Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1490. Clone N-ary Tree
Description
Given a root of an N-ary tree, return a deep copy (clone) of the tree.
Each node in the n-ary tree contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its children.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
}
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
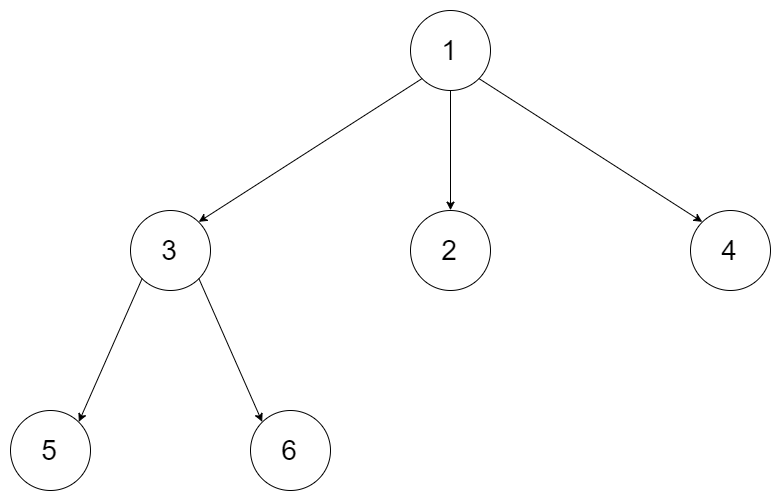
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Example 2:
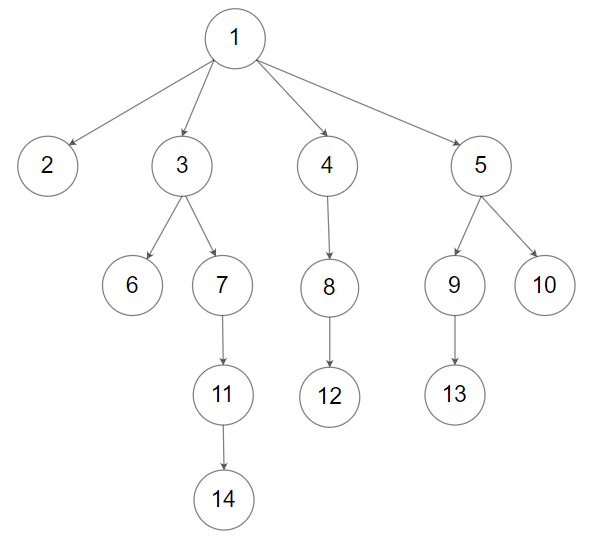
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Constraints:
- The depth of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000. - The total number of nodes is between
[0, 104].
Follow up: Can your solution work for the graph problem?
Solutions
DFS.
-
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() { children = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; children = new ArrayList<Node>(); } public Node(int _val,ArrayList<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public Node cloneTree(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } ArrayList<Node> children = new ArrayList<>(); for (Node child : root.children) { children.add(cloneTree(child)); } return new Node(root.val, children); } } -
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: Node* cloneTree(Node* root) { if (!root) { return root; } vector<Node*> children; for (Node* child : root->children) { children.emplace_back(cloneTree(child)); } return new Node(root->val, children); } }; -
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val=None, children=None): self.val = val self.children = children if children is not None else [] """ class Solution: def cloneTree(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node': if root is None: return None children = [self.cloneTree(child) for child in root.children] return Node(root.val, children) -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Children []*Node * } */ func cloneTree(root *Node) *Node { if root == nil { return nil } children := []*Node{} for _, child := range root.Children { children = append(children, cloneTree(child)) } return &Node{root.Val, children} }