Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1430. Check If a String Is a Valid Sequence from Root to Leaves Path in a Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree where each path going from the root to any leaf form a valid sequence, check if a given string is a valid sequence in such binary tree.
We get the given string from the concatenation of an array of integers arr and the concatenation of all values of the nodes along a path results in a sequence in the given binary tree.
Example 1:
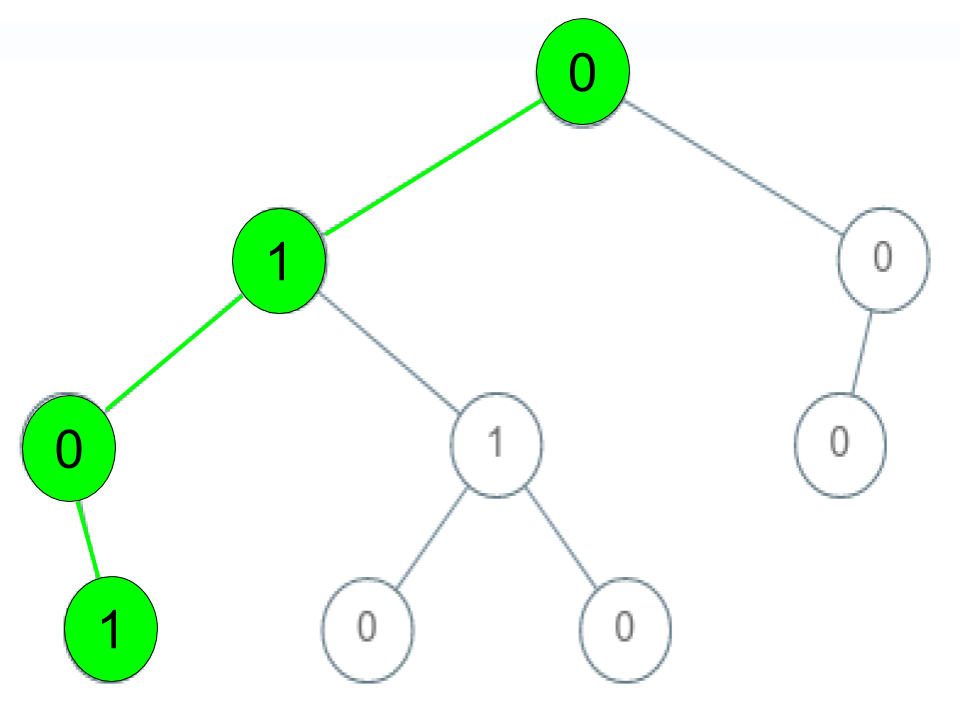
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,0,1] Output: true Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 is a valid sequence (green color in the figure). Other valid sequences are: 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 0 -> 0 -> 0
Example 2:
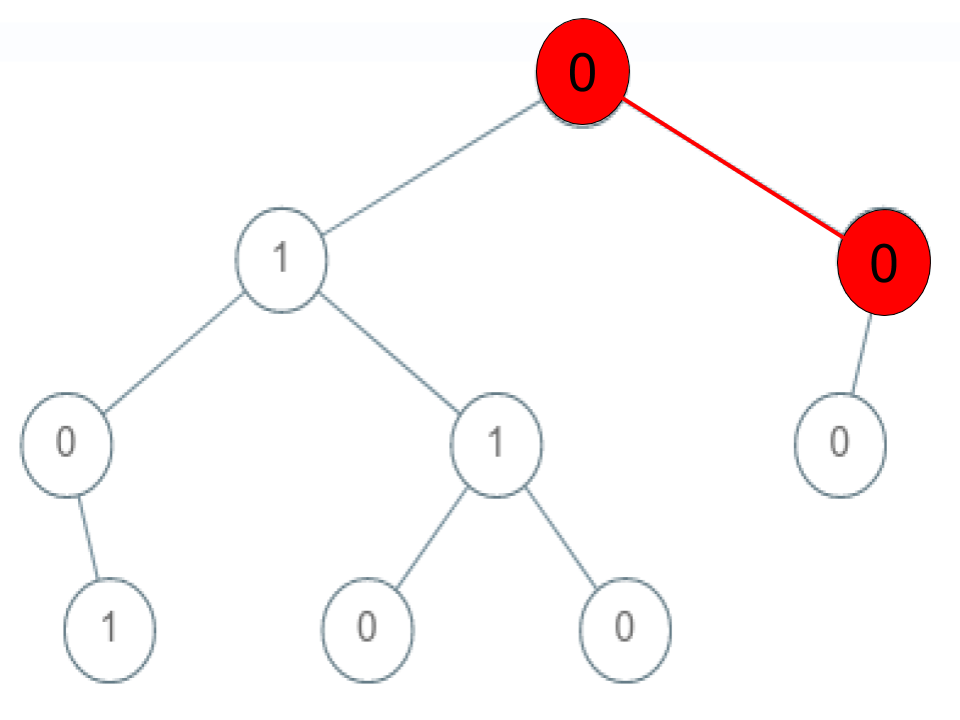
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,0,1] Output: false Explanation: The path 0 -> 0 -> 1 does not exist, therefore it is not even a sequence.
