Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree and an integer k, return true if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to k, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
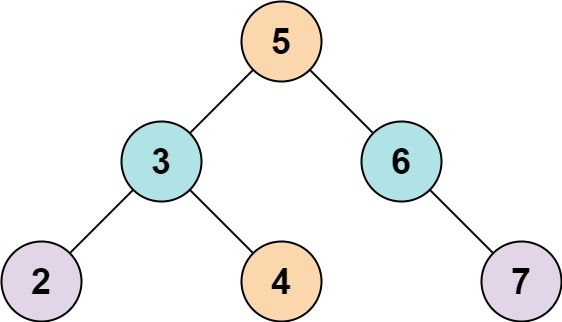
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9 Output: true
Example 2:
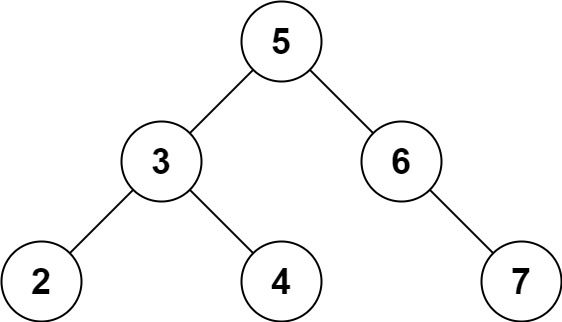
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 28 Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.-105 <= k <= 105
Solution 1 - set
As long as it is the question of the sum of two numbers, you must remember to try to do it with HashSet.
This question is just to turn the array into a binary tree. We need to traverse the binary tree and use a HashSet. In the recursive function function,
- if node is empty, return false.
- If k minus the current node value exists in the HashSet, return true directly;
- otherwise, add the current node value to the HashSet, and then call the recursive function on the left and right sub-nodes and return together.
Solution 2 - two pointers
This solution defines two classes: BSTIterator and Solution. The BSTIterator class is designed to iterate through a binary search tree (BST) in either ascending (left-to-right) or descending (right-to-left) order. The Solution class uses two instances of BSTIterator to find if there exists two elements in the BST such that their sum equals a given target value k.
Class: BSTIterator
-
Constructor
__init__: Initializes the iterator with the root of a BST and a boolean flagleftToRightindicating the direction of iteration (ascending ifTrue, descending ifFalse). It initializes an empty stack to facilitate controlled traversal of the BST and calls_pushUntilNoneto preload the stack with the initial path from the root towards the leftmost or rightmost node, depending on the iteration direction. -
Method
next: Returns the next integer in the sequence. It pops the top element from the stack (which is the next element in order), then, depending on the iteration direction, traverses towards the next node in that order, pushing nodes encountered along the way onto the stack. This ensures that the stack always contains the nodes that maintain the current path in the tree relevant to the iteration order. -
Method
_pushUntilNone: Given a starting node, it iteratively traverses the tree towards the leftmost (for ascending order) or rightmost (for descending order) node, pushing all encountered nodes onto the stack. This method ensures that the next call tonextwill return the next correct value in the sequence.
Class: Solution
- Method
findTarget: This method checks if there are two numbers in the BST that add up tok. It initializes twoBSTIteratorinstances, one for ascending order (left) and one for descending order (right). It then iterates through the BST from both ends simultaneously (smallest and largest values), comparing their sum tok.- If the sum equals
k, it returnsTrue. - If the sum is less than
k, it moves theleftiterator to the next larger value. - If the sum is greater than
k, it moves therightiterator to the next smaller value. - This process continues until the
leftvalue is no longer less than therightvalue, meaning the entire BST has been examined.
- If the sum equals
By approaching from both the smallest and largest values simultaneously and narrowing down the search space based on the sum comparison, this method efficiently determines whether any two elements in the BST add up to k.
Example Scenario
Consider a BST with elements [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] and a target sum k = 9.
