Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
802. Find Eventual Safe States
Description
There is a directed graph of n nodes with each node labeled from 0 to n - 1. The graph is represented by a 0-indexed 2D integer array graph where graph[i] is an integer array of nodes adjacent to node i, meaning there is an edge from node i to each node in graph[i].
A node is a terminal node if there are no outgoing edges. A node is a safe node if every possible path starting from that node leads to a terminal node (or another safe node).
Return an array containing all the safe nodes of the graph. The answer should be sorted in ascending order.
Example 1:
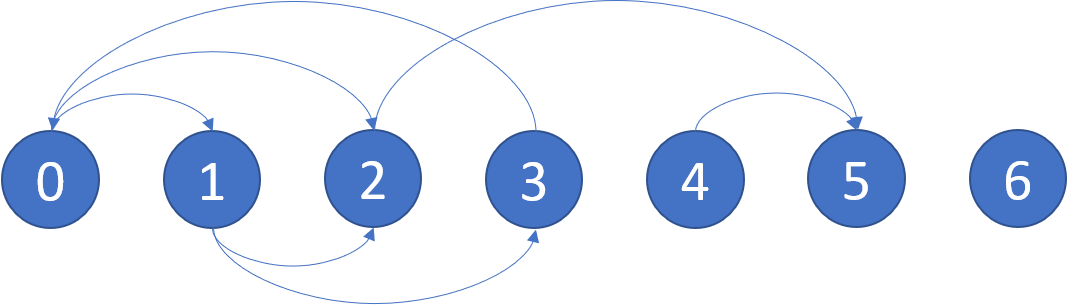
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]] Output: [2,4,5,6] Explanation: The given graph is shown above. Nodes 5 and 6 are terminal nodes as there are no outgoing edges from either of them. Every path starting at nodes 2, 4, 5, and 6 all lead to either node 5 or 6.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[1,2,3,4],[1,2],[3,4],[0,4],[]] Output: [4] Explanation: Only node 4 is a terminal node, and every path starting at node 4 leads to node 4.
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 1040 <= graph[i].length <= n0 <= graph[i][j] <= n - 1graph[i]is sorted in a strictly increasing order.- The graph may contain self-loops.
- The number of edges in the graph will be in the range
[1, 4 * 104].
Solutions
The point with zero out-degree is safe, and if a point can only reach the safe point, then it is also safe, so the problem can be converted to topological sorting.
-
class Solution { private int[] color; private int[][] g; public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes(int[][] graph) { int n = graph.length; color = new int[n]; g = graph; List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (dfs(i)) { ans.add(i); } } return ans; } private boolean dfs(int i) { if (color[i] > 0) { return color[i] == 2; } color[i] = 1; for (int j : g[i]) { if (!dfs(j)) { return false; } } color[i] = 2; return true; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> color; vector<int> eventualSafeNodes(vector<vector<int>>& graph) { int n = graph.size(); color.assign(n, 0); vector<int> ans; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (dfs(i, graph)) ans.push_back(i); return ans; } bool dfs(int i, vector<vector<int>>& g) { if (color[i]) return color[i] == 2; color[i] = 1; for (int j : g[i]) if (!dfs(j, g)) return false; color[i] = 2; return true; } }; -
class Solution: def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: def dfs(i): if color[i]: return color[i] == 2 color[i] = 1 for j in graph[i]: if not dfs(j): return False color[i] = 2 return True n = len(graph) color = [0] * n return [i for i in range(n) if dfs(i)] -
func eventualSafeNodes(graph [][]int) []int { n := len(graph) color := make([]int, n) var dfs func(int) bool dfs = func(i int) bool { if color[i] > 0 { return color[i] == 2 } color[i] = 1 for _, j := range graph[i] { if !dfs(j) { return false } } color[i] = 2 return true } ans := []int{} for i := range graph { if dfs(i) { ans = append(ans, i) } } return ans } -
/** * @param {number[][]} graph * @return {number[]} */ var eventualSafeNodes = function (graph) { const n = graph.length; const color = new Array(n).fill(0); function dfs(i) { if (color[i]) { return color[i] == 2; } color[i] = 1; for (const j of graph[i]) { if (!dfs(j)) { return false; } } color[i] = 2; return true; } let ans = []; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (dfs(i)) { ans.push(i); } } return ans; };