Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
373. Find K Pairs with Smallest Sums
Description
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2 sorted in non-decreasing order and an integer k.
Define a pair (u, v) which consists of one element from the first array and one element from the second array.
Return the k pairs (u1, v1), (u2, v2), ..., (uk, vk) with the smallest sums.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,7,11], nums2 = [2,4,6], k = 3 Output: [[1,2],[1,4],[1,6]] Explanation: The first 3 pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,2],[1,4],[1,6],[7,2],[7,4],[11,2],[7,6],[11,4],[11,6]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,1,2], nums2 = [1,2,3], k = 2 Output: [[1,1],[1,1]] Explanation: The first 2 pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,1],[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2],[1,3],[1,3],[2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3], k = 3 Output: [[1,3],[2,3]] Explanation: All possible pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,3],[2,3]
Constraints:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 105-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 109nums1andnums2both are sorted in non-decreasing order.1 <= k <= 104k <= nums1.length * nums2.length
Solutions
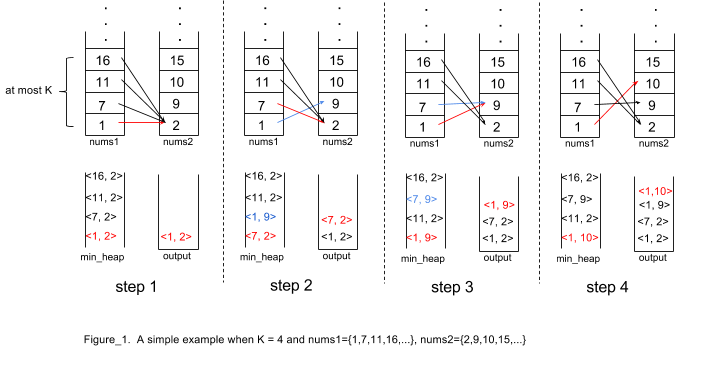
The value of num1[0]+num2[0] must be the smallest, so we first throw this value into the heap.
Then start traversing the next element.
The next value must be the smallest one from num1[1]+num2[0] and num1[0]+num2[1].
Loop all the combinations in turn until the extracted element is K.
Variation Question
input: nums=[3,1,9], k=3
goal: find the k-th smallest diff of pairs from nums
pairs from nums: (1,3) (1,9) (3,9)
- so diffs are (2,8,6)
- sort diffs (2,6,8)
- so 3-rd diff is 8
optimized solution:
- sort nums => get [1,3,9]
- start from neighbours, with
neighbour-distance=1get => (1,3), (3,9) - if len(pairs) still less than k pairs, then keep trying with
neighbour-distance=2get => (1,9) - and then
neighbour-distance=3, =4, so on - when len(pairs)==k , stop and ignore more further larger pair-diffs
-
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) { PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(nums1.length, k); ++i) { q.offer(new int[] {nums1[i] + nums2[0], i, 0}); } List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); while (!q.isEmpty() && k > 0) { int[] e = q.poll(); ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums1[e[1]], nums2[e[2]])); --k; if (e[2] + 1 < nums2.length) { q.offer(new int[] {nums1[e[1]] + nums2[e[2] + 1], e[1], e[2] + 1}); } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> kSmallestPairs(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int k) { auto cmp = [&nums1, &nums2](const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) { return nums1[a.first] + nums2[a.second] > nums1[b.first] + nums2[b.second]; }; int m = nums1.size(); int n = nums2.size(); vector<vector<int>> ans; priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp); for (int i = 0; i < min(k, m); i++) pq.emplace(i, 0); while (k-- && !pq.empty()) { auto [x, y] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); ans.emplace_back(initializer_list<int>{nums1[x], nums2[y]}); if (y + 1 < n) pq.emplace(x, y + 1); } return ans; } }; -
from heapq import heapify class Solution: def kSmallestPairs( self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int ) -> List[List[int]]: ''' k could be a super large number >>> [1,2,3][:99] [1, 2, 3] ''' q = [[u + nums2[0], i, 0] for i, u in enumerate(nums1[:k])] # still need '[u + nums2[0]', for q ordering heapify(q) ans = [] # both q and k should be checked # because k can be super larger than nums1+nums2 while q and k > 0: _, i, j = heappop(q) ans.append([nums1[i], nums2[j]]) k -= 1 if j + 1 < len(nums2): heappush(q, [nums1[i] + nums2[j + 1], i, j + 1]) return ans ############ import heapq class Solution(object): def kSmallestPairs(self, nums1, nums2, k): """ :type nums1: List[int] :type nums2: List[int] :type k: int :rtype: List[List[int]] """ if not nums1 or not nums2: return [] heap = [(nums1[0] + nums2[0], 0, 0)] ans = [] visited = {(0, 0)} while heap: val, i, j = heapq.heappop(heap) ans.append((nums1[i], nums2[j])) k -= 1 if k == 0: return ans if i + 1 < len(nums1) and (i + 1, j) not in visited: heapq.heappush(heap, (nums1[i + 1] + nums2[j], i + 1, j)) visited |= {(i + 1, j)} if j + 1 < len(nums2) and (i, j + 1) not in visited: heapq.heappush(heap, (nums1[i] + nums2[j + 1], i, j + 1)) visited |= {(i, j + 1)} return ans ############ # variation question # time complexity of O(n^2) def kth_smallest_diff(nums, k): # Step 1: Generate all possible pairs and calculate their differences diffs = [] nums.sort() # Sort nums first to make sure differences are calculated correctly for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)): diff = abs(nums[j] - nums[i]) diffs.append(diff) # Step 2 & 3: Sort the list of differences diffs.sort() # Step 4: Return the k-th smallest difference return diffs[k - 1] # Example usage nums = [3, 1, 9] k = 3 print(kth_smallest_diff(nums, k)) -
func kSmallestPairs(nums1, nums2 []int, k int) (ans [][]int) { m, n := len(nums1), len(nums2) h := hp{nil, nums1, nums2} for i := 0; i < k && i < m; i++ { h.data = append(h.data, pair{i, 0}) } for h.Len() > 0 && len(ans) < k { p := heap.Pop(&h).(pair) i, j := p.i, p.j ans = append(ans, []int{nums1[i], nums2[j]}) if j+1 < n { heap.Push(&h, pair{i, j + 1}) } } return } type pair struct{ i, j int } type hp struct { data []pair nums1, nums2 []int } func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h.data) } func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { a, b := h.data[i], h.data[j] return h.nums1[a.i]+h.nums2[a.j] < h.nums1[b.i]+h.nums2[b.j] } func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h.data[i], h.data[j] = h.data[j], h.data[i] } func (h *hp) Push(v any) { h.data = append(h.data, v.(pair)) } func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := h.data; v := a[len(a)-1]; h.data = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }