (auto& p : positions) { x += p[0]; y += p[1]; } x /= n; y /= n; double decay = 0.999; double eps = 1e-6; double alpha = 0.5; while (true) { double gradX = 0, gradY = 0; double dist = 0; for (auto& p : positions) { double a = x - p[0], b = y - p[1]; double c = sqrt(a * a + b * b); gradX += a / (c + 1e-8); gradY += b / (c + 1e-8); dist += c; } double dx = gradX * alpha, dy = gradY * alpha; if (abs(dx) <= eps && abs(dy) <= eps) { return dist; } x -= dx; y -= dy; alpha *= decay; } } }; -
class Solution: def getMinDistSum(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> float: n = len(positions) x = y = 0 for x1, y1 in positions: x += x1 y += y1 x, y = x / n, y / n decay = 0.999 eps = 1e-6 alpha = 0.5 while 1: grad_x = grad_y = 0 dist = 0 for x1, y1 in positions: a = x - x1 b = y - y1 c = sqrt(a * a + b * b) grad_x += a / (c + 1e-8) grad_y += b / (c + 1e-8) dist += c dx = grad_x * alpha dy = grad_y * alpha x -= dx y -= dy alpha *= decay if abs(dx) <= eps and abs(dy) <= eps: return dist -
func getMinDistSum(positions [][]int) float64 { n := len(positions) var x, y float64 for _, p := range positions { x += float64(p[0]) y += float64(p[1]) } x /= float64(n) y /= float64(n) const decay float64 = 0.999 const eps float64 = 1e-6 var alpha float64 = 0.5 for { var gradX, gradY float64 var dist float64 for _, p := range positions { a := x - float64(p[0]) b := y - float64(p[1]) c := math.Sqrt(a*a + b*b) gradX += a / (c + 1e-8) gradY += b / (c + 1e-8) dist += c } dx := gradX * alpha dy := gradY * alpha if math.Abs(dx) <= eps && math.Abs(dy) <= eps { return dist } x -= dx y -= dy alpha *= decay } } -
function getMinDistSum(positions: number[][]): number { const n = positions.length; let [x, y] = [0, 0]; for (const [px, py] of positions) { x += px; y += py; } x /= n; y /= n; const decay = 0.999; const eps = 1e-6; let alpha = 0.5; while (true) { let [gradX, gradY] = [0, 0]; let dist = 0; for (const [px, py] of positions) { const a = x - px; const b = y - py; const c = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b); gradX += a / (c + 1e-8); gradY += b / (c + 1e-8); dist += c; } const dx = gradX * alpha; const dy = gradY * alpha; if (Math.abs(dx) <= eps && Math.abs(dy) <= eps) { return dist; } x -= dx; y -= dy; alpha *= decay; } }