Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1367. Linked List in Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree root and a linked list with head as the first node.
Return True if all the elements in the linked list starting from the head correspond to some downward path connected in the binary tree otherwise return False.
In this context downward path means a path that starts at some node and goes downwards.
Example 1:
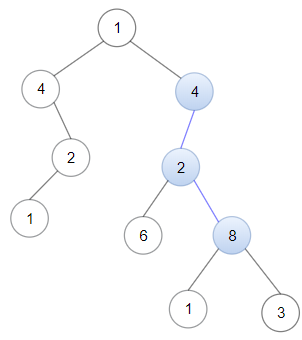
Input: head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] Output: true Explanation: Nodes in blue form a subpath in the binary Tree.
Example 2:
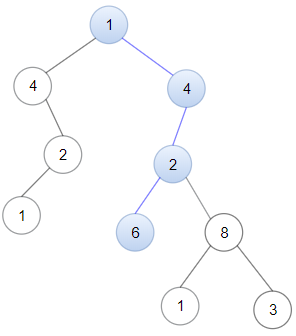
Input: head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] Output: true
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path in the binary tree that contains all the elements of the linked list from head.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 2500]. - The number of nodes in the list will be in the range
[1, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100for each node in the linked list and binary tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: Recursion
We design a recursive function $dfs(head, root)$, which indicates whether the linked list $head$ corresponds to a subpath on the path starting with $root$ in the binary tree. The logic of the function $dfs(head, root)$ is as follows:
- If the linked list $head$ is empty, it means that the linked list has been traversed, return
true; - If the binary tree $root$ is empty, it means that the binary tree has been traversed, but the linked list has not been traversed yet, return
false; - If the value of the binary tree $root$ is not equal to the value of the linked list $head$, return
false; - Otherwise, return $dfs(head.next, root.left)$ or $dfs(head.next, root.right)$.
In the main function, we call $dfs(head, root)$ for each node of the binary tree. As long as one returns true, it means that the linked list is a subpath of the binary tree, return true; if all nodes return false, it means that the linked list is not a subpath of the binary tree, return false.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public boolean isSubPath(ListNode head, TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return false; } return dfs(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.left) || isSubPath(head, root.right); } private boolean dfs(ListNode head, TreeNode root) { if (head == null) { return true; } if (root == null || head.val != root.val) { return false; } return dfs(head.next, root.left) || dfs(head.next, root.right); } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSubPath(ListNode* head, TreeNode* root) { if (!root) { return false; } return dfs(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root->left) || isSubPath(head, root->right); } bool dfs(ListNode* head, TreeNode* root) { if (!head) { return true; } if (!root || head->val != root->val) { return false; } return dfs(head->next, root->left) || dfs(head->next, root->right); } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def isSubPath(self, head: Optional[ListNode], root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: def dfs(head, root): if head is None: return True if root is None or root.val != head.val: return False return dfs(head.next, root.left) or dfs(head.next, root.right) if root is None: return False return ( dfs(head, root) or self.isSubPath(head, root.left) or self.isSubPath(head, root.right) ) -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func isSubPath(head *ListNode, root *TreeNode) bool { if root == nil { return false } return dfs(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.Left) || isSubPath(head, root.Right) } func dfs(head *ListNode, root *TreeNode) bool { if head == nil { return true } if root == nil || head.Val != root.Val { return false } return dfs(head.Next, root.Left) || dfs(head.Next, root.Right) } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ const dfs = (head: ListNode | null, root: TreeNode | null) => { if (head == null) { return true; } if (root == null || head.val !== root.val) { return false; } return dfs(head.next, root.left) || dfs(head.next, root.right); }; function isSubPath(head: ListNode | null, root: TreeNode | null): boolean { if (root == null) { return false; } return dfs(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.left) || isSubPath(head, root.right); } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } // Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { fn dfs(head: &Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool { if head.is_none() { return true; } if root.is_none() { return false; } let node = head.as_ref().unwrap(); let root = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow(); if node.val != root.val { return false; } Self::dfs(&node.next, &root.left) || Self::dfs(&node.next, &root.right) } fn my_is_sub_path(head: &Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool { if root.is_none() { return false; } let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow(); Self::dfs(head, root) || Self::my_is_sub_path(head, &node.left) || Self::my_is_sub_path(head, &node.right) } pub fn is_sub_path(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool { Self::my_is_sub_path(&head, &root) } }