Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
919. Complete Binary Tree Inserter
Description
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
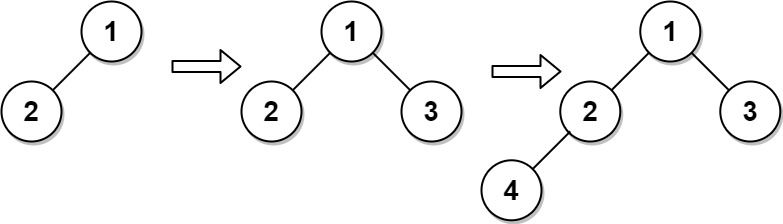
Input ["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"] [[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []] Output [null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]] Explanation CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]); cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1 cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2 cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class CBTInserter { private List<TreeNode> tree; public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) { tree = new ArrayList<>(); Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = q.pollFirst(); tree.add(node); if (node.left != null) { q.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { q.offer(node.right); } } } public int insert(int val) { int pid = (tree.size() - 1) >> 1; TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val); tree.add(node); TreeNode p = tree.get(pid); if (p.left == null) { p.left = node; } else { p.right = node; } return p.val; } public TreeNode get_root() { return tree.get(0); } } /** * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: * CBTInserter obj = new CBTInserter(root); * int param_1 = obj.insert(val); * TreeNode param_2 = obj.get_root(); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class CBTInserter { public: vector<TreeNode*> tree; CBTInserter(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> q{ {root} }; while (!q.empty()) { auto node = q.front(); q.pop(); tree.push_back(node); if (node->left) q.push(node->left); if (node->right) q.push(node->right); } } int insert(int val) { int pid = tree.size() - 1 >> 1; TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val); tree.push_back(node); TreeNode* p = tree[pid]; if (!p->left) p->left = node; else p->right = node; return p->val; } TreeNode* get_root() { return tree[0]; } }; /** * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: * CBTInserter* obj = new CBTInserter(root); * int param_1 = obj->insert(val); * TreeNode* param_2 = obj->get_root(); */ -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class CBTInserter: def __init__(self, root: TreeNode): self.tree = [] q = deque([root]) while q: for _ in range(len(q)): node = q.popleft() self.tree.append(node) if node.left: q.append(node.left) if node.right: q.append(node.right) def insert(self, val: int) -> int: pid = (len(self.tree) - 1) >> 1 node = TreeNode(val) self.tree.append(node) p = self.tree[pid] if p.left is None: p.left = node else: p.right = node return p.val def get_root(self) -> TreeNode: return self.tree[0] # Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = CBTInserter(root) # param_1 = obj.insert(val) # param_2 = obj.get_root() -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ type CBTInserter struct { tree []*TreeNode } func Constructor(root *TreeNode) CBTInserter { q := []*TreeNode{root} tree := []*TreeNode{} for len(q) > 0 { node := q[0] tree = append(tree, node) q = q[1:] if node.Left != nil { q = append(q, node.Left) } if node.Right != nil { q = append(q, node.Right) } } return CBTInserter{tree} } func (this *CBTInserter) Insert(val int) int { pid := (len(this.tree) - 1) >> 1 node := &TreeNode{Val: val} this.tree = append(this.tree, node) p := this.tree[pid] if p.Left == nil { p.Left = node } else { p.Right = node } return p.Val } func (this *CBTInserter) Get_root() *TreeNode { return this.tree[0] } /** * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: * obj := Constructor(root); * param_1 := obj.Insert(val); * param_2 := obj.Get_root(); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ class CBTInserter { private root: TreeNode; private queue: TreeNode[]; constructor(root: TreeNode | null) { this.root = root; this.queue = [this.root]; while (true) { if (this.queue[0].left == null) { break; } this.queue.push(this.queue[0].left); if (this.queue[0].right == null) { break; } this.queue.push(this.queue[0].right); this.queue.shift(); } } insert(val: number): number { if (this.queue[0].left != null && this.queue[0].right != null) { this.queue.shift(); } const newNode = new TreeNode(val); this.queue.push(newNode); if (this.queue[0].left == null) { this.queue[0].left = newNode; return this.queue[0].val; } if (this.queue[0].right == null) { this.queue[0].right = newNode; return this.queue[0].val; } return 0; } get_root(): TreeNode | null { return this.root; } } /** * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new CBTInserter(root) * var param_1 = obj.insert(val) * var param_2 = obj.get_root() */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root */ var CBTInserter = function (root) { this.tree = []; const q = [root]; while (q.length) { const node = q.shift(); this.tree.push(node); if (node.left) { q.push(node.left); } if (node.right) { q.push(node.right); } } }; /** * @param {number} val * @return {number} */ CBTInserter.prototype.insert = function (val) { const pid = (this.tree.length - 1) >> 1; const node = new TreeNode(val); this.tree.push(node); const p = this.tree[pid]; if (!p.left) { p.left = node; } else { p.right = node; } return p.val; }; /** * @return {TreeNode} */ CBTInserter.prototype.get_root = function () { return this.tree[0]; }; /** * Your CBTInserter object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new CBTInserter(root) * var param_1 = obj.insert(val) * var param_2 = obj.get_root() */