Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
573. Squirrel Simulation
Description
You are given two integers height and width representing a garden of size height x width. You are also given:
- an array
treewheretree = [treer, treec]is the position of the tree in the garden, - an array
squirrelwheresquirrel = [squirrelr, squirrelc]is the position of the squirrel in the garden, - and an array
nutswherenuts[i] = [nutir, nutic]is the position of theithnut in the garden.
The squirrel can only take at most one nut at one time and can move in four directions: up, down, left, and right, to the adjacent cell.
Return the minimal distance for the squirrel to collect all the nuts and put them under the tree one by one.
The distance is the number of moves.
Example 1:
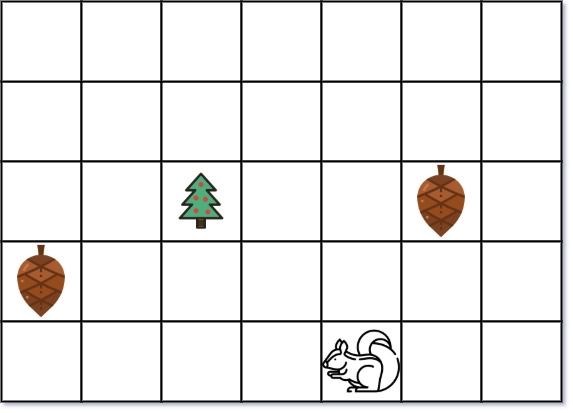
Input: height = 5, width = 7, tree = [2,2], squirrel = [4,4], nuts = [[3,0], [2,5]] Output: 12 Explanation: The squirrel should go to the nut at [2, 5] first to achieve a minimal distance.
Example 2:

Input: height = 1, width = 3, tree = [0,1], squirrel = [0,0], nuts = [[0,2]] Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= height, width <= 100tree.length == 2squirrel.length == 21 <= nuts.length <= 5000nuts[i].length == 20 <= treer, squirrelr, nutir <= height0 <= treec, squirrelc, nutic <= width
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int minDistance(int height, int width, int[] tree, int[] squirrel, int[][] nuts) { int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int s = 0; for (int[] a : nuts) { s += f(a, tree); } s *= 2; for (int[] a : nuts) { int c = f(a, tree); int d = f(a, squirrel) + c; ans = Math.min(ans, s + d - c * 2); } return ans; } private int f(int[] a, int[] b) { return Math.abs(a[0] - b[0]) + Math.abs(a[1] - b[1]); } } -
class Solution { public: int minDistance(int height, int width, vector<int>& tree, vector<int>& squirrel, vector<vector<int>>& nuts) { int ans = INT_MAX; int s = 0; for (auto& a : nuts) { s += f(a, tree); } s *= 2; for (auto& a : nuts) { int c = f(a, tree); int d = f(a, squirrel) + c; ans = min(ans, s + d - c * 2); } return ans; } int f(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) { return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1]); } }; -
class Solution: def minDistance( self, height: int, width: int, tree: List[int], squirrel: List[int], nuts: List[List[int]], ) -> int: x, y, a, b = *tree, *squirrel s = sum(abs(i - x) + abs(j - y) for i, j in nuts) * 2 ans = inf for i, j in nuts: c = abs(i - x) + abs(j - y) d = abs(i - a) + abs(j - b) + c ans = min(ans, s + d - c * 2) return ans -
func minDistance(height int, width int, tree []int, squirrel []int, nuts [][]int) int { f := func(a, b []int) int { return abs(a[0]-b[0]) + abs(a[1]-b[1]) } ans := math.MaxInt32 s := 0 for _, a := range nuts { s += f(a, tree) } s *= 2 for _, a := range nuts { c := f(a, tree) d := f(a, squirrel) + c ans = min(ans, s+d-c*2) } return ans } func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x } return x } -
function minDistance( height: number, width: number, tree: number[], squirrel: number[], nuts: number[][], ): number { const [tr, tc] = tree; const [sr, sc] = squirrel; const s = nuts.reduce((acc, [r, c]) => acc + (Math.abs(tr - r) + Math.abs(tc - c)) * 2, 0); let ans = Infinity; for (const [r, c] of nuts) { const a = Math.abs(tr - r) + Math.abs(tc - c); const b = Math.abs(sr - r) + Math.abs(sc - c); ans = Math.min(ans, s - a + b); } return ans; } -
public class Solution { public int MinDistance(int height, int width, int[] tree, int[] squirrel, int[][] nuts) { int tr = tree[0], tc = tree[1]; int sr = squirrel[0], sc = squirrel[1]; int s = 0; foreach (var e in nuts) { s += Math.Abs(e[0] - tr) + Math.Abs(e[1] - tc); } s <<= 1; int ans = int.MaxValue; foreach (var e in nuts) { int a = Math.Abs(e[0] - tr) + Math.Abs(e[1] - tc); int b = Math.Abs(e[0] - sr) + Math.Abs(e[1] - sc); ans = Math.Min(ans, s - a + b); } return ans; } } -
impl Solution { pub fn min_distance( height: i32, width: i32, tree: Vec<i32>, squirrel: Vec<i32>, nuts: Vec<Vec<i32>>, ) -> i32 { let (tr, tc) = (tree[0], tree[1]); let (sr, sc) = (squirrel[0], squirrel[1]); let s: i32 = nuts .iter() .map(|nut| (nut[0] - tr).abs() + (nut[1] - tc).abs()) .sum::<i32>() * 2; let mut ans = i32::MAX; for nut in &nuts { let a = (nut[0] - tr).abs() + (nut[1] - tc).abs(); let b = (nut[0] - sr).abs() + (nut[1] - sc).abs(); ans = ans.min(s - a + b); } ans } }