Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1489. Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree
Description
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
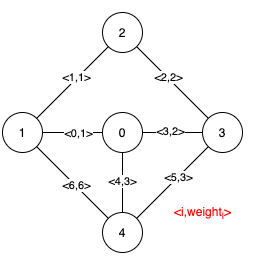
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]] Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]] Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output. The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
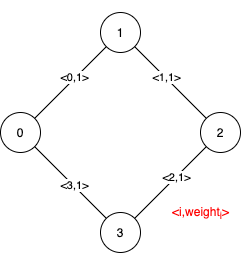
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]] Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]] Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000- All pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(int n, int[][] edges) { for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; ++i) { int[] e = edges[i]; int[] t = new int[4]; System.arraycopy(e, 0, t, 0, 3); t[3] = i; edges[i] = t; } Arrays.sort(edges, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[2])); int v = 0; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n); for (int[] e : edges) { int f = e[0], t = e[1], w = e[2]; if (uf.union(f, t)) { v += w; } } List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { ans.add(new ArrayList<>()); } for (int[] e : edges) { int f = e[0], t = e[1], w = e[2], i = e[3]; uf = new UnionFind(n); int k = 0; for (int[] ne : edges) { int x = ne[0], y = ne[1], z = ne[2], j = ne[3]; if (j != i && uf.union(x, y)) { k += z; } } if (uf.getN() > 1 || (uf.getN() == 1 && k > v)) { ans.get(0).add(i); continue; } uf = new UnionFind(n); uf.union(f, t); k = w; for (int[] ne : edges) { int x = ne[0], y = ne[1], z = ne[2], j = ne[3]; if (j != i && uf.union(x, y)) { k += z; } } if (k == v) { ans.get(1).add(i); } } return ans; } } class UnionFind { private int[] p; private int n; public UnionFind(int n) { p = new int[n]; this.n = n; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } } public int getN() { return n; } public boolean union(int a, int b) { if (find(a) == find(b)) { return false; } p[find(a)] = find(b); --n; return true; } public int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } } -
class UnionFind { public: vector<int> p; int n; UnionFind(int _n) : n(_n) , p(_n) { iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); } bool unite(int a, int b) { if (find(a) == find(b)) return false; p[find(a)] = find(b); --n; return true; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } }; class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) edges[i].push_back(i); sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; }); int v = 0; UnionFind uf(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int f = e[0], t = e[1], w = e[2]; if (uf.unite(f, t)) v += w; } vector<vector<int>> ans(2); for (auto& e : edges) { int f = e[0], t = e[1], w = e[2], i = e[3]; UnionFind ufa(n); int k = 0; for (auto& ne : edges) { int x = ne[0], y = ne[1], z = ne[2], j = ne[3]; if (j != i && ufa.unite(x, y)) k += z; } if (ufa.n > 1 || (ufa.n == 1 && k > v)) { ans[0].push_back(i); continue; } UnionFind ufb(n); ufb.unite(f, t); k = w; for (auto& ne : edges) { int x = ne[0], y = ne[1], z = ne[2], j = ne[3]; if (j != i && ufb.unite(x, y)) k += z; } if (k == v) ans[1].push_back(i); } return ans; } }; -
class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n): self.p = list(range(n)) self.n = n def union(self, a, b): if self.find(a) == self.find(b): return False self.p[self.find(a)] = self.find(b) self.n -= 1 return True def find(self, x): if self.p[x] != x: self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]) return self.p[x] class Solution: def findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges( self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]] ) -> List[List[int]]: for i, e in enumerate(edges): e.append(i) edges.sort(key=lambda x: x[2]) uf = UnionFind(n) v = sum(w for f, t, w, _ in edges if uf.union(f, t)) ans = [[], []] for f, t, w, i in edges: uf = UnionFind(n) k = sum(z for x, y, z, j in edges if j != i and uf.union(x, y)) if uf.n > 1 or (uf.n == 1 and k > v): ans[0].append(i) continue uf = UnionFind(n) uf.union(f, t) k = w + sum(z for x, y, z, j in edges if j != i and uf.union(x, y)) if k == v: ans[1].append(i) return ans -
type unionFind struct { p []int n int } func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind { p := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i } return &unionFind{p, n} } func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int { if uf.p[x] != x { uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x]) } return uf.p[x] } func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool { if uf.find(a) == uf.find(b) { return false } uf.p[uf.find(a)] = uf.find(b) uf.n-- return true } func findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n int, edges [][]int) [][]int { for i := range edges { edges[i] = append(edges[i], i) } sort.Slice(edges, func(i, j int) bool { return edges[i][2] < edges[j][2] }) v := 0 uf := newUnionFind(n) for _, e := range edges { f, t, w := e[0], e[1], e[2] if uf.union(f, t) { v += w } } ans := make([][]int, 2) for _, e := range edges { f, t, w, i := e[0], e[1], e[2], e[3] uf = newUnionFind(n) k := 0 for _, ne := range edges { x, y, z, j := ne[0], ne[1], ne[2], ne[3] if j != i && uf.union(x, y) { k += z } } if uf.n > 1 || (uf.n == 1 && k > v) { ans[0] = append(ans[0], i) continue } uf = newUnionFind(n) uf.union(f, t) k = w for _, ne := range edges { x, y, z, j := ne[0], ne[1], ne[2], ne[3] if j != i && uf.union(x, y) { k += z } } if k == v { ans[1] = append(ans[1], i) } } return ans }