Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
814. Binary Tree Pruning
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the same tree where every subtree (of the given tree) not containing a 1 has been removed.
A subtree of a node node is node plus every node that is a descendant of node.
Example 1:
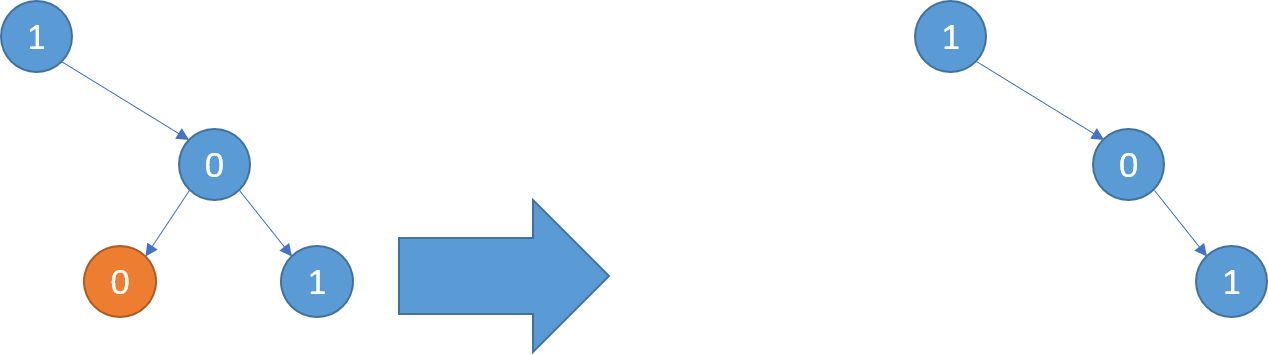
Input: root = [1,null,0,0,1] Output: [1,null,0,null,1] Explanation: Only the red nodes satisfy the property "every subtree not containing a 1". The diagram on the right represents the answer.
Example 2:
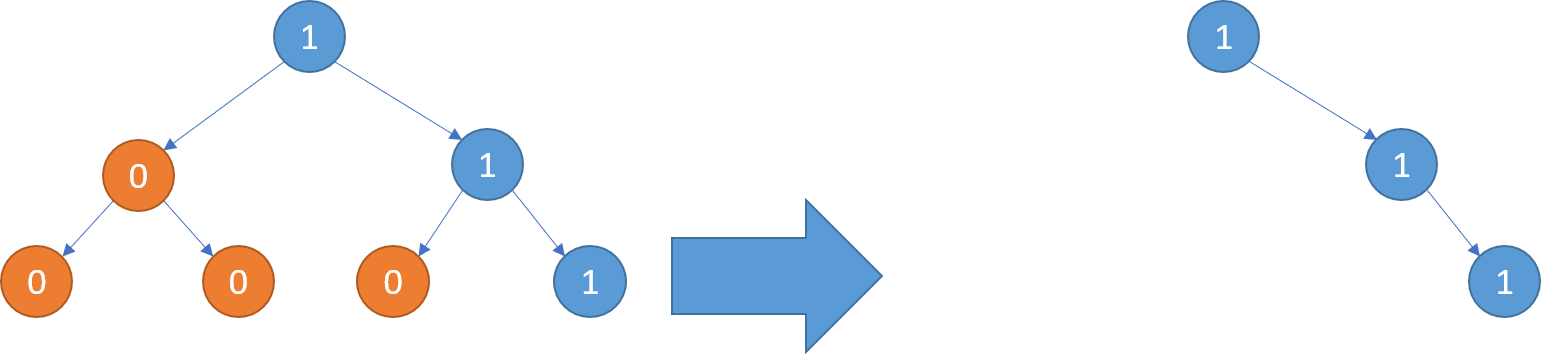
Input: root = [1,0,1,0,0,0,1] Output: [1,null,1,null,1]
Example 3:
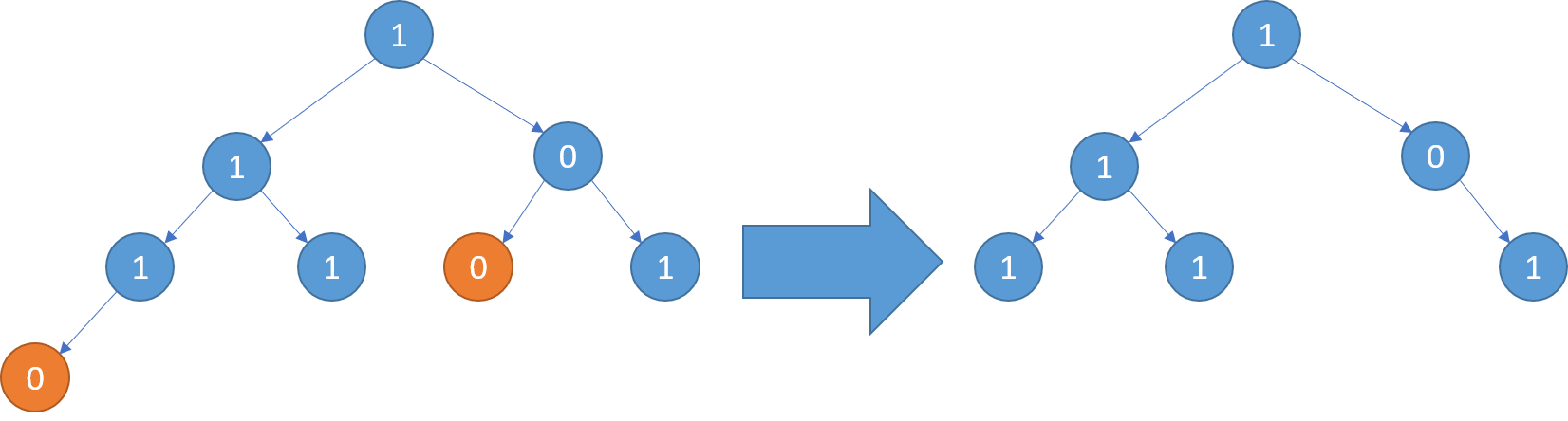
Input: root = [1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0] Output: [1,1,0,1,1,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 200]. Node.valis either0or1.
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode pruneTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } root.left = pruneTree(root.left); root.right = pruneTree(root.right); if (root.val == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) { return null; } return root; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* pruneTree(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return nullptr; root->left = pruneTree(root->left); root->right = pruneTree(root->right); if (!root->val && !root->left && !root->right) return nullptr; return root; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def pruneTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: if root is None: return None root.left = self.pruneTree(root.left) root.right = self.pruneTree(root.right) if root.val == 0 and root.left is None and root.right is None: return None return root -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func pruneTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { if root == nil { return nil } root.Left = pruneTree(root.Left) root.Right = pruneTree(root.Right) if root.Val == 0 && root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil { return nil } return root } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function pruneTree(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null { if (root == null) { return root; } root.left = pruneTree(root.left); root.right = pruneTree(root.right); if (root.val == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) { return null; } return root; } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {TreeNode} */ var pruneTree = function (root) { if (!root) return null; root.left = pruneTree(root.left); root.right = pruneTree(root.right); if (root.val == 0 && !root.left && !root.right) { return null; } return root; }; -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { pub fn prune_tree(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { if root.is_none() { return None; } let root = root.unwrap(); let left = Self::prune_tree(root.borrow_mut().left.take()); let right = Self::prune_tree(root.borrow_mut().right.take()); if root.borrow().val == 0 && left.is_none() && right.is_none() { return None; } root.borrow_mut().left = left; root.borrow_mut().right = right; Some(root) } }