Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
606. Construct String from Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, construct a string consisting of parenthesis and integers from a binary tree with the preorder traversal way, and return it.
Omit all the empty parenthesis pairs that do not affect the one-to-one mapping relationship between the string and the original binary tree.
Example 1:
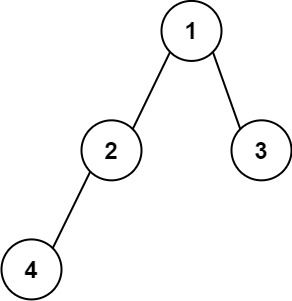
Input: root = [1,2,3,4] Output: "1(2(4))(3)" Explanation: Originally, it needs to be "1(2(4)())(3()())", but you need to omit all the unnecessary empty parenthesis pairs. And it will be "1(2(4))(3)"
Example 2:
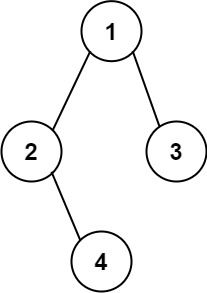
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4] Output: "1(2()(4))(3)" Explanation: Almost the same as the first example, except we cannot omit the first parenthesis pair to break the one-to-one mapping relationship between the input and the output.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public String tree2str(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return ""; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return root.val + ""; } if (root.right == null) { return root.val + "(" + tree2str(root.left) + ")"; } return root.val + "(" + tree2str(root.left) + ")(" + tree2str(root.right) + ")"; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: string tree2str(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return ""; if (!root->left && !root->right) return to_string(root->val); if (!root->right) return to_string(root->val) + "(" + tree2str(root->left) + ")"; return to_string(root->val) + "(" + tree2str(root->left) + ")(" + tree2str(root->right) + ")"; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def tree2str(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str: def dfs(root): if root is None: return '' if root.left is None and root.right is None: return str(root.val) if root.right is None: return f'{root.val}({dfs(root.left)})' return f'{root.val}({dfs(root.left)})({dfs(root.right)})' return dfs(root) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func tree2str(root *TreeNode) string { if root == nil { return "" } if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil { return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) } if root.Right == nil { return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) + "(" + tree2str(root.Left) + ")" } return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) + "(" + tree2str(root.Left) + ")(" + tree2str(root.Right) + ")" } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function tree2str(root: TreeNode | null): string { if (root == null) { return ''; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return `${root.val}`; } return `${root.val}(${root.left ? tree2str(root.left) : ''})${ root.right ? `(${tree2str(root.right)})` : '' }`; } -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::cell::RefCell; use std::rc::Rc; impl Solution { fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, res: &mut String) { if let Some(node) = root { let node = node.borrow(); res.push_str(node.val.to_string().as_str()); if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() { return; } res.push('('); if node.left.is_some() { Self::dfs(&node.left, res); } res.push(')'); if node.right.is_some() { res.push('('); Self::dfs(&node.right, res); res.push(')'); } } } pub fn tree2str(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> String { let mut res = String::new(); Self::dfs(&root, &mut res); res } }