Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
847. Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes
Description
You have an undirected, connected graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an array graph where graph[i] is a list of all the nodes connected with node i by an edge.
Return the length of the shortest path that visits every node. You may start and stop at any node, you may revisit nodes multiple times, and you may reuse edges.
Example 1:
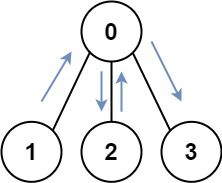
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0],[0],[0]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [1,0,2,0,3]
Example 2:
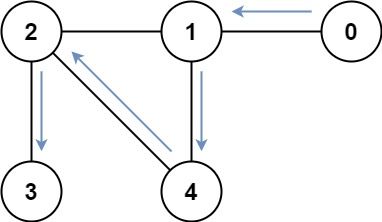
Input: graph = [[1],[0,2,4],[1,3,4],[2],[1,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [0,1,4,2,3]
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 120 <= graph[i].length < ngraph[i]does not containi.- If
graph[a]containsb, thengraph[b]containsa. - The input graph is always connected.
Solutions
Because each edge has the same weight, the shortest path can be solution by using BFS, and the access of the point can be recorded by state compression.
-
class Solution { public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) { int n = graph.length; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); boolean[][] vis = new boolean[n][1 << n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { q.offer(new int[] {i, 1 << i}); vis[i][1 << i] = true; } for (int ans = 0;; ++ans) { for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) { var p = q.poll(); int i = p[0], st = p[1]; if (st == (1 << n) - 1) { return ans; } for (int j : graph[i]) { int nst = st | 1 << j; if (!vis[j][nst]) { vis[j][nst] = true; q.offer(new int[] {j, nst}); } } } } } } -
class Solution { public: int shortestPathLength(vector<vector<int>>& graph) { int n = graph.size(); queue<pair<int, int>> q; bool vis[n][1 << n]; memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { q.emplace(i, 1 << i); vis[i][1 << i] = true; } for (int ans = 0;; ++ans) { for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) { auto [i, st] = q.front(); q.pop(); if (st == (1 << n) - 1) { return ans; } for (int j : graph[i]) { int nst = st | 1 << j; if (!vis[j][nst]) { vis[j][nst] = true; q.emplace(j, nst); } } } } } }; -
class Solution: def shortestPathLength(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> int: n = len(graph) q = deque() vis = set() for i in range(n): q.append((i, 1 << i)) vis.add((i, 1 << i)) ans = 0 while 1: for _ in range(len(q)): i, st = q.popleft() if st == (1 << n) - 1: return ans for j in graph[i]: nst = st | 1 << j if (j, nst) not in vis: vis.add((j, nst)) q.append((j, nst)) ans += 1 -
func shortestPathLength(graph [][]int) int { n := len(graph) q := [][2]int{} vis := make([][]bool, n) for i := range vis { vis[i] = make([]bool, 1<<n) vis[i][1<<i] = true q = append(q, [2]int{i, 1 << i}) } for ans := 0; ; ans++ { for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- { p := q[0] q = q[1:] i, st := p[0], p[1] if st == (1<<n)-1 { return ans } for _, j := range graph[i] { nst := st | 1<<j if !vis[j][nst] { vis[j][nst] = true q = append(q, [2]int{j, nst}) } } } } } -
function shortestPathLength(graph: number[][]): number { const n = graph.length; const q: number[][] = []; const vis: boolean[][] = new Array(n).fill(false).map(() => new Array(1 << n).fill(false)); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { q.push([i, 1 << i]); vis[i][1 << i] = true; } for (let ans = 0; ; ++ans) { for (let k = q.length; k; --k) { const [i, st] = q.shift()!; if (st === (1 << n) - 1) { return ans; } for (const j of graph[i]) { const nst = st | (1 << j); if (!vis[j][nst]) { vis[j][nst] = true; q.push([j, nst]); } } } } } -
use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn shortest_path_length(graph: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let n = graph.len(); let mut vis = vec![vec![false; 1 << n]; n]; let mut q = VecDeque::new(); // Initialize the queue for i in 0..n { q.push_back(((i, 1 << i), 0)); vis[i][1 << i] = true; } // Begin BFS while !q.is_empty() { let ((i, st), count) = q.pop_front().unwrap(); if st == (1 << n) - 1 { return count; } // If the path has not been visited for j in &graph[i] { let nst = st | (1 << *j); if !vis[*j as usize][nst] { q.push_back(((*j as usize, nst), count + 1)); vis[*j as usize][nst] = true; } } } -1 } }