Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
867. Transpose Matrix
Description
Given a 2D integer array matrix, return the transpose of matrix.
The transpose of a matrix is the matrix flipped over its main diagonal, switching the matrix's row and column indices.
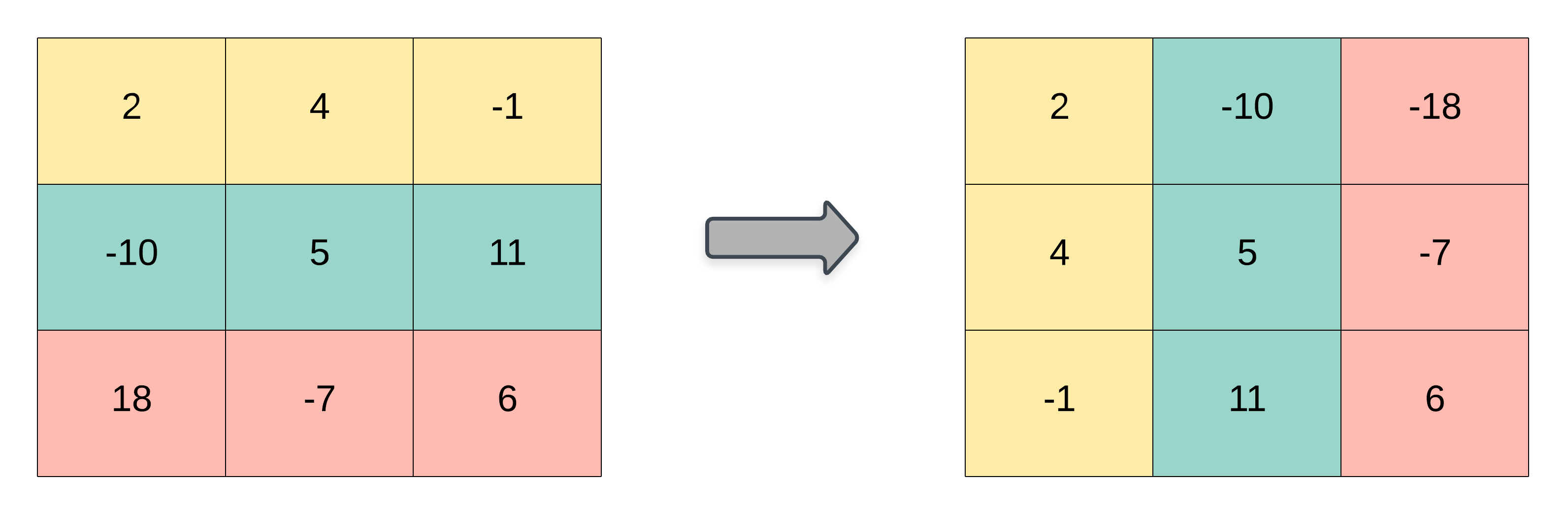
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] Output: [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10001 <= m * n <= 105-109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int[][] transpose(int[][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length; int[][] ans = new int[n][m]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) { ans[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> transpose(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> ans(n, vector<int>(m)); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) ans[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def transpose(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: return list(zip(*matrix)) -
func transpose(matrix [][]int) [][]int { m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) ans := make([][]int, n) for i := range ans { ans[i] = make([]int, m) for j := range ans[i] { ans[i][j] = matrix[j][i] } } return ans } -
/** * @param {number[][]} matrix * @return {number[][]} */ var transpose = function (matrix) { const m = matrix.length; const n = matrix[0].length; const ans = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => new Array(m).fill(0)); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < m; ++j) { ans[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; } } return ans; };