Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1335. Minimum Difficulty of a Job Schedule
Description
You want to schedule a list of jobs in d days. Jobs are dependent (i.e To work on the ith job, you have to finish all the jobs j where 0 <= j < i).
You have to finish at least one task every day. The difficulty of a job schedule is the sum of difficulties of each day of the d days. The difficulty of a day is the maximum difficulty of a job done on that day.
You are given an integer array jobDifficulty and an integer d. The difficulty of the ith job is jobDifficulty[i].
Return the minimum difficulty of a job schedule. If you cannot find a schedule for the jobs return -1.
Example 1:
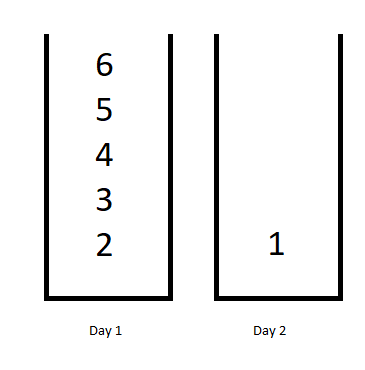
Input: jobDifficulty = [6,5,4,3,2,1], d = 2 Output: 7 Explanation: First day you can finish the first 5 jobs, total difficulty = 6. Second day you can finish the last job, total difficulty = 1. The difficulty of the schedule = 6 + 1 = 7
Example 2:
Input: jobDifficulty = [9,9,9], d = 4 Output: -1 Explanation: If you finish a job per day you will still have a free day. you cannot find a schedule for the given jobs.
Example 3:
Input: jobDifficulty = [1,1,1], d = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: The schedule is one job per day. total difficulty will be 3.
Constraints:
1 <= jobDifficulty.length <= 3000 <= jobDifficulty[i] <= 10001 <= d <= 10
Solutions
Solution 1: Dynamic Programming
We define $f[i][j]$ as the minimum difficulty to finish the first $i$ jobs within $j$ days. Initially $f[0][0] = 0$, and all other $f[i][j]$ are $\infty$.
For the $j$-th day, we can choose to finish jobs $[k,..i]$ on this day. Therefore, we have the following state transition equation:
\[f[i][j] = \min_{k \in [1,i]} \{f[k-1][j-1] + \max_{k \leq t \leq i} \{jobDifficulty[t]\}\}\]The final answer is $f[n][d]$.
The time complexity is $O(n^2 \times d)$, and the space complexity is $O(n \times d)$. Here $n$ and $d$ are the number of jobs and the number of days respectively.
-
class Solution { public int minDifficulty(int[] jobDifficulty, int d) { final int inf = 1 << 30; int n = jobDifficulty.length; int[][] f = new int[n + 1][d + 1]; for (var g : f) { Arrays.fill(g, inf); } f[0][0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= Math.min(d, i); ++j) { int mx = 0; for (int k = i; k > 0; --k) { mx = Math.max(mx, jobDifficulty[k - 1]); f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[k - 1][j - 1] + mx); } } } return f[n][d] >= inf ? -1 : f[n][d]; } } -
class Solution { public: int minDifficulty(vector<int>& jobDifficulty, int d) { int n = jobDifficulty.size(); int f[n + 1][d + 1]; memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(f)); f[0][0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= min(d, i); ++j) { int mx = 0; for (int k = i; k; --k) { mx = max(mx, jobDifficulty[k - 1]); f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[k - 1][j - 1] + mx); } } } return f[n][d] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : f[n][d]; } }; -
class Solution: def minDifficulty(self, jobDifficulty: List[int], d: int) -> int: n = len(jobDifficulty) f = [[inf] * (d + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)] f[0][0] = 0 for i in range(1, n + 1): for j in range(1, min(d + 1, i + 1)): mx = 0 for k in range(i, 0, -1): mx = max(mx, jobDifficulty[k - 1]) f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[k - 1][j - 1] + mx) return -1 if f[n][d] >= inf else f[n][d] -
func minDifficulty(jobDifficulty []int, d int) int { n := len(jobDifficulty) f := make([][]int, n+1) const inf = 1 << 30 for i := range f { f[i] = make([]int, d+1) for j := range f[i] { f[i][j] = inf } } f[0][0] = 0 for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { for j := 1; j <= min(d, i); j++ { mx := 0 for k := i; k > 0; k-- { mx = max(mx, jobDifficulty[k-1]) f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[k-1][j-1]+mx) } } } if f[n][d] == inf { return -1 } return f[n][d] } -
function minDifficulty(jobDifficulty: number[], d: number): number { const n = jobDifficulty.length; const inf = 1 << 30; const f: number[][] = new Array(n + 1).fill(0).map(() => new Array(d + 1).fill(inf)); f[0][0] = 0; for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for (let j = 1; j <= Math.min(d, i); ++j) { let mx = 0; for (let k = i; k > 0; --k) { mx = Math.max(mx, jobDifficulty[k - 1]); f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[k - 1][j - 1] + mx); } } } return f[n][d] < inf ? f[n][d] : -1; }