Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
366. Find Leaves of Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, collect a tree's nodes as if you were doing this:
- Collect all the leaf nodes.
- Remove all the leaf nodes.
- Repeat until the tree is empty.
Example 1:
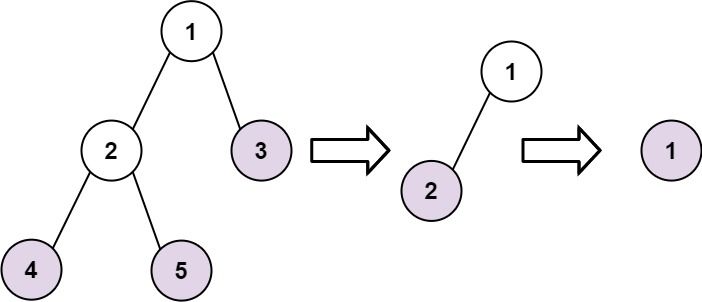
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]] Explanation: [[3,5,4],[2],[1]] and [[3,4,5],[2],[1]] are also considered correct answers since per each level it does not matter the order on which elements are returned.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> findLeaves(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); TreeNode prev = new TreeNode(0, root, null); while (prev.left != null) { List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(prev.left, prev, t); res.add(t); } return res; } private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode prev, List<Integer> t) { if (root == null) { return; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { t.add(root.val); if (prev.left == root) { prev.left = null; } else { prev.right = null; } } dfs(root.left, root, t); dfs(root.right, root, t); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> findLeaves(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> res; TreeNode* prev = new TreeNode(0, root, nullptr); while (prev->left) { vector<int> t; dfs(prev->left, prev, t); res.push_back(t); } return res; } void dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* prev, vector<int>& t) { if (!root) return; if (!root->left && !root->right) { t.push_back(root->val); if (prev->left == root) prev->left = nullptr; else prev->right = nullptr; } dfs(root->left, root, t); dfs(root->right, root, t); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def findLeaves(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]: def dfs(root, prev, t): if root is None: return if root.left is None and root.right is None: t.append(root.val) if prev.left == root: prev.left = None else: prev.right = None dfs(root.left, root, t) dfs(root.right, root, t) res = [] prev = TreeNode(left=root) while prev.left: t = [] dfs(prev.left, prev, t) res.append(t) return res -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func findLeaves(root *TreeNode) [][]int { prev := &TreeNode{ Val: 0, Left: root, Right: nil, } var res [][]int for prev.Left != nil { var t []int dfs(prev.Left, prev, &t) res = append(res, t) } return res } func dfs(root, prev *TreeNode, t *[]int) { if root == nil { return } if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil { *t = append(*t, root.Val) if prev.Left == root { prev.Left = nil } else { prev.Right = nil } } dfs(root.Left, root, t) dfs(root.Right, root, t) } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function findLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number[][] { const ans: number[][] = []; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): number => { if (root === null) { return 0; } const l = dfs(root.left); const r = dfs(root.right); const h = Math.max(l, r); if (ans.length === h) { ans.push([]); } ans[h].push(root.val); return h + 1; }; dfs(root); return ans; } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * public int val; * public TreeNode left; * public TreeNode right; * public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ public class Solution { public IList<IList<int>> FindLeaves(TreeNode root) { var ans = new List<IList<int>>(); int Dfs(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return 0; } int l = Dfs(node.left); int r = Dfs(node.right); int h = Math.Max(l, r); if (ans.Count == h) { ans.Add(new List<int>()); } ans[h].Add(node.val); return h + 1; } Dfs(root); return ans; } }