Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
785. Is Graph Bipartite
Description
There is an undirected graph with n nodes, where each node is numbered between 0 and n - 1. You are given a 2D array graph, where graph[u] is an array of nodes that node u is adjacent to. More formally, for each v in graph[u], there is an undirected edge between node u and node v. The graph has the following properties:
- There are no self-edges (
graph[u]does not containu). - There are no parallel edges (
graph[u]does not contain duplicate values). - If
vis ingraph[u], thenuis ingraph[v](the graph is undirected). - The graph may not be connected, meaning there may be two nodes
uandvsuch that there is no path between them.
A graph is bipartite if the nodes can be partitioned into two independent sets A and B such that every edge in the graph connects a node in set A and a node in set B.
Return true if and only if it is bipartite.
Example 1:
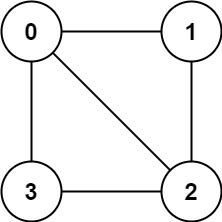
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,2]] Output: false Explanation: There is no way to partition the nodes into two independent sets such that every edge connects a node in one and a node in the other.
Example 2:
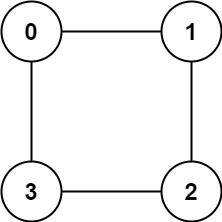
Input: graph = [[1,3],[0,2],[1,3],[0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation: We can partition the nodes into two sets: {0, 2} and {1, 3}.
Constraints:
graph.length == n1 <= n <= 1000 <= graph[u].length < n0 <= graph[u][i] <= n - 1graph[u]does not containu.- All the values of
graph[u]are unique. - If
graph[u]containsv, thengraph[v]containsu.
Solutions
-
class Solution { private int[] color; private int[][] g; public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) { int n = graph.length; color = new int[n]; g = graph; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (color[i] == 0 && !dfs(i, 1)) { return false; } } return true; } private boolean dfs(int u, int c) { color[u] = c; for (int v : g[u]) { if (color[v] == 0) { if (!dfs(v, 3 - c)) { return false; } } else if (color[v] == c) { return false; } } return true; } } -
class Solution { public: bool isBipartite(vector<vector<int>>& graph) { int n = graph.size(); vector<int> color(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (!color[i] && !dfs(i, 1, color, graph)) return false; return true; } bool dfs(int u, int c, vector<int>& color, vector<vector<int>>& g) { color[u] = c; for (int& v : g[u]) { if (!color[v]) { if (!dfs(v, 3 - c, color, g)) return false; } else if (color[v] == c) return false; } return true; } }; -
class Solution: def isBipartite(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> bool: def dfs(u, c): color[u] = c for v in graph[u]: if not color[v]: if not dfs(v, 3 - c): return False elif color[v] == c: return False return True n = len(graph) color = [0] * n for i in range(n): if not color[i] and not dfs(i, 1): return False return True -
func isBipartite(graph [][]int) bool { n := len(graph) color := make([]int, n) var dfs func(u, c int) bool dfs = func(u, c int) bool { color[u] = c for _, v := range graph[u] { if color[v] == 0 { if !dfs(v, 3-c) { return false } } else if color[v] == c { return false } } return true } for i := range graph { if color[i] == 0 && !dfs(i, 1) { return false } } return true } -
function isBipartite(graph: number[][]): boolean { const n = graph.length; let valid = true; let colors = new Array(n).fill(0); function dfs(idx: number, color: number, graph: number[][]) { colors[idx] = color; const nextColor = 3 - color; for (let j of graph[idx]) { if (!colors[j]) { dfs(j, nextColor, graph); if (!valid) return; } else if (colors[j] != nextColor) { valid = false; return; } } } for (let i = 0; i < n && valid; i++) { if (!colors[i]) { dfs(i, 1, graph); } } return valid; } -
impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn is_bipartite(graph: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool { let mut graph = graph; let n = graph.len(); let mut color_vec: Vec<usize> = vec![0; n]; for i in 0..n { if color_vec[i] == 0 && !Self::traverse(i, 1, &mut color_vec, &mut graph) { return false; } } true } #[allow(dead_code)] fn traverse( v: usize, color: usize, color_vec: &mut Vec<usize>, graph: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>> ) -> bool { color_vec[v] = color; for n in graph[v].clone() { if color_vec[n as usize] == 0 { // This node hasn't been colored if !Self::traverse(n as usize, 3 - color, color_vec, graph) { return false; } } else if color_vec[n as usize] == color { // The color is the same return false; } } true } }