- The
leftiterator starts at2(the smallest value), and therightiterator starts at7(the largest value). - Since their sum
2 + 7 = 9equalsk, the method immediately returnsTrue.
This approach effectively leverages the BST property (left child < parent < right child) and two-pointer technique to find the target sum with optimal efficiency.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ public class Two_Sum_IV_Input_is_a_BST { /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ // https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/solution/ public class Solution_queue { public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { if (queue.peek() != null) { TreeNode node = queue.remove(); if (set.contains(k - node.val)) return true; set.add(node.val); queue.add(node.right); queue.add(node.left); } else queue.remove(); } return false; } } // time: O(N) // space: O(N) public class Solution_usingBST { // inorder traversal to get sorted list public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { List< Integer > list = new ArrayList<>(); inorder(root, list); int l = 0, r = list.size() - 1; while (l < r) { int sum = list.get(l) + list.get(r); if (sum == k) return true; if (sum < k) l++; else r--; } return false; } public void inorder(TreeNode root, List < Integer > list) { if (root == null) return; inorder(root.left, list); list.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, list); } } // time: O(N) // space: O(N) public class Solution { public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { Set < Integer > set = new HashSet(); return find(root, k, set); } public boolean find(TreeNode root, int k, Set< Integer > set) { if (root == null) { return false; } if (set.contains(k - root.val)) { return true; } set.add(root.val); return find(root.left, k, set) || find(root.right, k, set); } } } ////// class Solution { private Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(); private int k; public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { this.k = k; return dfs(root); } private boolean dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return false; } if (vis.contains(k - root.val)) { return true; } vis.add(root.val); return dfs(root.left) || dfs(root.right); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool findTarget(TreeNode* root, int k) { unordered_set<int> vis; function<bool(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) { if (!root) { return false; } if (vis.count(k - root->val)) { return true; } vis.insert(root->val); return dfs(root->left) || dfs(root->right); }; return dfs(root); } }; -
class BSTIterator: def __init__(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], leftToRight: bool): self.stack = [] self.leftToRight = leftToRight self._pushUntilNone(root) def next(self) -> int: node = self.stack.pop() if self.leftToRight: self._pushUntilNone(node.right) else: self._pushUntilNone(node.left) return node.val # if passed in a None node, then None will not be pushed to stack def _pushUntilNone(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]): while root: self.stack.append(root) root = root.left if self.leftToRight else root.right class Solution: def findTarget(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> bool: if not root: return False left = BSTIterator(root, True) right = BSTIterator(root, False) l = left.next() r = right.next() while l < r: summ = l + r if summ == k: return True if summ < k: l = left.next() else: r = right.next() return False ########### # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def findTarget(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> bool: def dfs(root): if root is None: return False if k - root.val in vis: return True vis.add(root.val) return dfs(root.left) or dfs(root.right) vis = set() return dfs(root) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func findTarget(root *TreeNode, k int) bool { vis := map[int]bool{} var dfs func(*TreeNode) bool dfs = func(root *TreeNode) bool { if root == nil { return false } if vis[k-root.Val] { return true } vis[root.Val] = true return dfs(root.Left) || dfs(root.Right) } return dfs(root) } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function findTarget(root: TreeNode | null, k: number): boolean { const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => { if (!root) { return false; } if (vis.has(k - root.val)) { return true; } vis.add(root.val); return dfs(root.left) || dfs(root.right); }; const vis = new Set<number>(); return dfs(root); } -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::cell::RefCell; use std::collections::{ HashSet, VecDeque }; use std::rc::Rc; impl Solution { pub fn find_target(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, k: i32) -> bool { let mut set = HashSet::new(); let mut q = VecDeque::new(); q.push_back(root); while let Some(node) = q.pop_front() { if let Some(node) = node { let mut node = node.as_ref().borrow_mut(); if set.contains(&node.val) { return true; } set.insert(k - node.val); q.push_back(node.left.take()); q.push_back(node.right.take()); } } false } }