Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
563. Binary Tree Tilt
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of every tree node's tilt.
The tilt of a tree node is the absolute difference between the sum of all left subtree node values and all right subtree node values. If a node does not have a left child, then the sum of the left subtree node values is treated as 0. The rule is similar if the node does not have a right child.
Example 1:
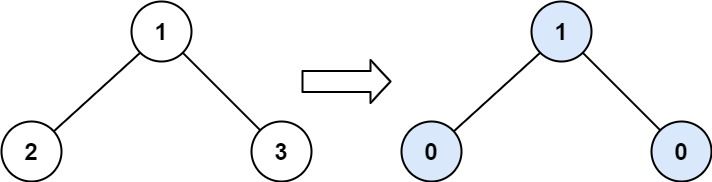
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 1 Explanation: Tilt of node 2 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 3 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 1 : |2-3| = 1 (left subtree is just left child, so sum is 2; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 3) Sum of every tilt : 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
Example 2:
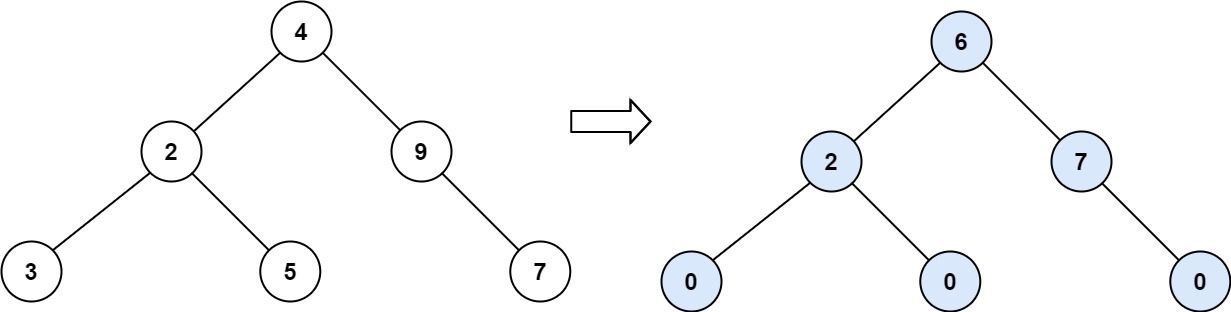
Input: root = [4,2,9,3,5,null,7] Output: 15 Explanation: Tilt of node 3 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 5 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 7 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 2 : |3-5| = 2 (left subtree is just left child, so sum is 3; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 5) Tilt of node 9 : |0-7| = 7 (no left child, so sum is 0; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 7) Tilt of node 4 : |(3+5+2)-(9+7)| = |10-16| = 6 (left subtree values are 3, 5, and 2, which sums to 10; right subtree values are 9 and 7, which sums to 16) Sum of every tilt : 0 + 0 + 0 + 2 + 7 + 6 = 15
Example 3:
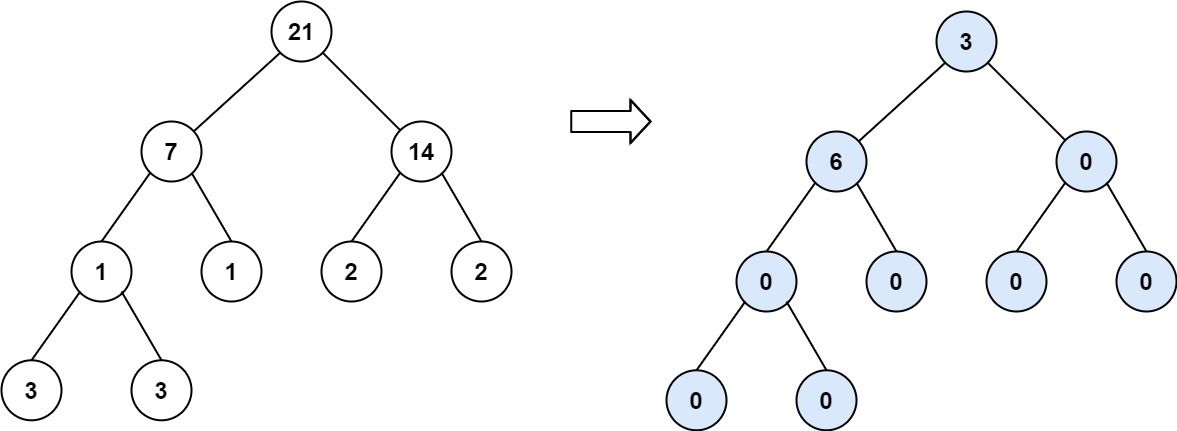
Input: root = [21,7,14,1,1,2,2,3,3] Output: 9
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; public int findTilt(TreeNode root) { ans = 0; sum(root); return ans; } private int sum(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int left = sum(root.left); int right = sum(root.right); ans += Math.abs(left - right); return root.val + left + right; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int ans; int findTilt(TreeNode* root) { ans = 0; sum(root); return ans; } int sum(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; int left = sum(root->left), right = sum(root->right); ans += abs(left - right); return root->val + left + right; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def findTilt(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: ans = 0 def sum(root): if root is None: return 0 nonlocal ans left = sum(root.left) right = sum(root.right) ans += abs(left - right) return root.val + left + right sum(root) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ var ans int func findTilt(root *TreeNode) int { ans = 0 sum(root) return ans } func sum(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } left, right := sum(root.Left), sum(root.Right) ans += abs(left - right) return root.Val + left + right } func abs(x int) int { if x > 0 { return x } return -x }