Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
370. Range Addition
Description
You are given an integer length and an array updates where updates[i] = [startIdxi, endIdxi, inci].
You have an array arr of length length with all zeros, and you have some operation to apply on arr. In the ith operation, you should increment all the elements arr[startIdxi], arr[startIdxi + 1], ..., arr[endIdxi] by inci.
Return arr after applying all the updates.
Example 1:
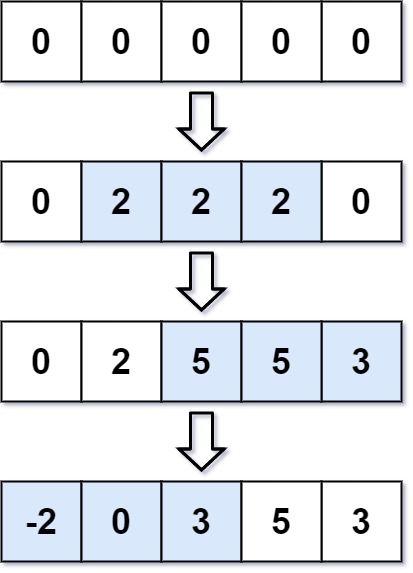
Input: length = 5, updates = [[1,3,2],[2,4,3],[0,2,-2]] Output: [-2,0,3,5,3]
Example 2:
Input: length = 10, updates = [[2,4,6],[5,6,8],[1,9,-4]] Output: [0,-4,2,2,2,4,4,-4,-4,-4]
Constraints:
1 <= length <= 1050 <= updates.length <= 1040 <= startIdxi <= endIdxi < length-1000 <= inci <= 1000
Solutions
Suppose our array range is [0, n), the interval to be updated is [start, end], and the updated value is inc.
Then add inc to each number in the interval [start, end], which is equivalent to
- Add inc to all numbers in the interval
(start, n) - Then subtract inc from all the numbers in the interval
(end+1, n)
After understanding that this conversion can be done, we still can’t update all the values in the interval every time, so we need to change the marking method.
- The method is to add
incto the start position at the beginning of the coordinate, and add-incto the position whereend adds 1.
For example, we need to add 2 to the numbers in the new interval [1, 3], then we add 2 at the position of 1, and subtract 2 at the position of 4, so the array becomes [0, 2, 0, 0, -2].
If there is only one operation, how to get the final result?
The answer is to create a cumulative sum array, which becomes [0, 2, 2, 2, 0]
We found that it is exactly equivalent to directly adding 2 to the numbers in the interval [1, 3]. Further analysis, the operation of establishing the accumulation and array actually means that the current number has an effect on the numbers in all subsequent positions.
- Then we add 2 to the start position, which means that every number in the range of [start, n) is added 2
- In fact, only the numbers in the [start, end] interval need to be added by 2
- In order to
eliminate this effect, we need tosubtract 2 from the numbers in the [end+1, n) interval, so we subtract 2 from the end+1 position
Then when the accumulation and array is created, it is equivalent to subtracting 2 from all the numbers behind. It should be noted that end may be equal to n-1, then end+1 may be out of range, so we initialize the length of the array to n+1 to avoid the out of range.
Then according to the example in the title, we can get an array, nums = {-2, 2, 3, 2, -2, -3}, and then add it up and it is the result we require result = {-2, 0 , 3, 5, 3}
-
class Solution { public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) { int[] d = new int[length]; for (var e : updates) { int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2]; d[l] += c; if (r + 1 < length) { d[r + 1] -= c; } } for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) { d[i] += d[i - 1]; } return d; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> getModifiedArray(int length, vector<vector<int>>& updates) { vector<int> d(length); for (auto& e : updates) { int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2]; d[l] += c; if (r + 1 < length) d[r + 1] -= c; } for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) d[i] += d[i - 1]; return d; } }; -
from itertools import accumulate class Solution: def getModifiedArray(self, length: int, updates: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: d = [0] * length for l, r, c in updates: d[l] += c if r + 1 < length: d[r + 1] -= c return list(accumulate(d)) ############ class Solution(object): def getModifiedArray(self, length, updates): """ :type length: int :type updates: List[List[int]] :rtype: List[int] """ ans = [0] * length for update in updates: start, end, delta = update ans[start] += delta if end + 1 < length: ans[end + 1] -= delta delta = 0 for i in range(0, length): delta += ans[i] ans[i] = delta return ans -
func getModifiedArray(length int, updates [][]int) []int { d := make([]int, length) for _, e := range updates { l, r, c := e[0], e[1], e[2] d[l] += c if r+1 < length { d[r+1] -= c } } for i := 1; i < length; i++ { d[i] += d[i-1] } return d } -
/** * @param {number} length * @param {number[][]} updates * @return {number[]} */ var getModifiedArray = function (length, updates) { const d = new Array(length).fill(0); for (const [l, r, c] of updates) { d[l] += c; if (r + 1 < length) { d[r + 1] -= c; } } for (let i = 1; i < length; ++i) { d[i] += d[i - 1]; } return d; };