Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Description
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
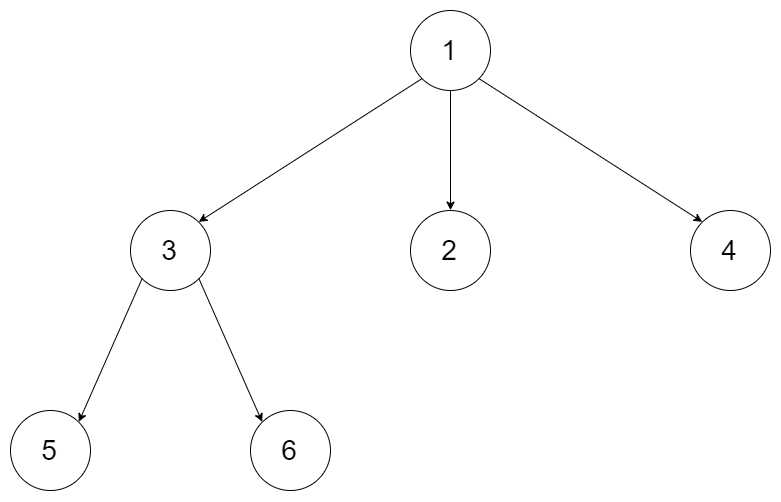
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2:
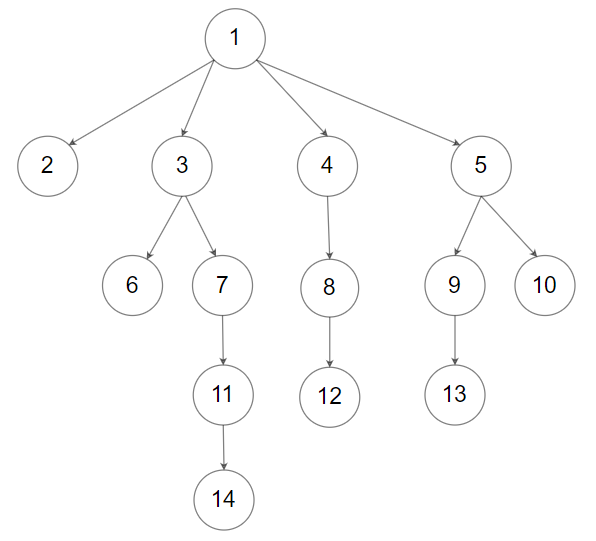
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Constraints:
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000 - The total number of nodes is between
[0, 104]
Solutions
BFS or DFS.
-
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return ans; } Deque<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>(); for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) { root = q.poll(); t.add(root.val); q.addAll(root.children); } ans.add(t); } return ans; } } -
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val) { val = _val; } Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) { vector<vector<int>> ans; if (!root) return ans; queue<Node*> q{ {root} }; while (!q.empty()) { vector<int> t; for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) { root = q.front(); q.pop(); t.push_back(root->val); for (auto& child : root->children) q.push(child); } ans.push_back(t); } return ans; } }; -
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val=None, children=None): self.val = val self.children = children """ class Solution: def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]: ans = [] if root is None: return ans q = deque([root]) while q: t = [] for _ in range(len(q)): root = q.popleft() t.append(root.val) q.extend(root.children) ans.append(t) return ans -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Children []*Node * } */ func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int { var ans [][]int if root == nil { return ans } q := []*Node{root} for len(q) > 0 { var t []int for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- { root = q[0] q = q[1:] t = append(t, root.Val) for _, child := range root.Children { q = append(q, child) } } ans = append(ans, t) } return ans } -
/** * Definition for node. * class Node { * val: number * children: Node[] * constructor(val?: number) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.children = [] * } * } */ function levelOrder(root: Node | null): number[][] { const res = []; if (root == null) { return res; } const queue = [root]; while (queue.length !== 0) { const n = queue.length; const vals = []; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { const { val, children } = queue.shift(); vals.push(val); queue.push(...children); } res.push(vals); } return res; }