Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
666. Path Sum IV
Description
If the depth of a tree is smaller than 5, then this tree can be represented by an array of three-digit integers. For each integer in this array:
- The hundreds digit represents the depth
dof this node where1 <= d <= 4. - The tens digit represents the position
pof this node in the level it belongs to where1 <= p <= 8. The position is the same as that in a full binary tree. - The units digit represents the value
vof this node where0 <= v <= 9.
Given an array of ascending three-digit integers nums representing a binary tree with a depth smaller than 5, return the sum of all paths from the root towards the leaves.
It is guaranteed that the given array represents a valid connected binary tree.
Example 1:
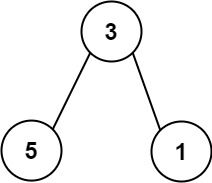
Input: nums = [113,215,221] Output: 12 Explanation: The tree that the list represents is shown. The path sum is (3 + 5) + (3 + 1) = 12.
Example 2:
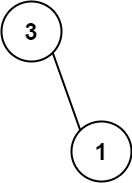
Input: nums = [113,221] Output: 4 Explanation: The tree that the list represents is shown. The path sum is (3 + 1) = 4.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 15110 <= nums[i] <= 489numsrepresents a valid binary tree with depth less than5.
Solutions
DFS.
-
class Solution { private int ans; private Map<Integer, Integer> mp; public int pathSum(int[] nums) { ans = 0; mp = new HashMap<>(nums.length); for (int num : nums) { mp.put(num / 10, num % 10); } dfs(11, 0); return ans; } private void dfs(int node, int t) { if (!mp.containsKey(node)) { return; } t += mp.get(node); int d = node / 10, p = node % 10; int l = (d + 1) * 10 + (p * 2) - 1; int r = l + 1; if (!mp.containsKey(l) && !mp.containsKey(r)) { ans += t; return; } dfs(l, t); dfs(r, t); } } -
class Solution { public: int ans; unordered_map<int, int> mp; int pathSum(vector<int>& nums) { ans = 0; mp.clear(); for (int num : nums) mp[num / 10] = num % 10; dfs(11, 0); return ans; } void dfs(int node, int t) { if (!mp.count(node)) return; t += mp[node]; int d = node / 10, p = node % 10; int l = (d + 1) * 10 + (p * 2) - 1; int r = l + 1; if (!mp.count(l) && !mp.count(r)) { ans += t; return; } dfs(l, t); dfs(r, t); } }; -
class Solution: def pathSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: def dfs(node, t): if node not in mp: return t += mp[node] d, p = divmod(node, 10) l = (d + 1) * 10 + (p * 2) - 1 r = l + 1 nonlocal ans if l not in mp and r not in mp: ans += t return dfs(l, t) dfs(r, t) ans = 0 mp = {num // 10: num % 10 for num in nums} dfs(11, 0) return ans -
func pathSum(nums []int) int { ans := 0 mp := make(map[int]int) for _, num := range nums { mp[num/10] = num % 10 } var dfs func(node, t int) dfs = func(node, t int) { if v, ok := mp[node]; ok { t += v d, p := node/10, node%10 l := (d+1)*10 + (p * 2) - 1 r := l + 1 if _, ok1 := mp[l]; !ok1 { if _, ok2 := mp[r]; !ok2 { ans += t return } } dfs(l, t) dfs(r, t) } } dfs(11, 0) return ans }