Example 3:
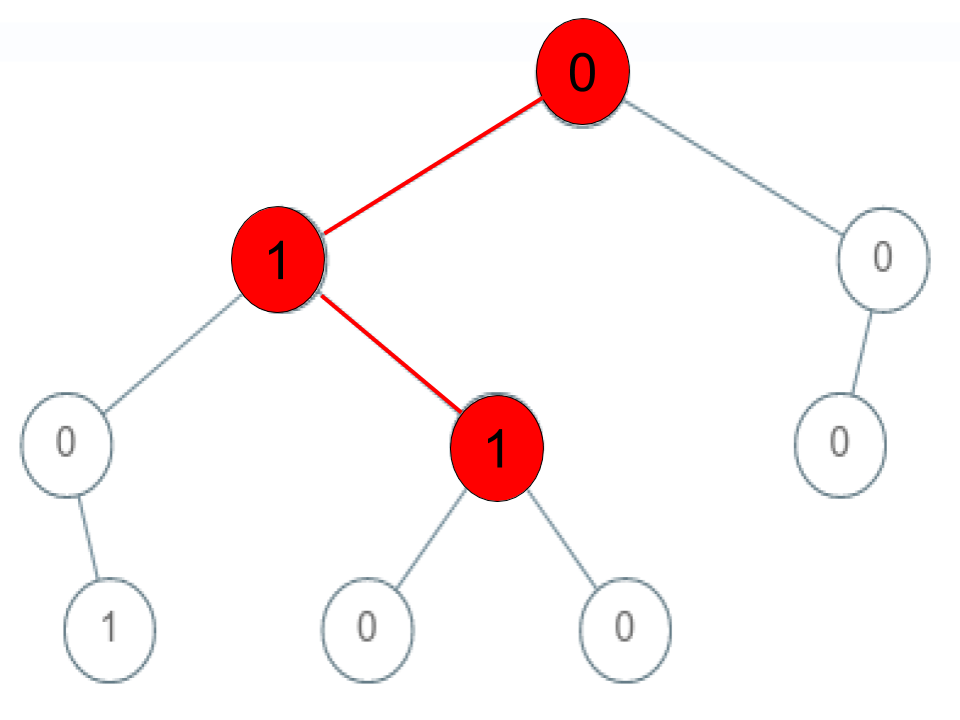
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,1] Output: false Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 1 is a sequence, but it is not a valid sequence.
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 50000 <= arr[i] <= 9- Each node's value is between [0 - 9].
Solutions
DFS.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int[] arr; public boolean isValidSequence(TreeNode root, int[] arr) { this.arr = arr; return dfs(root, 0); } private boolean dfs(TreeNode root, int u) { if (root == null || root.val != arr[u]) { return false; } if (u == arr.length - 1) { return root.left == null && root.right == null; } return dfs(root.left, u + 1) || dfs(root.right, u + 1); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isValidSequence(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& arr) { function<bool(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int u) -> bool { if (!root || root->val != arr[u]) return false; if (u == arr.size() - 1) return !root->left && !root->right; return dfs(root->left, u + 1) || dfs(root->right, u + 1); }; return dfs(root, 0); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def isValidSequence(self, root: TreeNode, arr: List[int]) -> bool: def dfs(root, u): if root is None or root.val != arr[u]: return False if u == len(arr) - 1: return root.left is None and root.right is None return dfs(root.left, u + 1) or dfs(root.right, u + 1) return dfs(root, 0) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func isValidSequence(root *TreeNode, arr []int) bool { var dfs func(root *TreeNode, u int) bool dfs = func(root *TreeNode, u int) bool { if root == nil || root.Val != arr[u] { return false } if u == len(arr)-1 { return root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil } return dfs(root.Left, u+1) || dfs(root.Right, u+1) } return dfs(root, 0) }