Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1028. Recover a Tree From Preorder Traversal
Description
We run a preorder depth-first search (DFS) on the root of a binary tree.
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D + 1. The depth of the root node is 0.
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output traversal of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
Example 1:
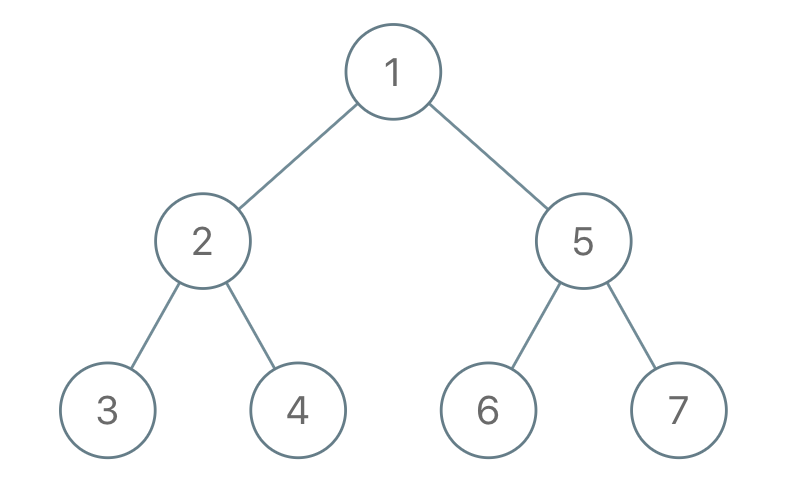
Input: traversal = "1-2--3--4-5--6--7" Output: [1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
Example 2:
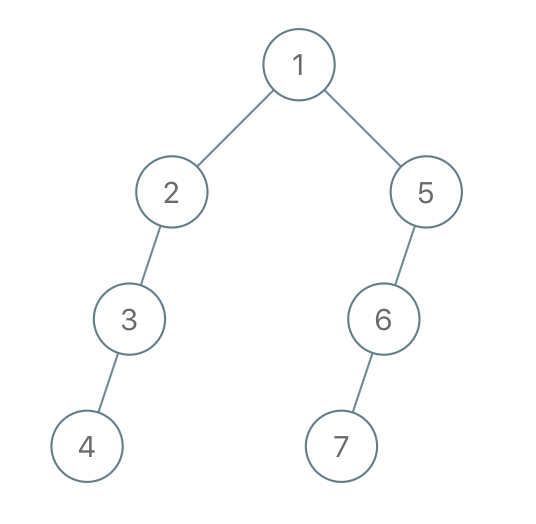
Input: traversal = "1-2--3---4-5--6---7" Output: [1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
Example 3:
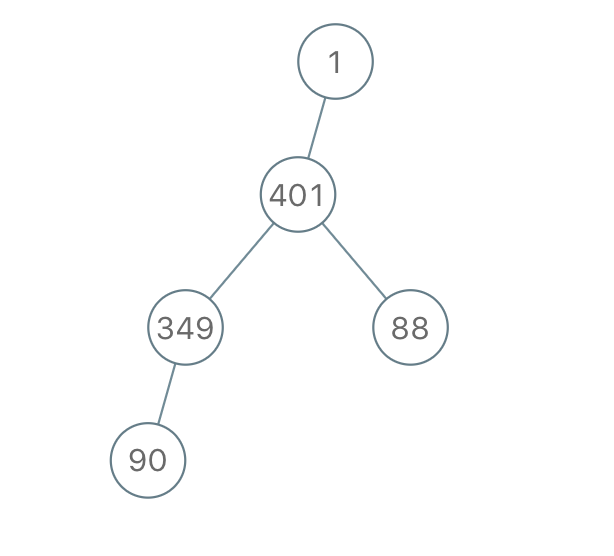
Input: traversal = "1-401--349---90--88" Output: [1,401,null,349,88,90]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the original tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 109
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* recoverFromPreorder(string S) { stack<TreeNode*> st; int depth = 0; int num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); ++i) { if (S[i] == '-') { depth++; } else { num = 10 * num + S[i] - '0'; } if (i + 1 >= S.length() || (isdigit(S[i]) && S[i + 1] == '-')) { TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(num); while (st.size() > depth) { st.pop(); } if (!st.empty()) { if (st.top()->left == nullptr) { st.top()->left = newNode; } else { st.top()->right = newNode; } } st.push(newNode); depth = 0; num = 0; } } TreeNode* res; while (!st.empty()) { res = st.top(); st.pop(); } return res; } }; -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode recoverFromPreorder(String traversal) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); int i = 0; while (i < traversal.length()) { int depth = 0; while (i < traversal.length() && traversal.charAt(i) == '-') { depth++; i++; } int num = 0; while (i < traversal.length() && Character.isDigit(traversal.charAt(i))) { num = num * 10 + (traversal.charAt(i) - '0'); i++; } // Create the new node TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(num); while (stack.size() > depth) { stack.pop(); } if (!stack.isEmpty()) { if (stack.peek().left == null) { stack.peek().left = newNode; } else { stack.peek().right = newNode; } } stack.push(newNode); } return stack.isEmpty() ? null : stack.get(0); } } -
function recoverFromPreorder(traversal: string): TreeNode | null { const stack: TreeNode[] = []; let i = 0; while (i < traversal.length) { let depth = 0; while (i < traversal.length && traversal[i] === '-') { depth++; i++; } let num = 0; while (i < traversal.length && !Number.isNaN(+traversal[i])) { num = num * 10 + +traversal[i]; i++; } // Create the new node const newNode = new TreeNode(num); while (stack.length > depth) { stack.pop(); } if (stack.length > 0) { const i = stack.length - 1; if (stack[i].left === null) { stack[i].left = newNode; } else { stack[i].right = newNode; } } stack.push(newNode); } return stack.length ? stack[0] : null; } -
function recoverFromPreorder(traversal) { const stack = []; let i = 0; while (i < traversal.length) { let depth = 0; while (i < traversal.length && traversal[i] === '-') { depth++; i++; } let num = 0; while (i < traversal.length && !Number.isNaN(+traversal[i])) { num = num * 10 + +traversal[i]; i++; } // Create the new node const newNode = new TreeNode(num); while (stack.length > depth) { stack.pop(); } if (stack.length > 0) { const i = stack.length - 1; if (stack[i].left === null) { stack[i].left = newNode; } else { stack[i].right = newNode; } } stack.push(newNode); } return stack.length ? stack[0] : null; }