Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
743. Network Delay Time
Description
You are given a network of n nodes, labeled from 1 to n. You are also given times, a list of travel times as directed edges times[i] = (ui, vi, wi), where ui is the source node, vi is the target node, and wi is the time it takes for a signal to travel from source to target.
We will send a signal from a given node k. Return the minimum time it takes for all the n nodes to receive the signal. If it is impossible for all the n nodes to receive the signal, return -1.
Example 1:
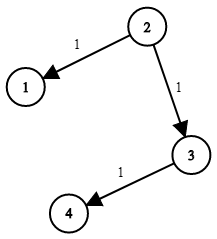
Input: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 Output: -1
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100- All the pairs
(ui, vi)are unique. (i.e., no multiple edges.)
Solutions
-
class Solution { private static final int N = 110; private static final int INF = 0x3f3f; public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) { int[][] g = new int[N][N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { Arrays.fill(g[i], INF); } for (int[] e : times) { g[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2]; } int[] dist = new int[N]; Arrays.fill(dist, INF); dist[k] = 0; boolean[] vis = new boolean[N]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int t = -1; for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) { t = j; } } vis[t] = true; for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]); } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { ans = Math.max(ans, dist[i]); } return ans == INF ? -1 : ans; } } -
class Solution { public: const int inf = 0x3f3f; int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) { vector<vector<int>> g(n, vector<int>(n, inf)); for (auto& t : times) g[t[0] - 1][t[1] - 1] = t[2]; vector<bool> vis(n); vector<int> dist(n, inf); dist[k - 1] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int t = -1; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) { t = j; } } vis[t] = true; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]); } } int ans = *max_element(dist.begin(), dist.end()); return ans == inf ? -1 : ans; } }; -
class Solution: def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int: INF = 0x3F3F g = defaultdict(list) for u, v, w in times: g[u - 1].append((v - 1, w)) dist = [INF] * n dist[k - 1] = 0 q = [(0, k - 1)] while q: _, u = heappop(q) for v, w in g[u]: if dist[v] > dist[u] + w: dist[v] = dist[u] + w heappush(q, (dist[v], v)) ans = max(dist) return -1 if ans == INF else ans -
const Inf = 0x3f3f3f3f type pair struct { first int second int } var _ heap.Interface = (*pairs)(nil) type pairs []pair func (a pairs) Len() int { return len(a) } func (a pairs) Less(i int, j int) bool { return a[i].first < a[j].first || a[i].first == a[j].first && a[i].second < a[j].second } func (a pairs) Swap(i int, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] } func (a *pairs) Push(x any) { *a = append(*a, x.(pair)) } func (a *pairs) Pop() any { l := len(*a); t := (*a)[l-1]; *a = (*a)[:l-1]; return t } func networkDelayTime(times [][]int, n int, k int) int { graph := make([]pairs, n) for _, time := range times { from, to, time := time[0]-1, time[1]-1, time[2] graph[from] = append(graph[from], pair{to, time}) } dis := make([]int, n) for i := range dis { dis[i] = Inf } dis[k-1] = 0 vis := make([]bool, n) h := make(pairs, 0) heap.Push(&h, pair{0, k - 1}) for len(h) > 0 { from := heap.Pop(&h).(pair).second if vis[from] { continue } vis[from] = true for _, e := range graph[from] { to, d := e.first, dis[from]+e.second if d < dis[to] { dis[to] = d heap.Push(&h, pair{d, to}) } } } ans := slices.Max(dis) if ans == Inf { return -1 } return ans } -
function networkDelayTime(times: number[][], n: number, k: number): number { const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill(Infinity)); for (const [u, v, w] of times) { g[u - 1][v - 1] = w; } const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(Infinity); dist[k - 1] = 0; const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { let t = -1; for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (!vis[j] && (t === -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) { t = j; } } vis[t] = true; for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]); } } const ans = Math.max(...dist); return ans === Infinity ? -1 : ans; }