Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
951. Flip Equivalent Binary Trees
Description
For a binary tree T, we can define a flip operation as follows: choose any node, and swap the left and right child subtrees.
A binary tree X is flip equivalent to a binary tree Y if and only if we can make X equal to Y after some number of flip operations.
Given the roots of two binary trees root1 and root2, return true if the two trees are flip equivalent or false otherwise.
Example 1:
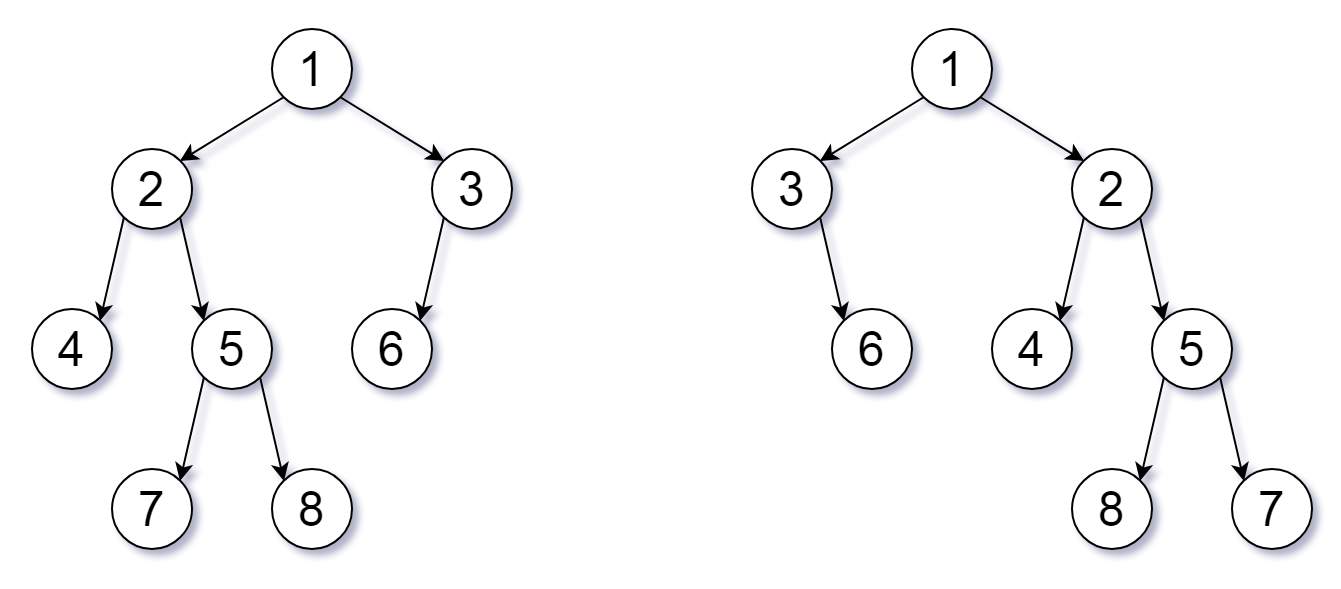
Input: root1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8], root2 = [1,3,2,null,6,4,5,null,null,null,null,8,7] Output: true Explanation: We flipped at nodes with values 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [] Output: true
Example 3:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [1] Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[0, 100]. - Each tree will have unique node values in the range
[0, 99].
Solutions
DFS.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public boolean flipEquiv(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { return dfs(root1, root2); } private boolean dfs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == root2 || (root1 == null && root2 == null)) { return true; } if (root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val) { return false; } return (dfs(root1.left, root2.left) && dfs(root1.right, root2.right)) || (dfs(root1.left, root2.right) && dfs(root1.right, root2.left)); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool flipEquiv(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { return dfs(root1, root2); } bool dfs(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { if (root1 == root2 || (!root1 && !root2)) return true; if (!root1 || !root2 || root1->val != root2->val) return false; return (dfs(root1->left, root2->left) && dfs(root1->right, root2->right)) || (dfs(root1->left, root2->right) && dfs(root1->right, root2->left)); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def flipEquiv(self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: def dfs(root1, root2): if root1 == root2 or (root1 is None and root2 is None): return True if root1 is None or root2 is None or root1.val != root2.val: return False return (dfs(root1.left, root2.left) and dfs(root1.right, root2.right)) or ( dfs(root1.left, root2.right) and dfs(root1.right, root2.left) ) return dfs(root1, root2) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func flipEquiv(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) bool { var dfs func(root1, root2 *TreeNode) bool dfs = func(root1, root2 *TreeNode) bool { if root1 == root2 || (root1 == nil && root2 == nil) { return true } if root1 == nil || root2 == nil || root1.Val != root2.Val { return false } return (dfs(root1.Left, root2.Left) && dfs(root1.Right, root2.Right)) || (dfs(root1.Left, root2.Right) && dfs(root1.Right, root2.Left)) } return dfs(root1, root2) }